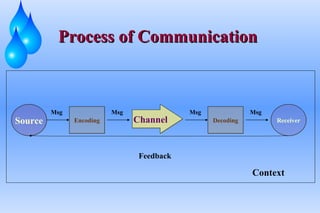
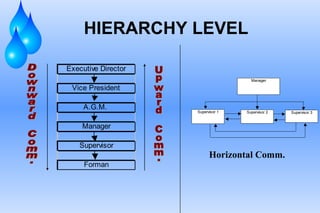
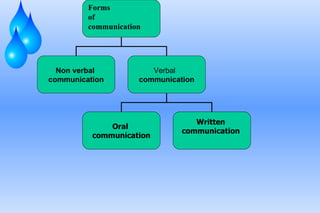
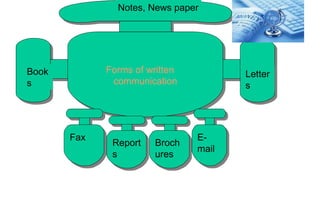
The document defines communication and outlines the communication process. It discusses the key elements of communication including the sender, message, encoding, medium, receiver, decoding, feedback and context. Barriers to communication like noise and assumptions are also covered. Different types of communication such as downward, upward and lateral are explained. Both verbal and non-verbal communication are important parts of the overall process. Tips for improving communication skills through language, listening and self-improvement are provided.