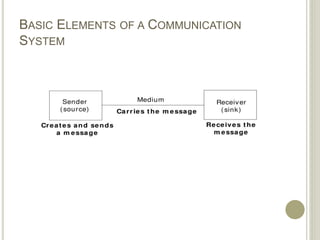
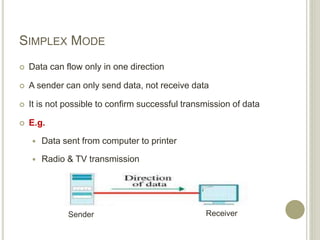
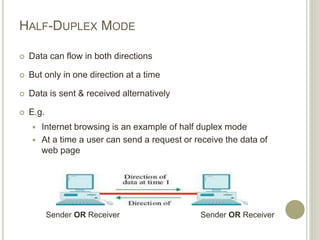
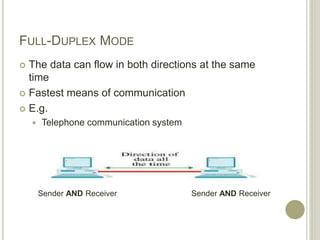
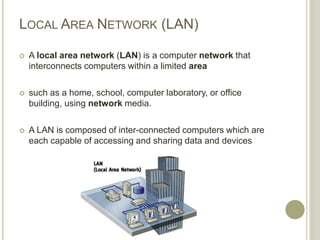
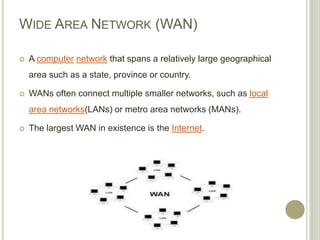
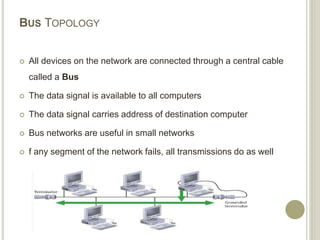
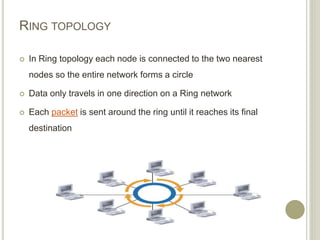
This document provides an overview of data communications and computer networks. It defines key concepts like data communication, the basic elements of a communication system including message, sender, receiver, medium and protocol. It also describes different communication modes, types of computer networks including LAN, MAN and WAN, common network topologies like bus, ring and star, and several communication protocols used in computer networks such as Ethernet, Token Ring, TCP/IP and WAP.