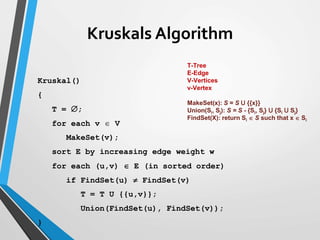
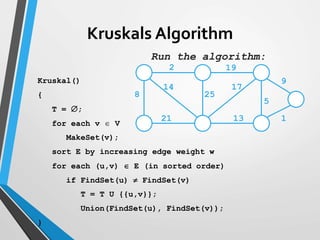
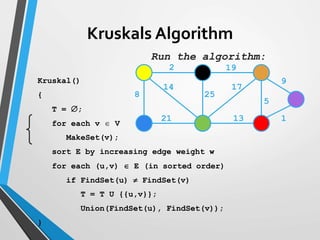
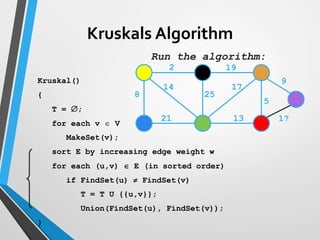
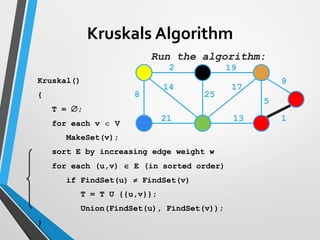
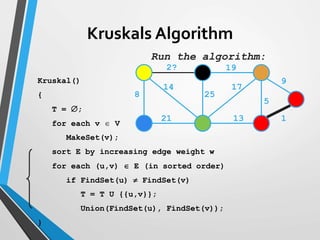
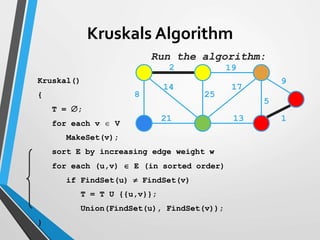
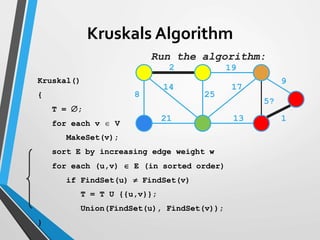
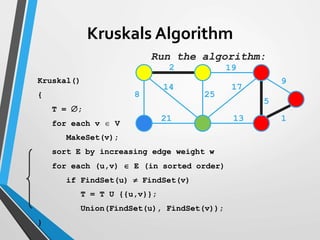
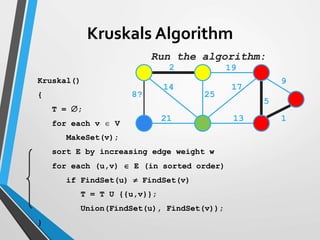
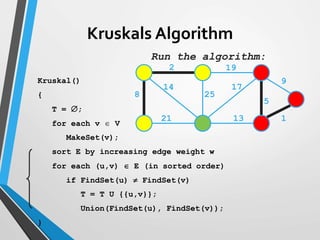
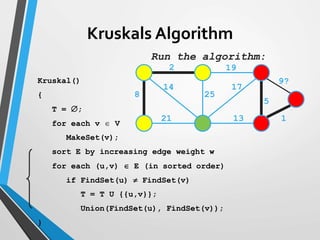
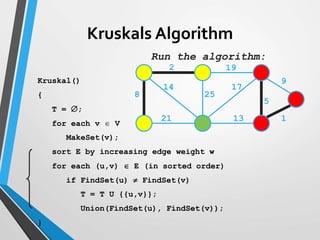
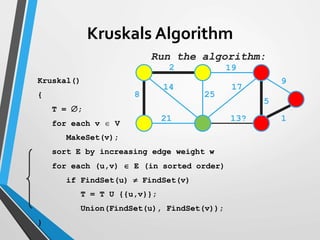
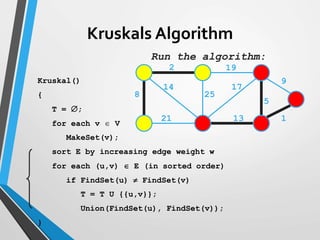
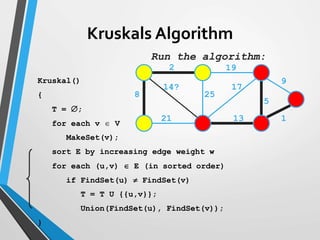
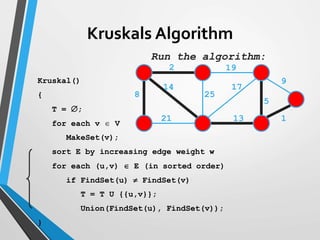
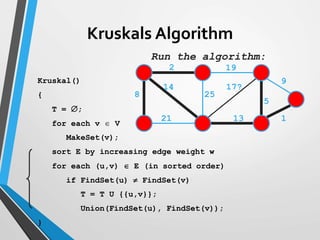
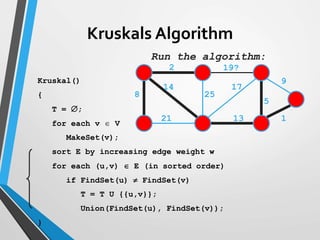
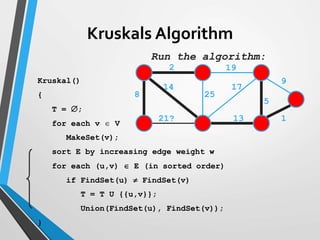
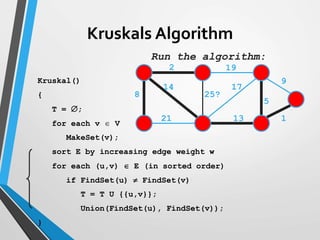
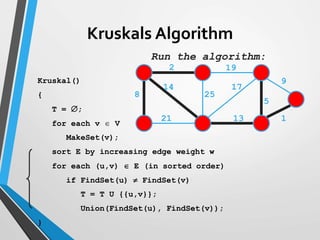
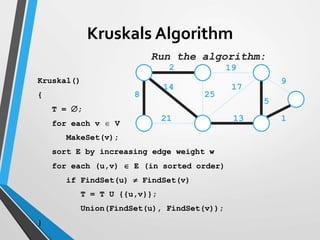
The document discusses minimum spanning trees (MST) and two algorithms for finding them: Prim's algorithm and Kruskal's algorithm. Prim's algorithm operates by building the MST one vertex at a time, starting from an arbitrary root vertex and at each step adding the cheapest connection to another vertex not yet included. Kruskal's algorithm finds the MST by sorting the edges by weight and sequentially adding edges that connect different components without creating cycles.




![MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
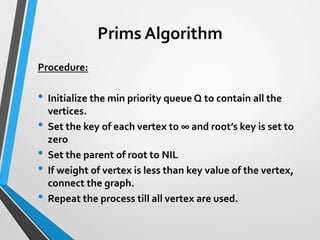
Initialize the min priority queue Q to contain
all the vertices.
Set the key of each vertex to ∞
Set the parent of root to NIL
Root’s key is set to 0
Until queue become null set
Input– Graph, Weight, Root
Set the parent of ‘v’ as ‘u’
Set the key of v = weight of edge
connecting uv
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-6-320.jpg)
![MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Run on example graph
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-7-320.jpg)
![
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Run on example graph
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-8-320.jpg)
![
0
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Pick a start vertex r
r
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-9-320.jpg)
![
0
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Black vertices have been removed from Q
u
Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-10-320.jpg)
![
0
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Black arrows indicate parent pointers
u
Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-11-320.jpg)
![14
0
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-12-320.jpg)
![14
0
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-13-320.jpg)
![14
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-14-320.jpg)
![10
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-15-320.jpg)
![10
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-16-320.jpg)
![10 2
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-17-320.jpg)
![10 2
0 8 15
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-18-320.jpg)
![10 2
0 8 15
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-19-320.jpg)
![10 2 9
0 8 15
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-20-320.jpg)
![10 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-21-320.jpg)
![5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-22-320.jpg)
![5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-23-320.jpg)
![5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-24-320.jpg)
![5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-25-320.jpg)
![5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-26-320.jpg)
![MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v Adj[u]
if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
3
4
5
2
9
15
8
Prims Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primskruskalalgorithms-161101153404/85/Prims-and-kruskal-algorithms-27-320.jpg)