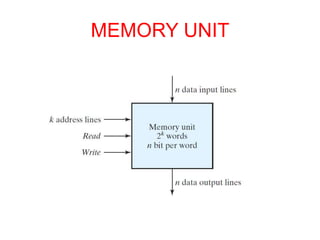
Memory devices can be classified in several ways:
1. By location as registers, main memory, and secondary memory. Registers are inside the CPU while main memory is external but faster than secondary memory like hard disks.
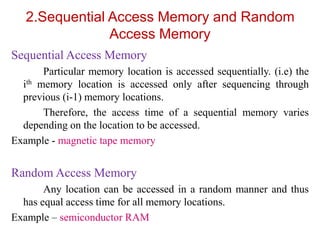
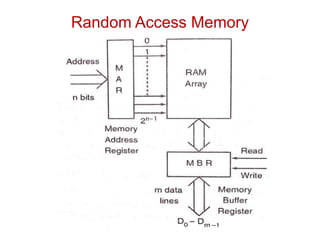
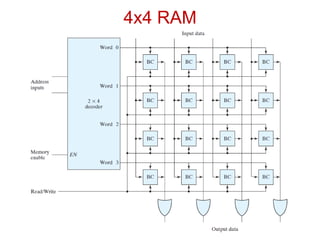
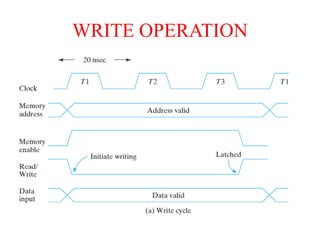
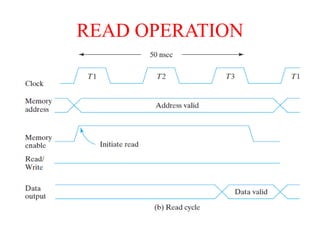
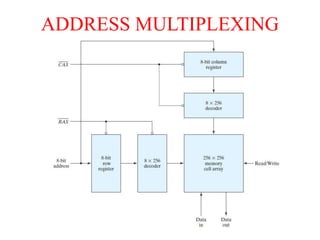
2. By access as sequential (location must be accessed in order) vs random access memory (RAM) which allows random access.
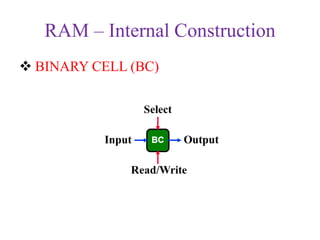
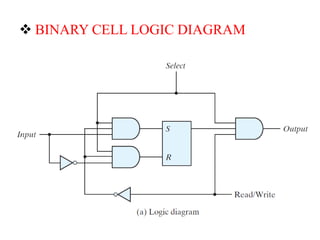
3. As static (maintains data without refresh) vs dynamic RAM which must be periodically refreshed.
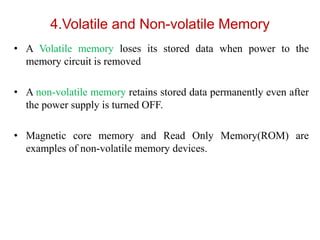
4. As volatile (loses data on power off) vs non-volatile like ROM and magnetic storage.
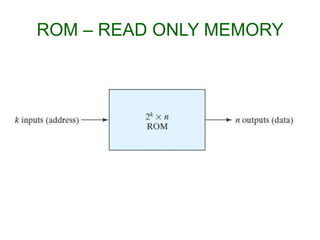
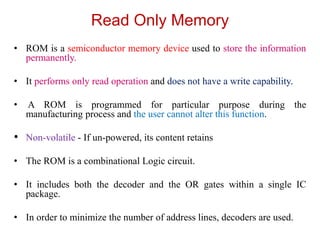
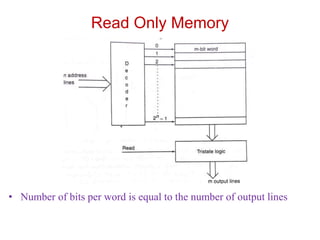
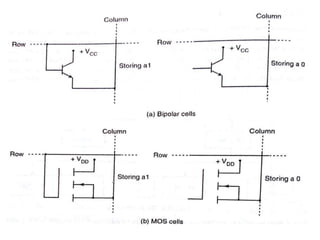
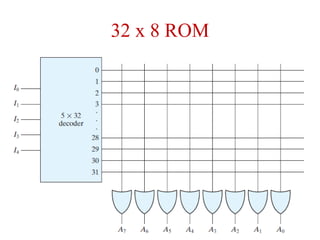
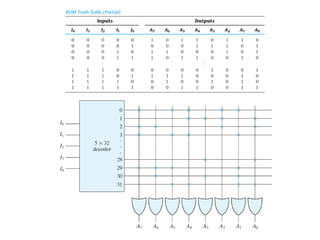
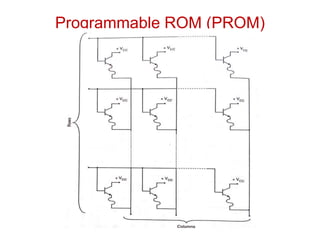
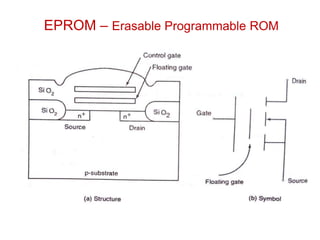
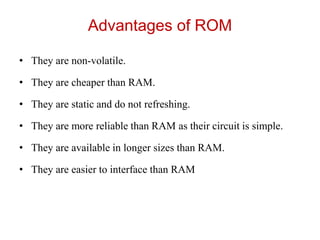
Read-only memory (ROM) is non-volatile and only allows reading. It is used to permanently store information. Various RO