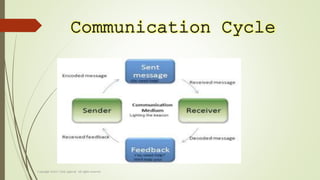
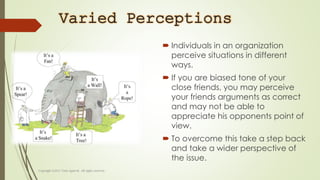
This document discusses communication skills and barriers to effective communication. It defines communication and outlines the essentials, which include having a common environment, cooperation between parties, selecting the right channel, properly encoding and decoding messages, and getting feedback. It then describes three levels of barriers: intrapersonal (e.g. assumptions, perceptions), interpersonal (e.g. limited vocabulary, poor listening), and organizational (e.g. too many transfer points, fear of superiors). Finally, it provides tips for overcoming barriers like creating an open environment and considering the receiver.