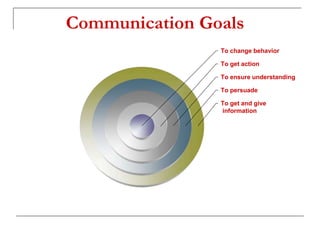
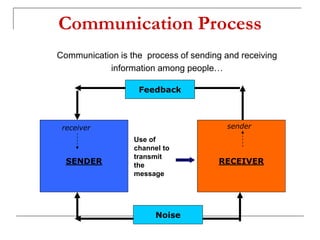
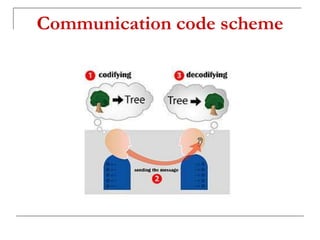
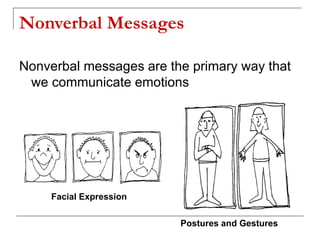
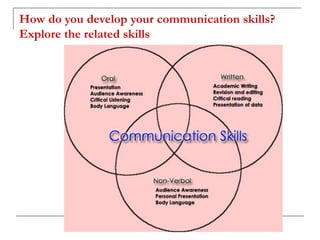
The document outlines the importance of communication skills, emphasizing their role in both personal and professional contexts. It describes various types of communication, potential barriers, and the components that contribute to effective communication, including verbal, paraverbal, and nonverbal messages. It also highlights key listening skills and tips for developing better communication practices.