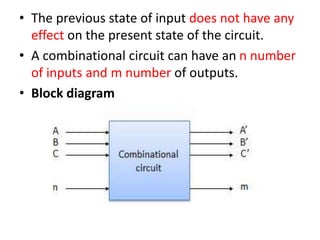
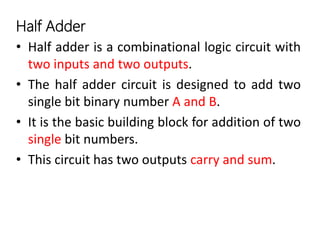
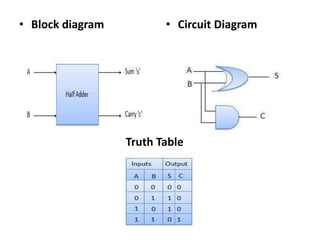
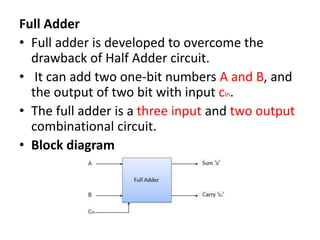
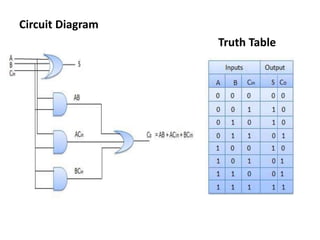
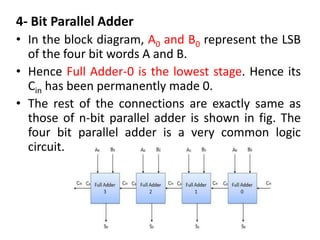
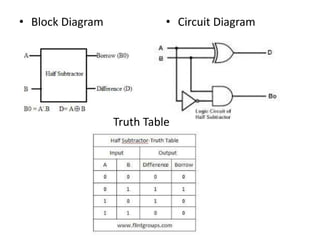
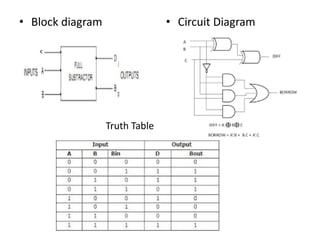
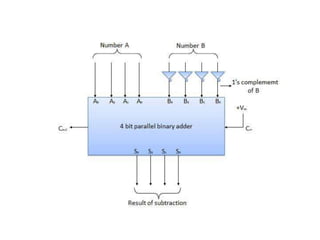
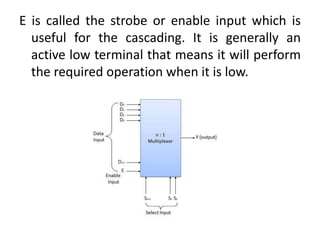
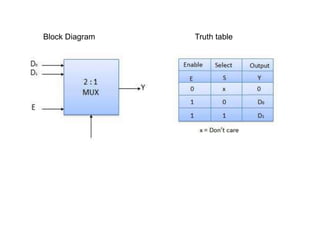
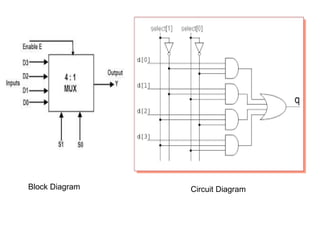
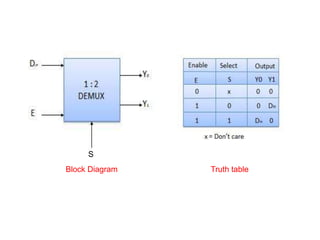
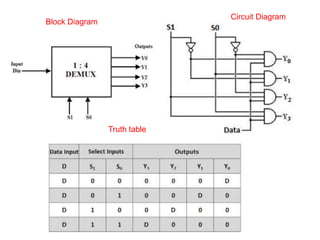
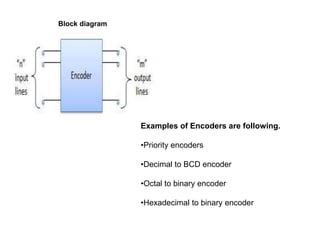
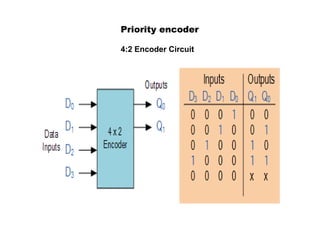
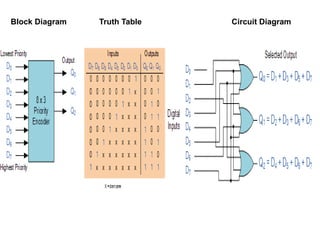
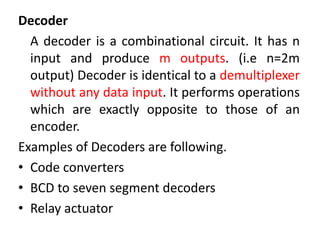
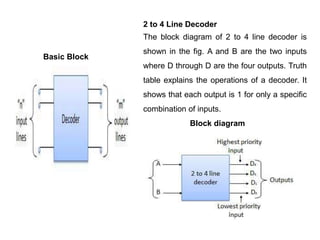
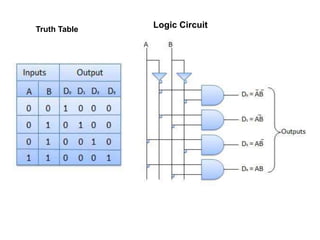
This document describes various types of combinational logic circuits. It discusses half adders and full adders which can add single bits and pairs of bits along with a carry bit. Parallel adders are formed from cascaded full adders to add multiple bit numbers. Half subtractors, full subtractors, and parallel subtractors can perform single and multi-bit binary subtraction. Multiplexers and demultiplexers are described which can select single inputs from multiple options or distribute a single input to multiple outputs. Encoders and decoders are covered which convert between binary and coded representations.