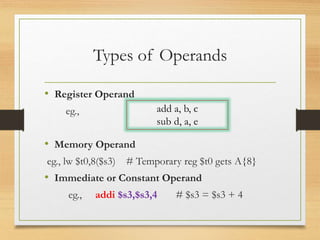
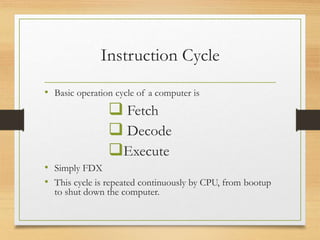
This document defines computer instructions and discusses their format, operations, and types. It begins by defining an instruction as an order given to a processor by a program. Instructions contain operation codes and operands. There are different types of instruction set operations like data transfer, arithmetic, logical, and program control. Instruction formats can have register, memory, or immediate operands. Instructions sets are classified as either Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) or Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) depending on the number of instructions. The basic instruction cycle that a CPU performs is fetch, decode, and execute.