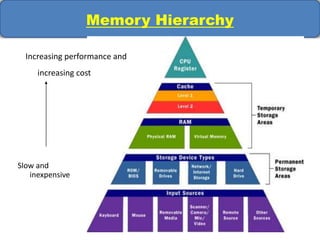
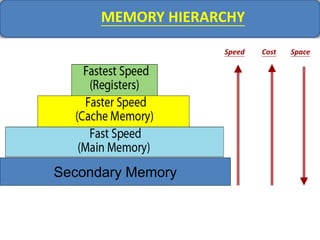
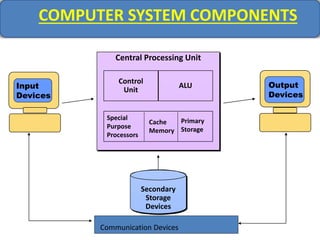
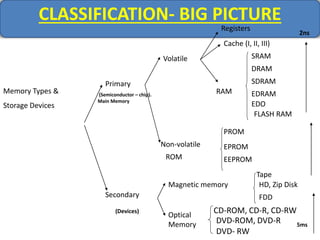
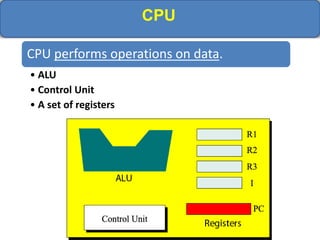
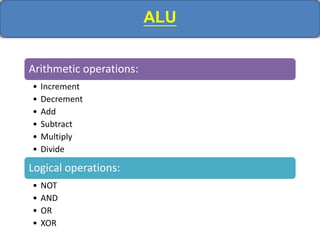
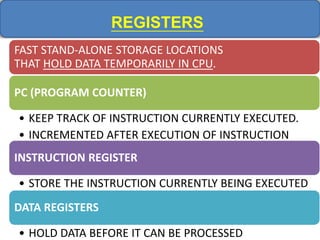
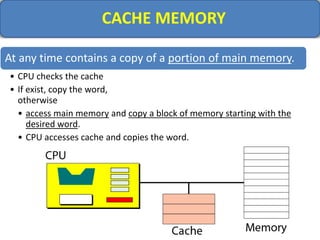
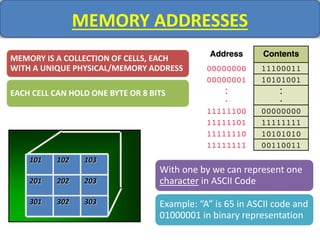
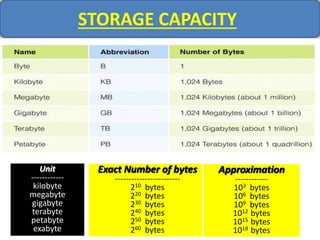
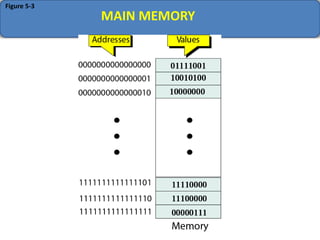
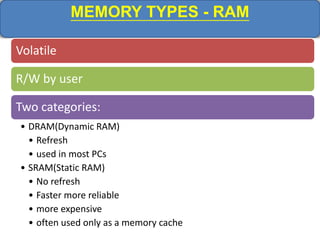
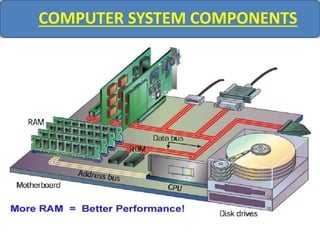
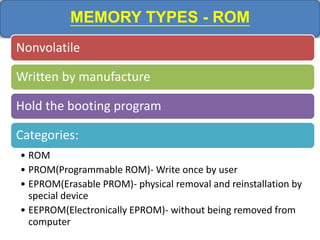
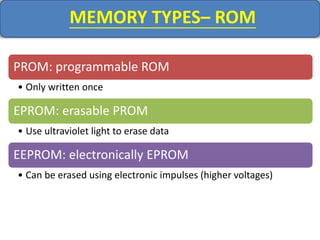
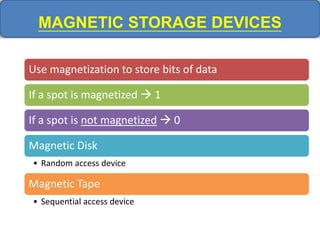
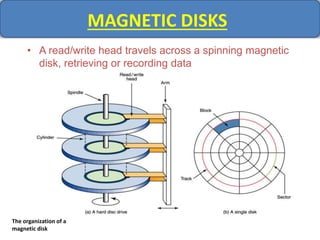
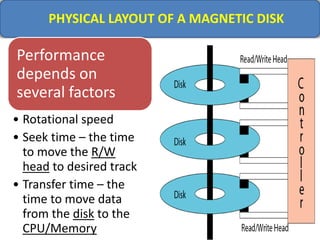
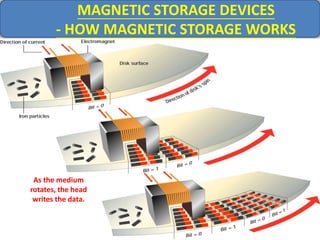
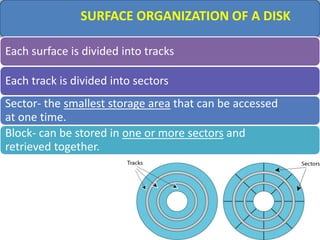
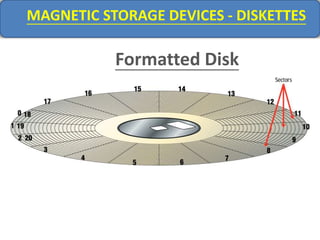
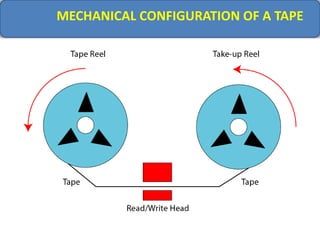
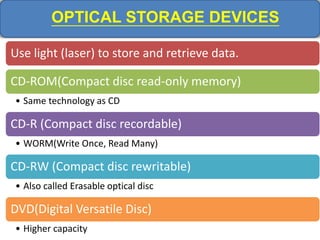
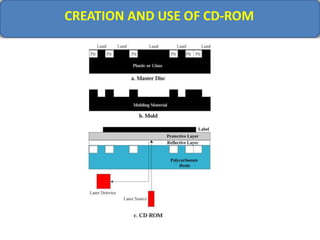
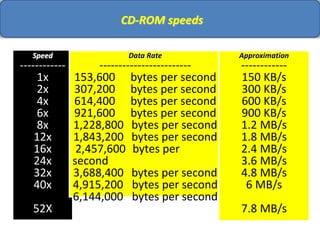
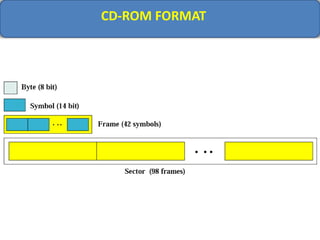
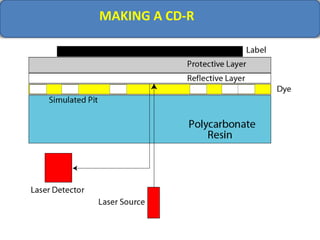
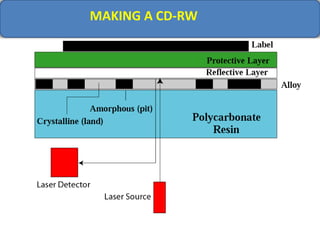
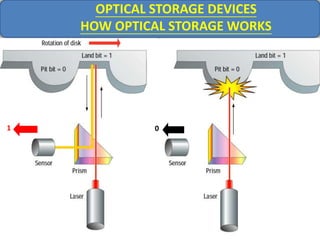
Computer memory comes in a memory hierarchy from fastest and smallest to slower and larger. At the top are CPU registers for temporary storage, followed by cache memory for faster access. Main memory (RAM) is volatile storage inside the computer. Secondary storage devices like hard disks and optical disks provide non-volatile storage of large amounts of data. Memory and storage technologies use electrical charges, magnetic fields, or pits and lands on optical media to store binary data representing 0s and 1s.