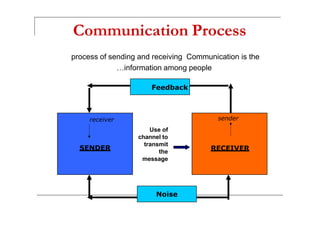
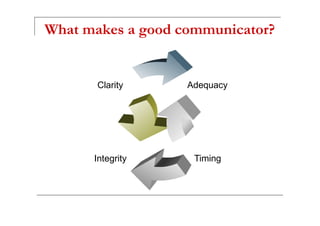
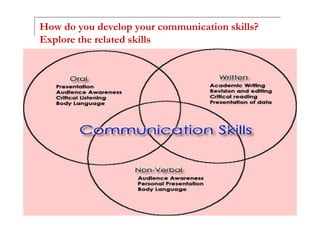
Communication involves three components: verbal messages, paraverbal messages, and nonverbal messages. Effective communication requires sending clear messages using all three components and properly receiving and understanding messages from others. It is a process that can be hindered by various barriers from both the sender and receiver such as lack of attention, assumptions, emotions, and cultural or language differences. Developing good communication skills involves exploring related skills like listening, clarity, integrity, and practicing effective communication strategies such as maintaining eye contact and conveying thoughts clearly.