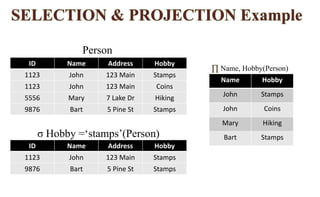
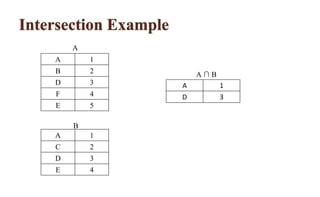
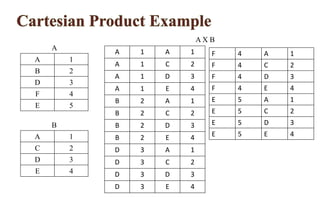
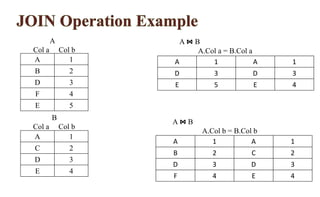
Relational algebra is a procedural query language used for processing relations, performing operations such as select, projection, union, intersection, Cartesian product, and join. Each operation manipulates relations to produce new relations based on specified conditions, with the output being formed from one or more input relations. Types of joins include various forms such as inner joins and outer joins, and several symbols, like σ and ∪, represent different operations.