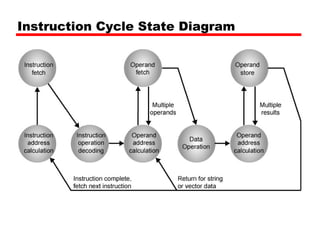
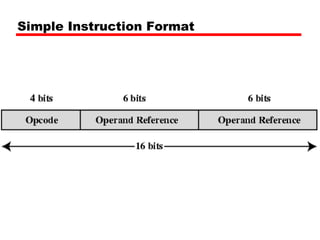
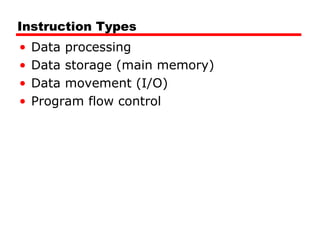
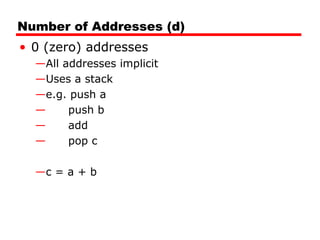
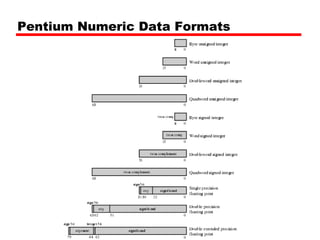
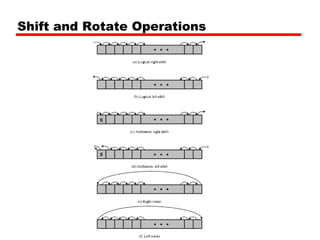
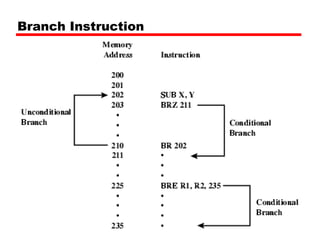
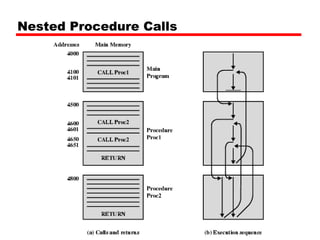
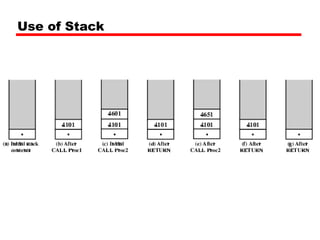
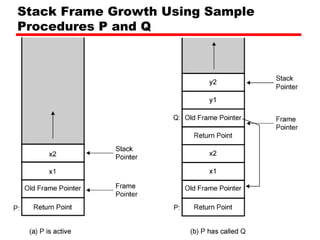
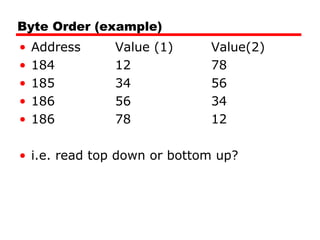
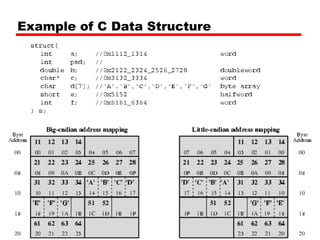
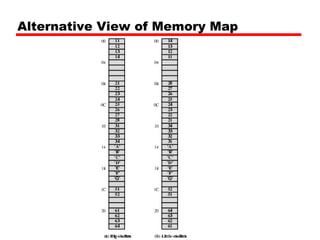
This document discusses instruction sets and their characteristics. It covers topics such as the elements of an instruction including operation code and operands. It describes different instruction formats, types, addressing modes, and design decisions in instruction set architecture. Examples of instruction sets from processors like Pentium, PowerPC, and others are provided to illustrate concepts like data types, operations, and byte ordering.