Embed presentation
Downloaded 87 times







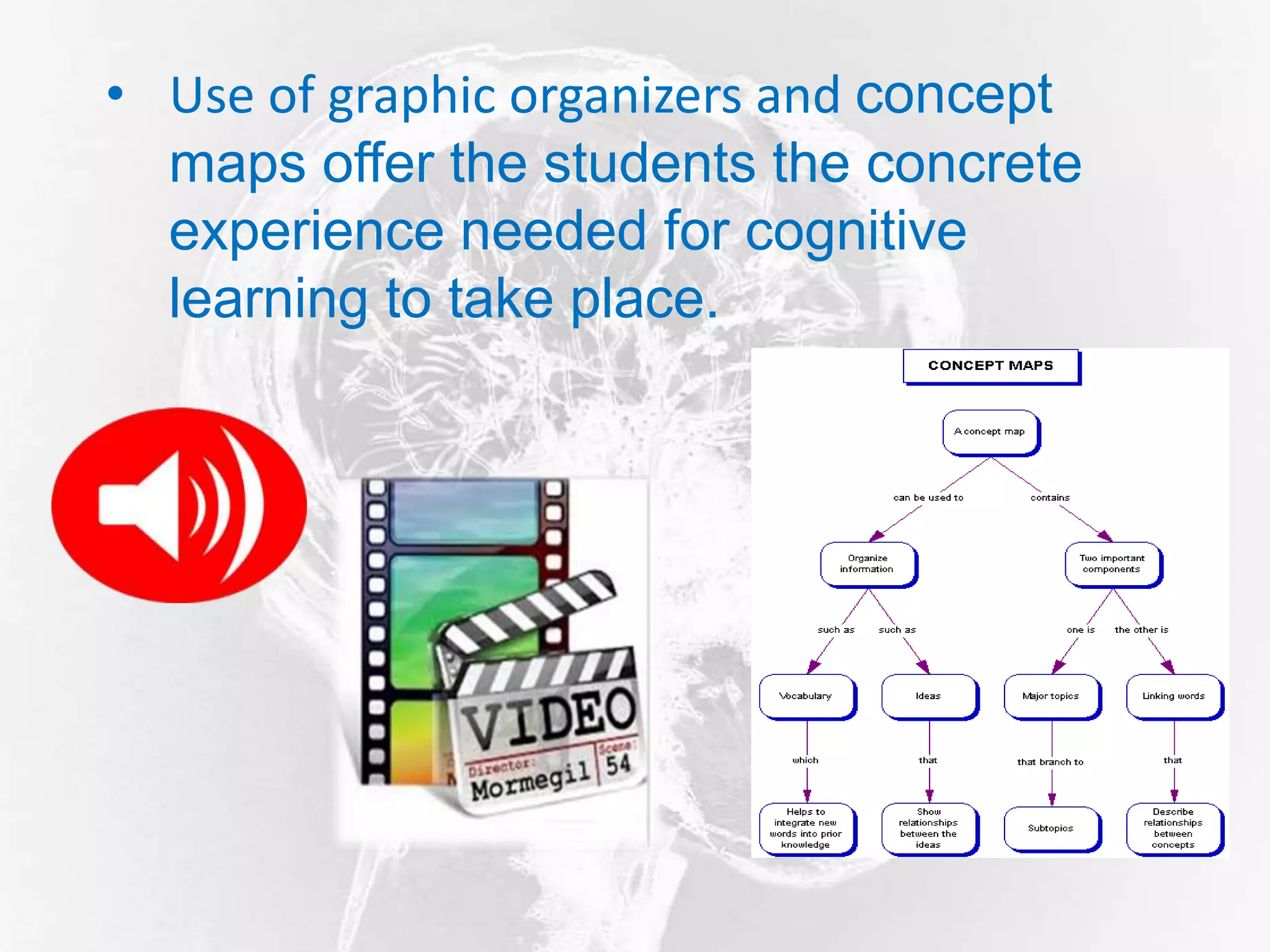


Cognitivism theory examines how people think and gain knowledge through learning, memory, problem solving, and intelligence. It views the mind as a "black box" where learning occurs through recalling and making sense of stored information. Key factors that influence learning according to cognitivism include a person's existing schemas and previous experiences. Memory plays an important role through encoding, storing, and retrieving information. Learning theories best explained by cognitivism include reasoning, problem solving, and learning with clear objectives. Major theorists in cognitivism include Piaget with his cognitive development theory and Ausubel with his meaningful learning theory.









