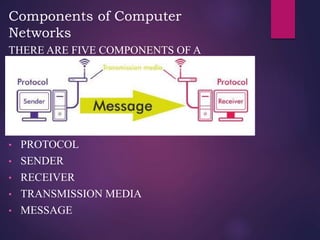
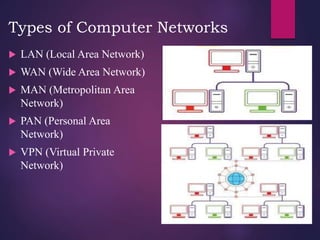
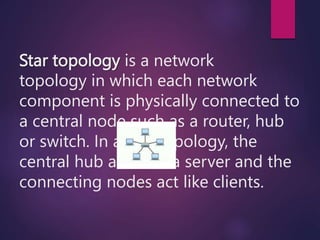
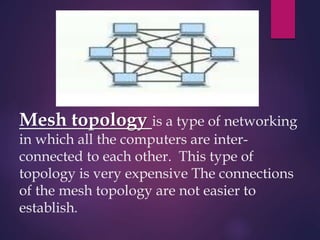
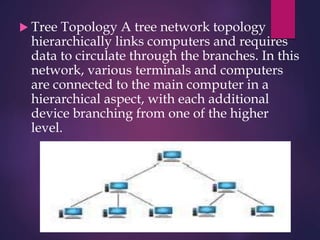
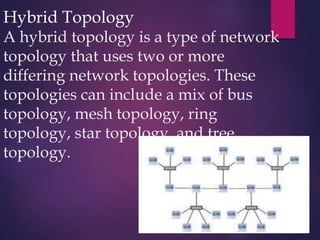
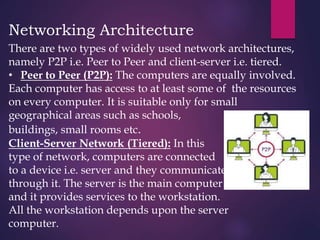
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer networking, detailing what computer networks are, their functions, and core components. It outlines various types of networks, such as LAN, WAN, and VPN, as well as network topologies like bus, star, and mesh. Additionally, it introduces essential devices, terminologies, and protocols required for setting up and maintaining computer networks.