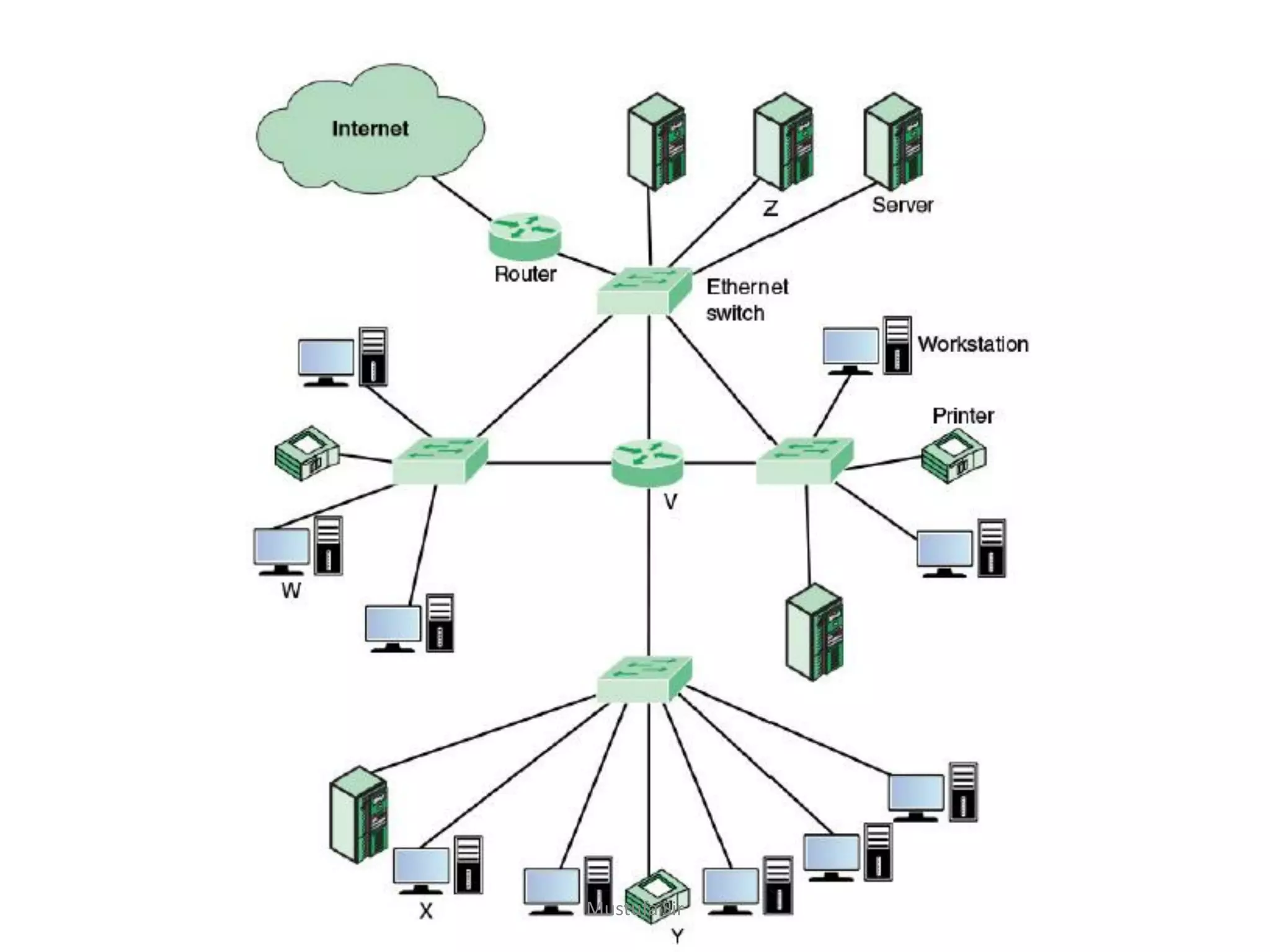
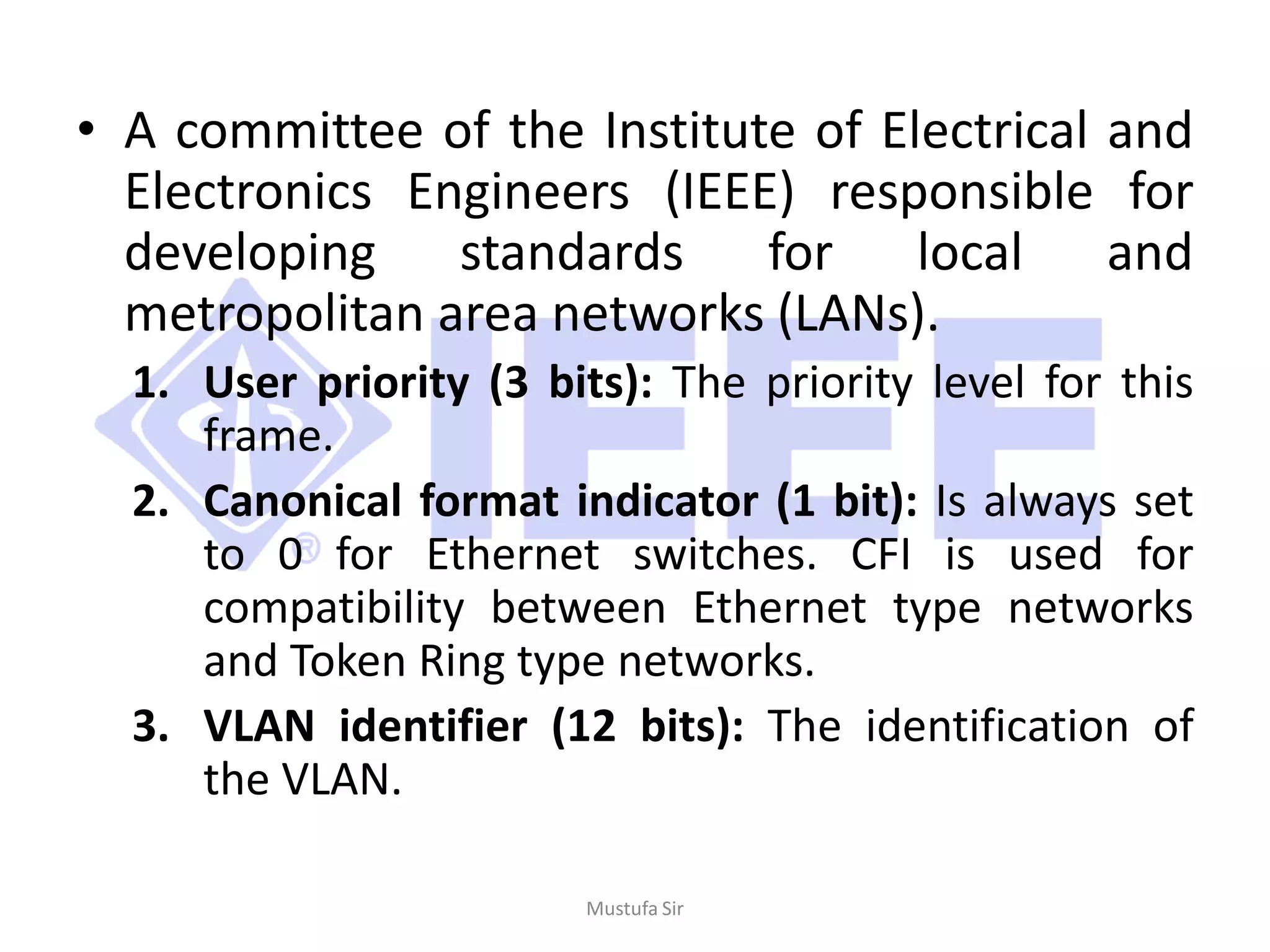
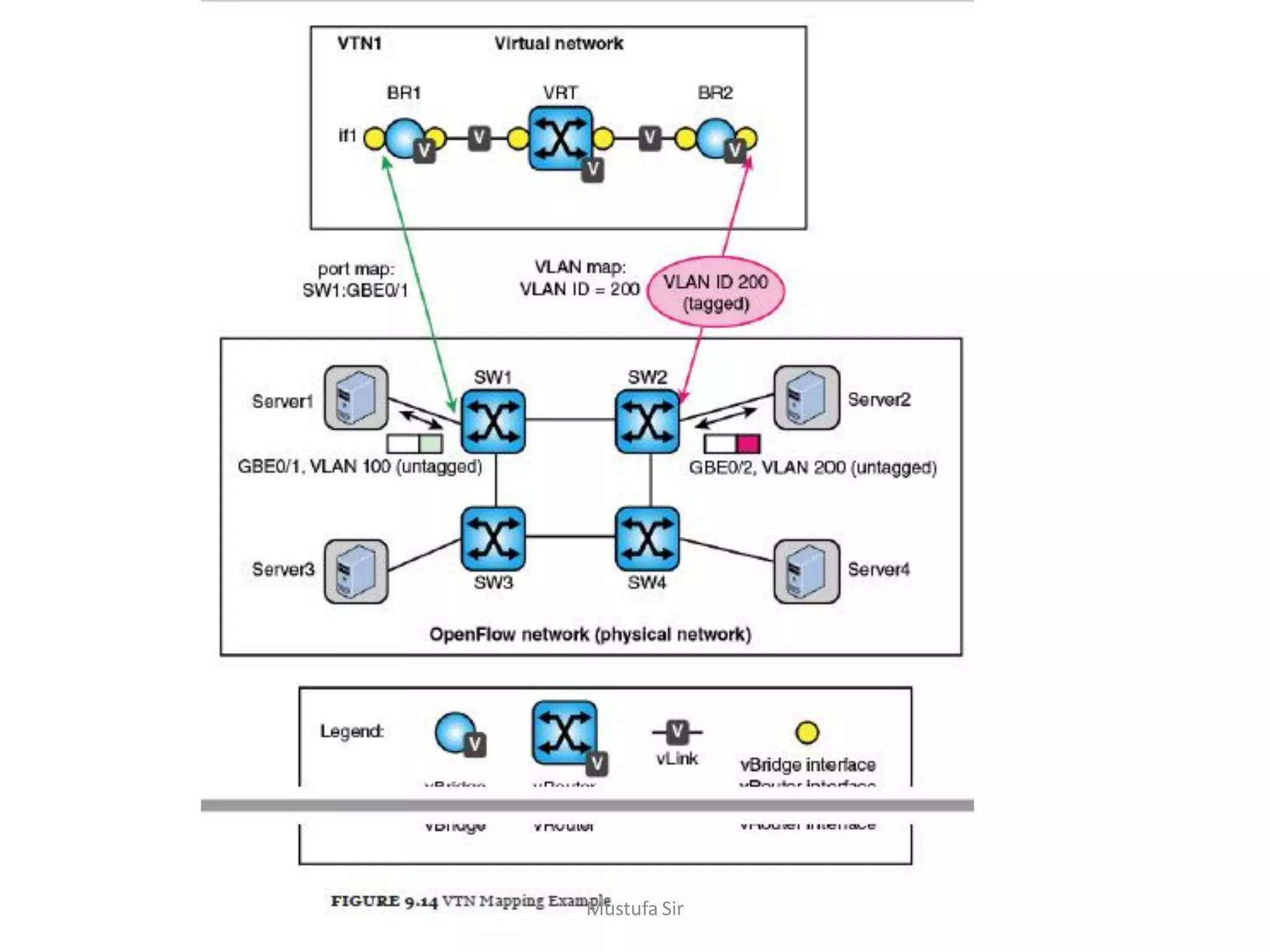
This document discusses various concepts related to network virtualization. It begins by explaining virtual LANs (VLANs) and how they create broadcast domains on a physical network using VLAN tags. It then discusses how OpenFlow can implement more flexible VLAN support and how virtual private networks (VPNs) can provide private networks over public infrastructure using IPsec or MPLS. Network virtualization is defined as the ability to run multiple logical networks over a shared physical network. OpenDaylight's Virtual Tenant Network plugin provides multitenant virtual networks on a SDN using VLAN technology. The document concludes with a brief discussion of software-defined infrastructure.