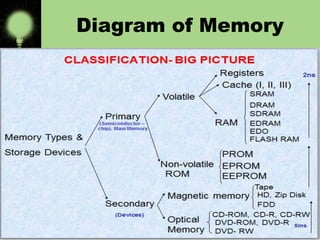
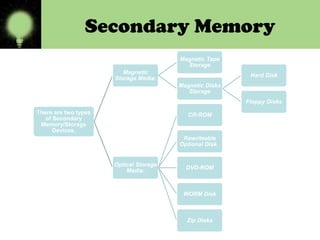
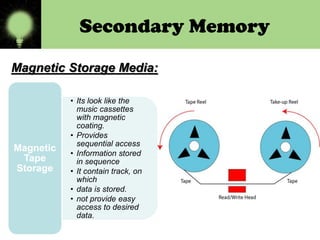
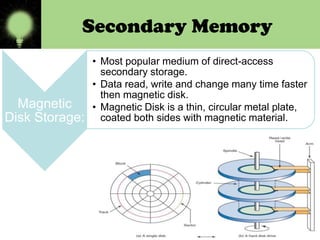
Memory is divided into primary and secondary storage. Primary memory (RAM and ROM) is temporary and allows for quick access, while secondary memory provides permanent storage of large amounts of data even when the computer is off. Secondary storage devices include magnetic hard disks and floppy disks, as well as optical disks like CD-ROMs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs that store data using lasers.