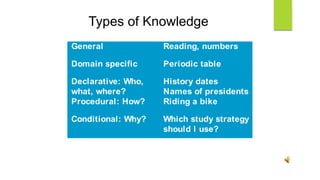
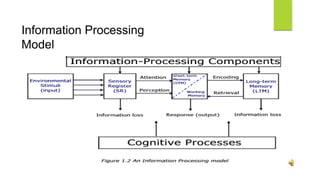
The document discusses cognitive views of learning, specifically the information processing model, defining learning as the process of acquiring knowledge and skills through various experiences. It covers cognitive learning theories, including social cognitive theory and cognitive behavioral theory, and distinguishes between types of knowledge such as declarative, procedural, and conditional. Additionally, it explains the processes of sensory memory, working memory, and long-term memory, as well as the concept of metacognition and its three essential skills: planning, monitoring, and evaluation.