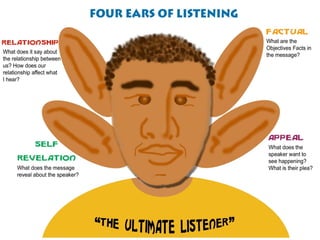
The document discusses barriers to communication, dividing them into those caused by the sender/recipient and those from outside influences. Barriers caused by the sender/recipient include distortion, inadequate communication skills, lack of listening ability, attitudes/feelings, differences in background, opinions, beliefs, and personal characteristics. Non-verbal behavior can also create barriers if it sends a different message than the words. The document provides tips for overcoming barriers, such as developing communication skills, listening actively, choosing when/who to communicate with carefully, and matching the expression to the recipient.