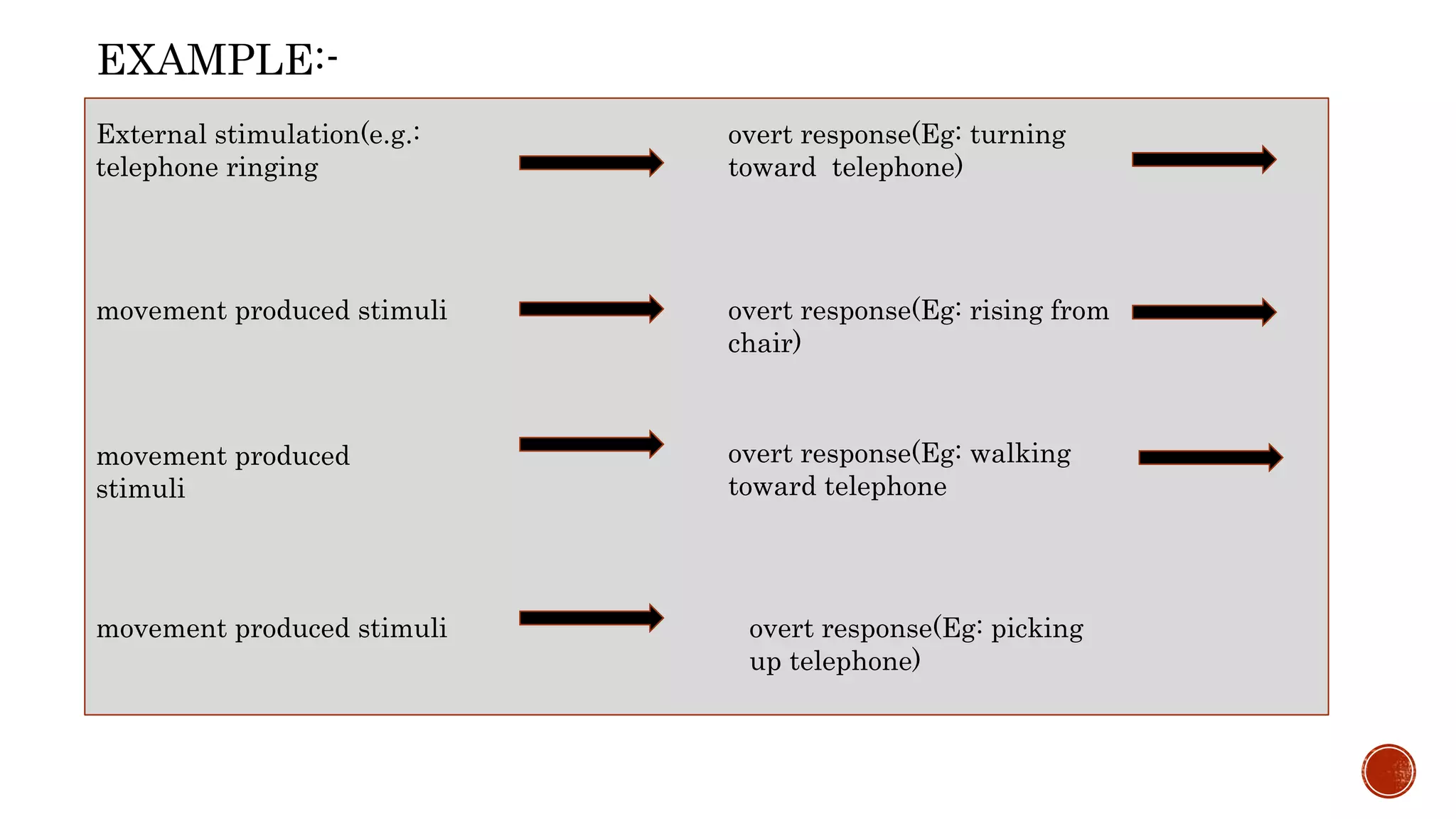
The document summarizes the work and learning theory of Edwin Guthrie. It discusses that Guthrie proposed one law of learning - the law of contiguity, which states that stimuli and responses become associated based on their closeness in time and space. Guthrie believed that learning occurred through a single pairing of a stimulus and response, in contrast to theorists like Thorndike who argued learning required repetition. The document also describes Guthrie's experiments with cats in a puzzle box and how they informed his views on learning, forgetting, and the lack of need for reinforcement. Overall, the document provides an overview of Guthrie's influential law of contiguity and its implications for understanding learning.