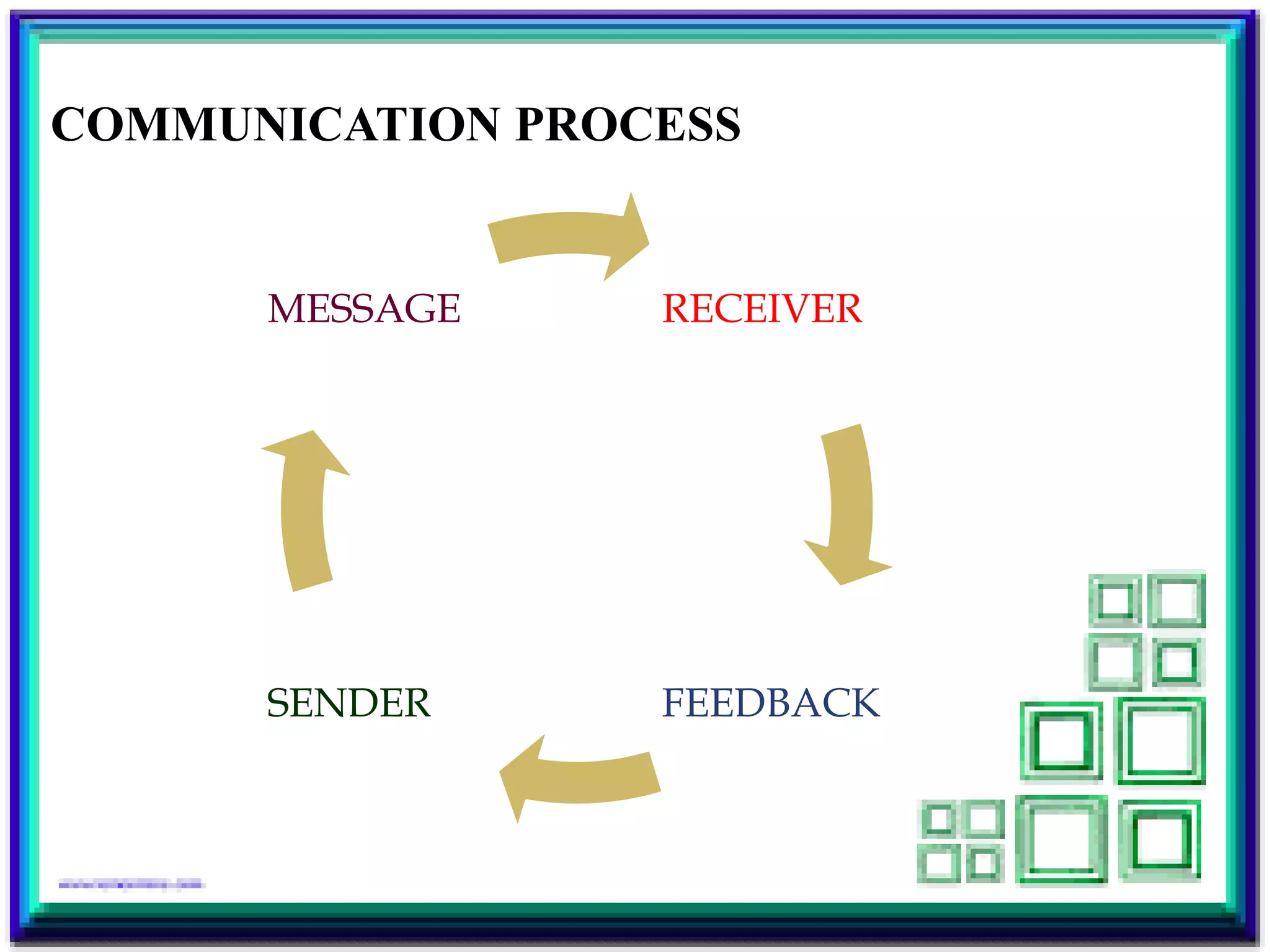
This document discusses various topics related to communication including communication modes, barriers to communication, the communication process, multimedia approaches, mass media, and Flander's Interaction Analysis technique. It defines communication and describes the three modes of communication as interpretive, interpersonal, and presentational. It also outlines internal and external barriers to communication and defines the key components of the communication process as the sender, message, receiver, and feedback.