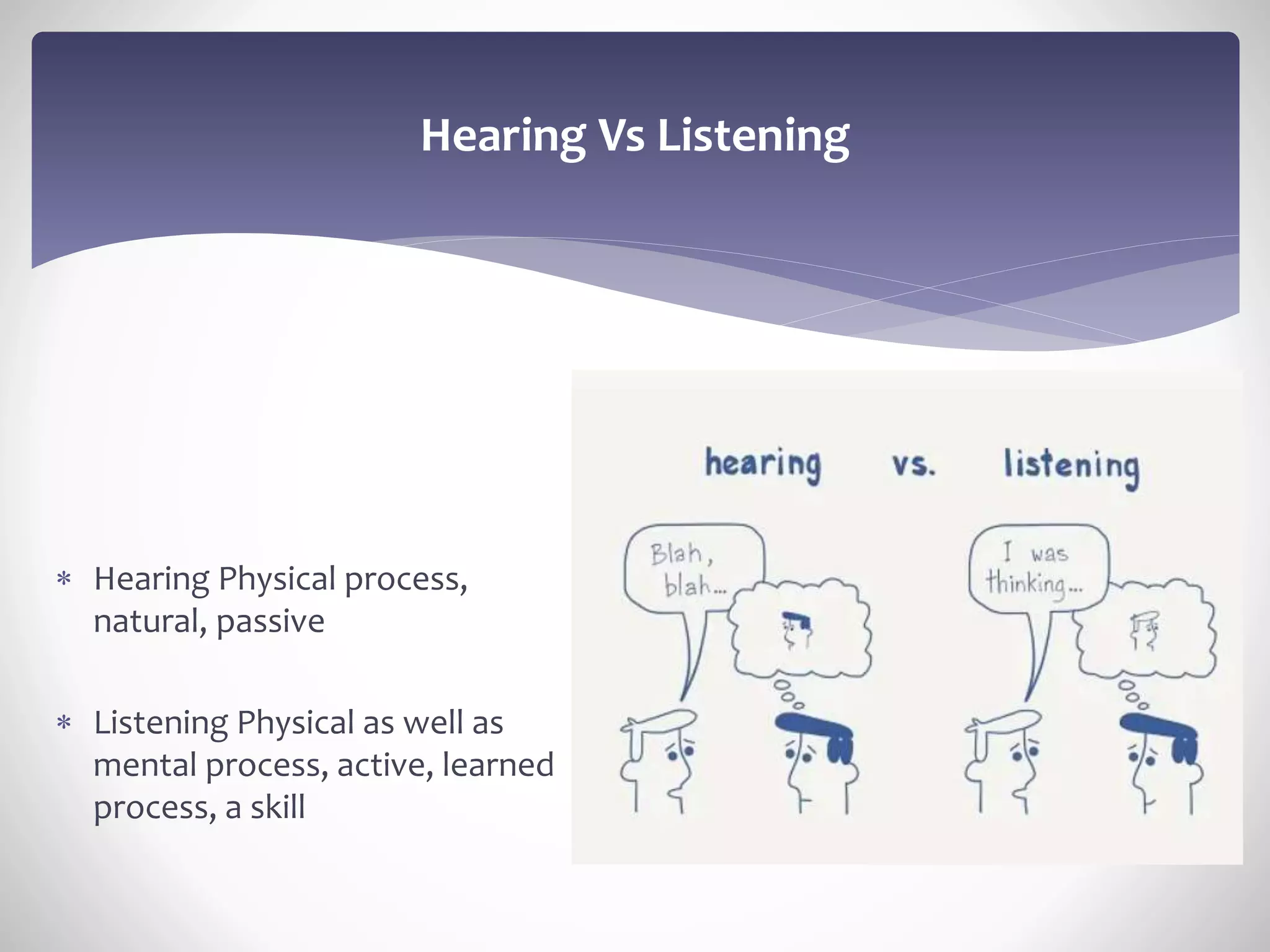
This document discusses communication and the communication process. It defines communication as the transmission of information, ideas, and attitudes between people through expression. The document then discusses the need for effective communication in working with others who have different perspectives. It outlines the common barriers to communication like noise and filters. It also discusses the key components of the communication process like common environment, encoding and decoding messages, and feedback. Finally, it provides tips for improving communication skills like using simple language, active listening, and overcoming communication barriers.