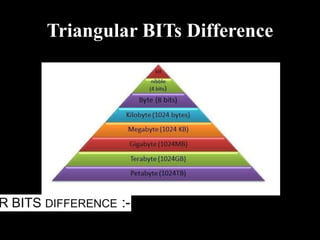
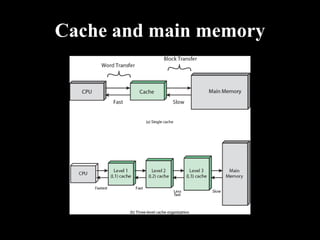
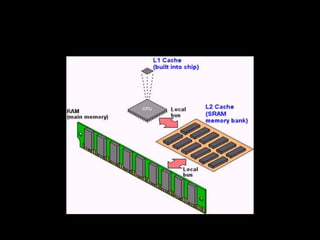
Memory can be either primary (internal/main memory) or secondary (external storage). Primary memory is volatile and holds data temporarily, while secondary memory is non-volatile for permanent storage. Primary memory includes RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read only memory). RAM is used to run programs and can be DRAM (dynamic RAM) or SRAM (static RAM). ROM includes PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM which cannot be written to like RAM. Caches like L1, L2, and L3 exist between the CPU and main memory for faster access to frequently used instructions and data.