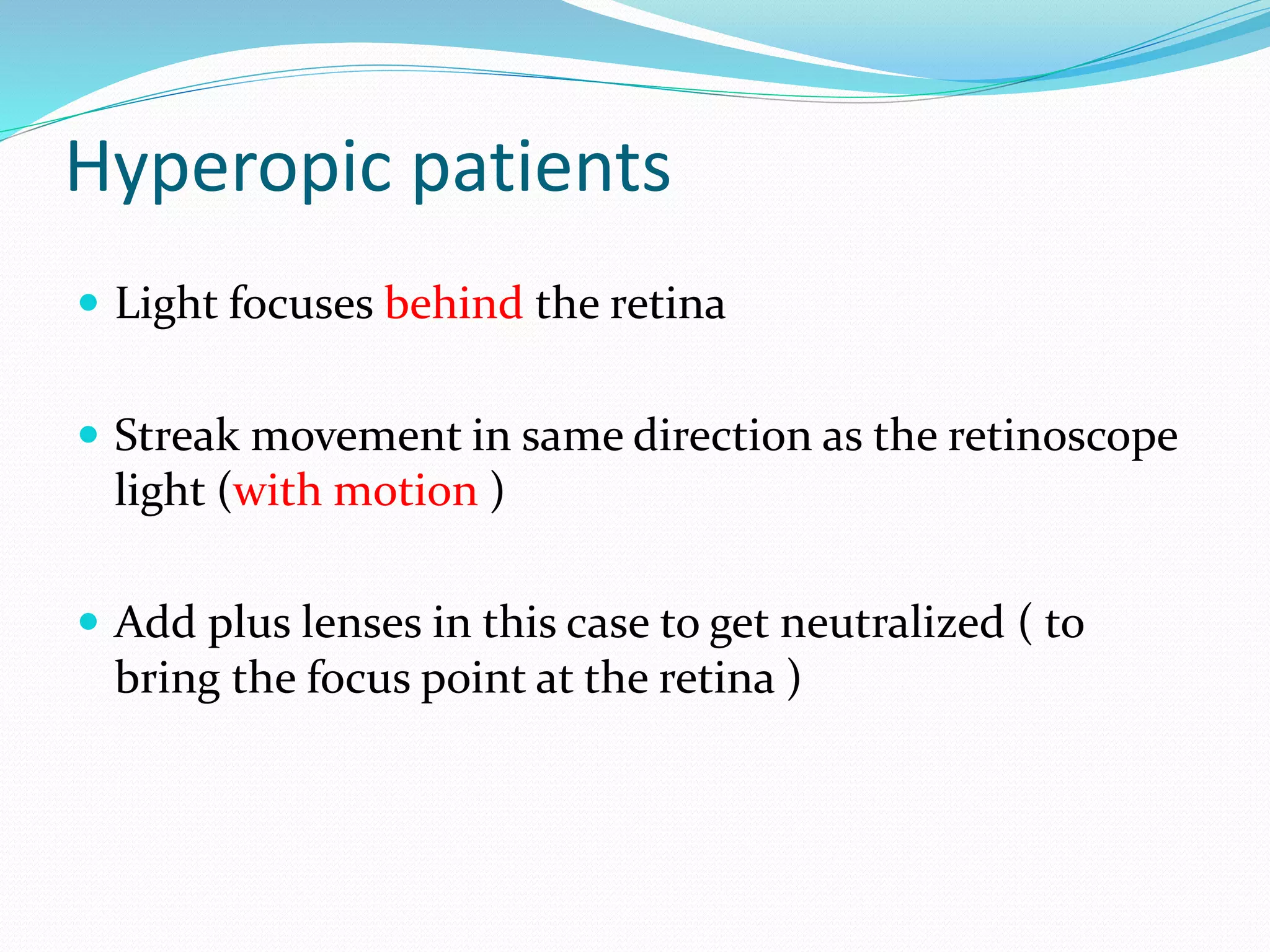
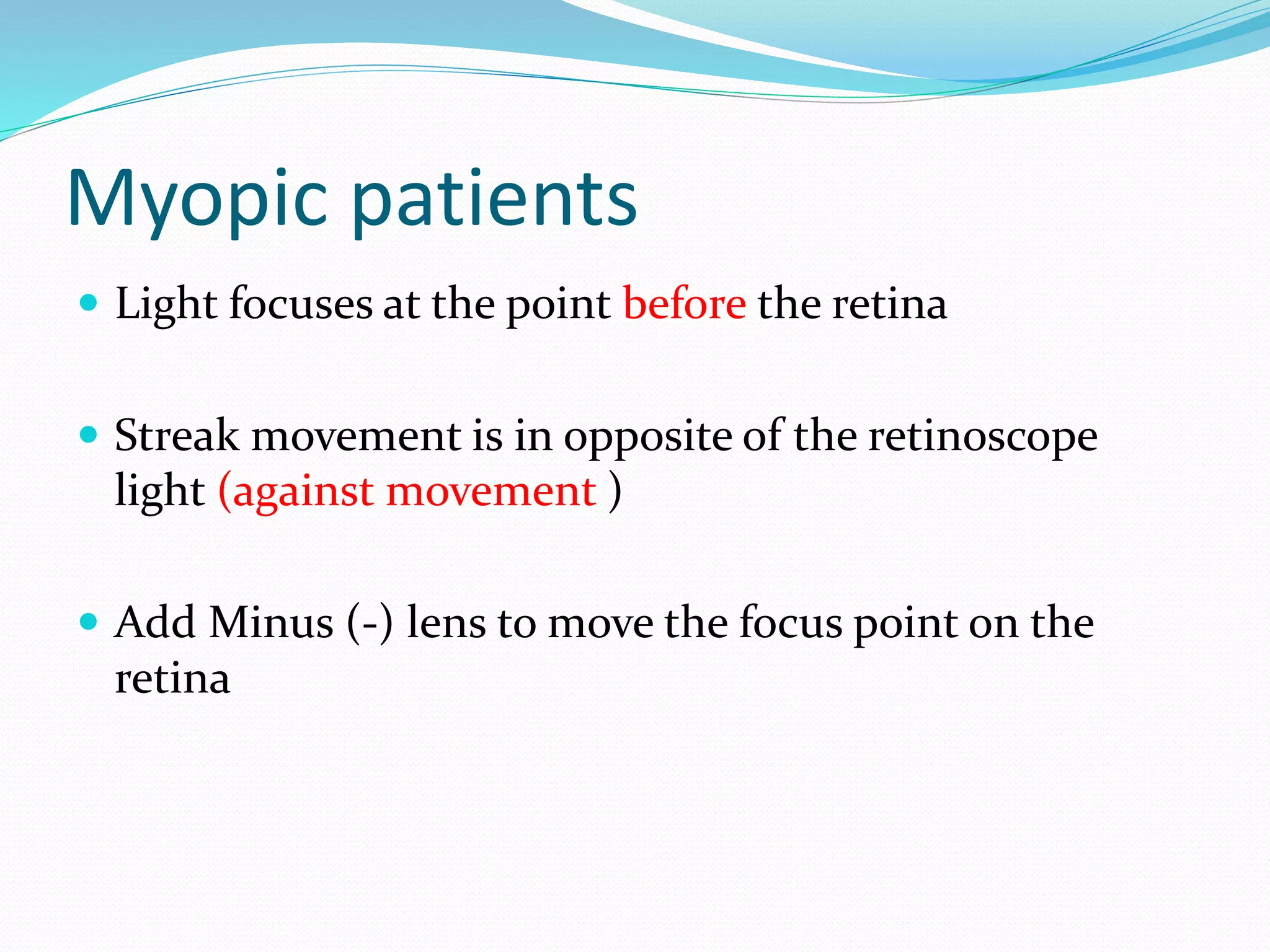
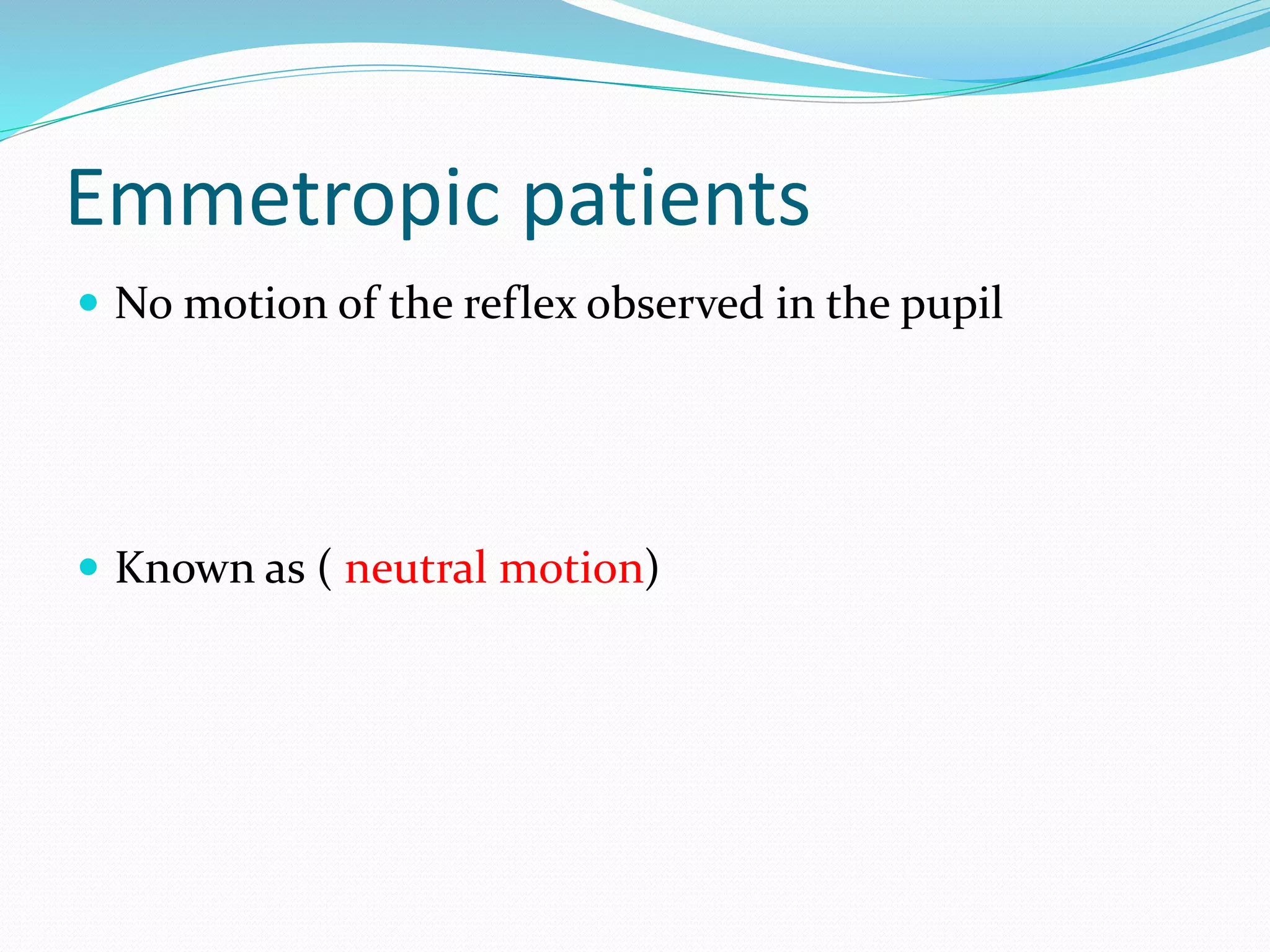
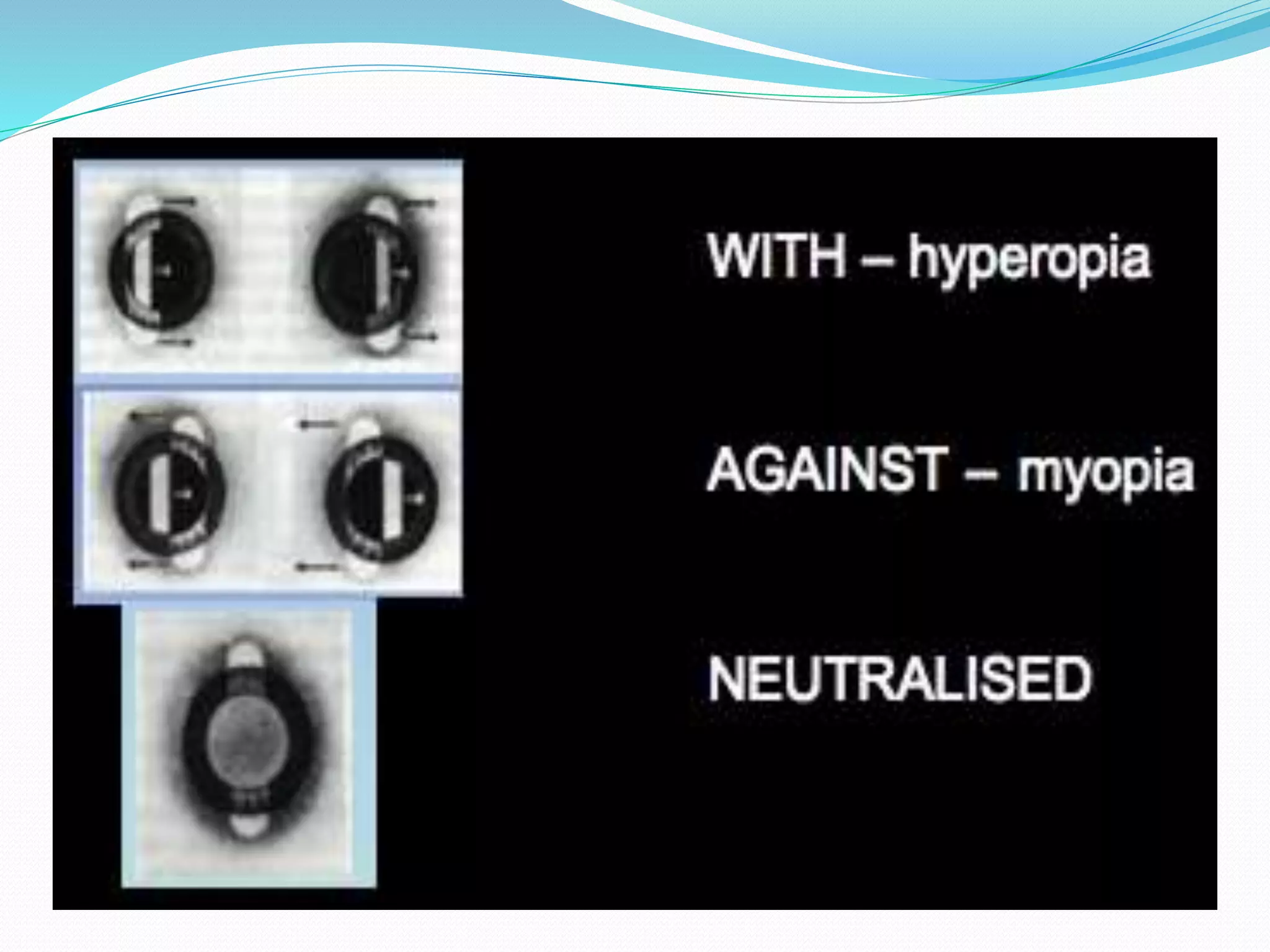
Retinoscopy is a technique used to determine refractive errors by analyzing the light reflex in the pupil that reflects from the retina through a retinoscope. It can be performed statically or dynamically on patients, including infants and those with low vision, and involves the use of either streak or spot retinoscopes, with streak retinoscopy generally preferred for its clinical utility. The findings serve as a foundational starting point for further subjective refraction, and specific techniques are employed to assess the patient's refractive status based on the observed motion of the light reflex.


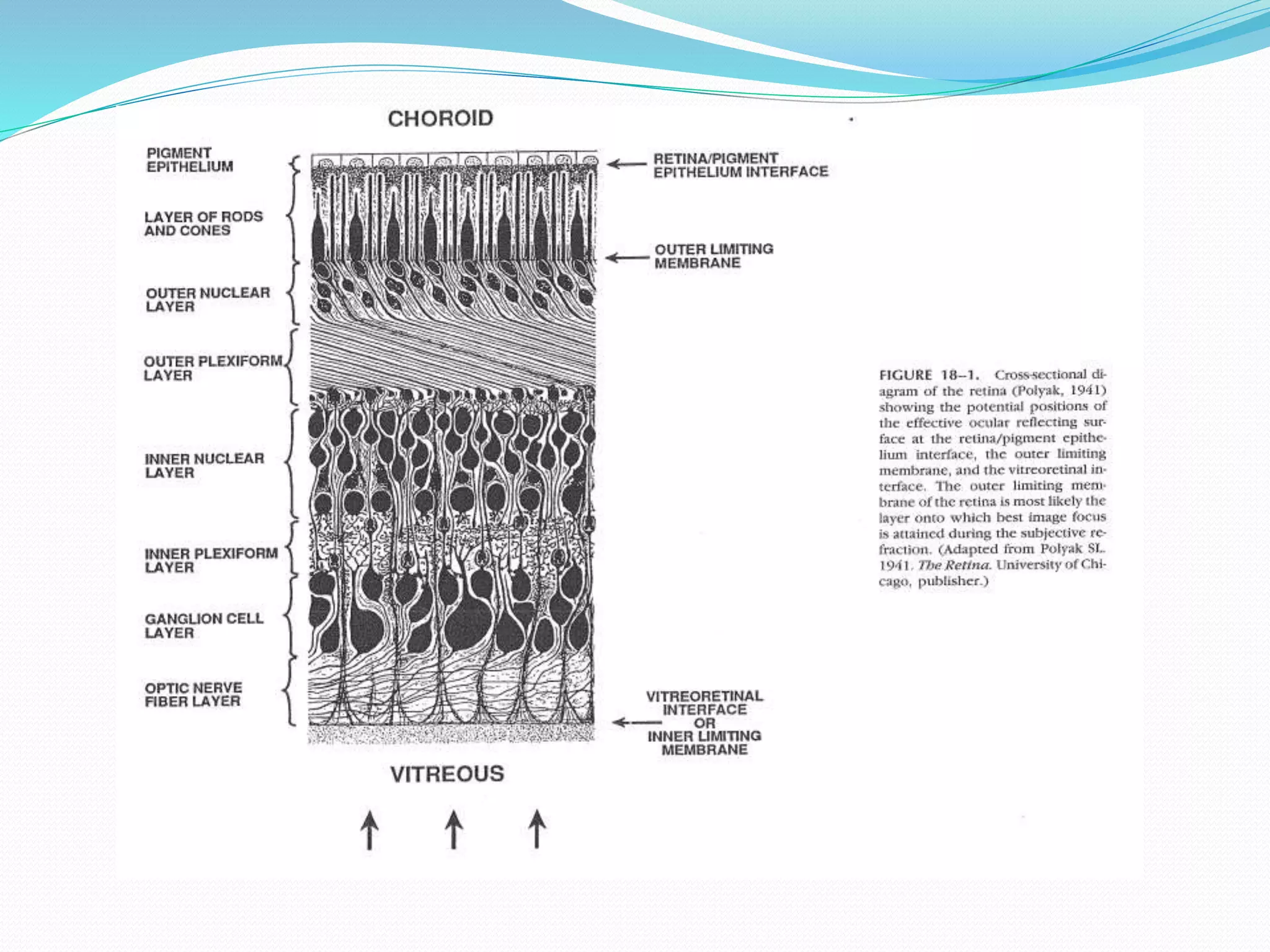





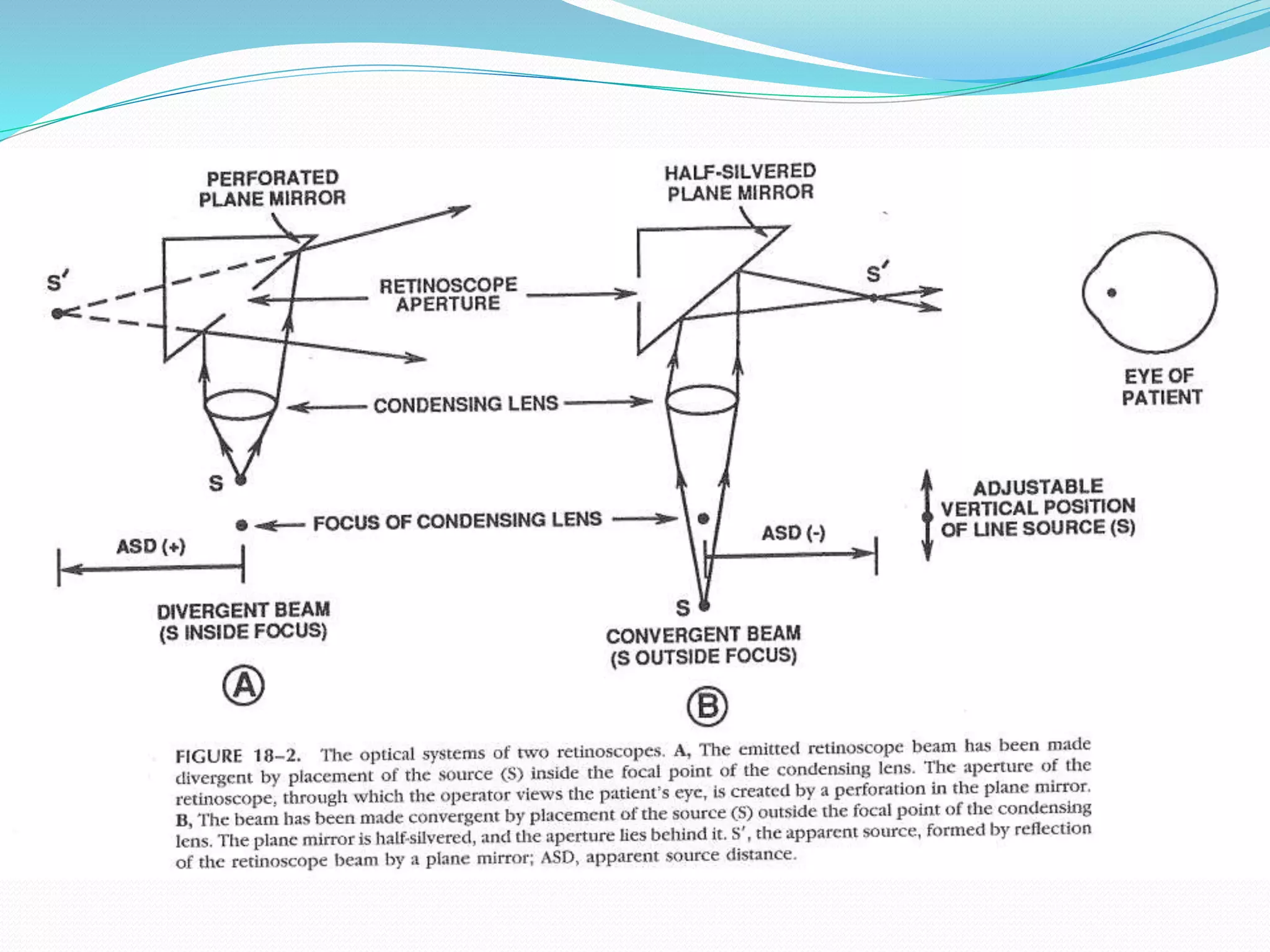
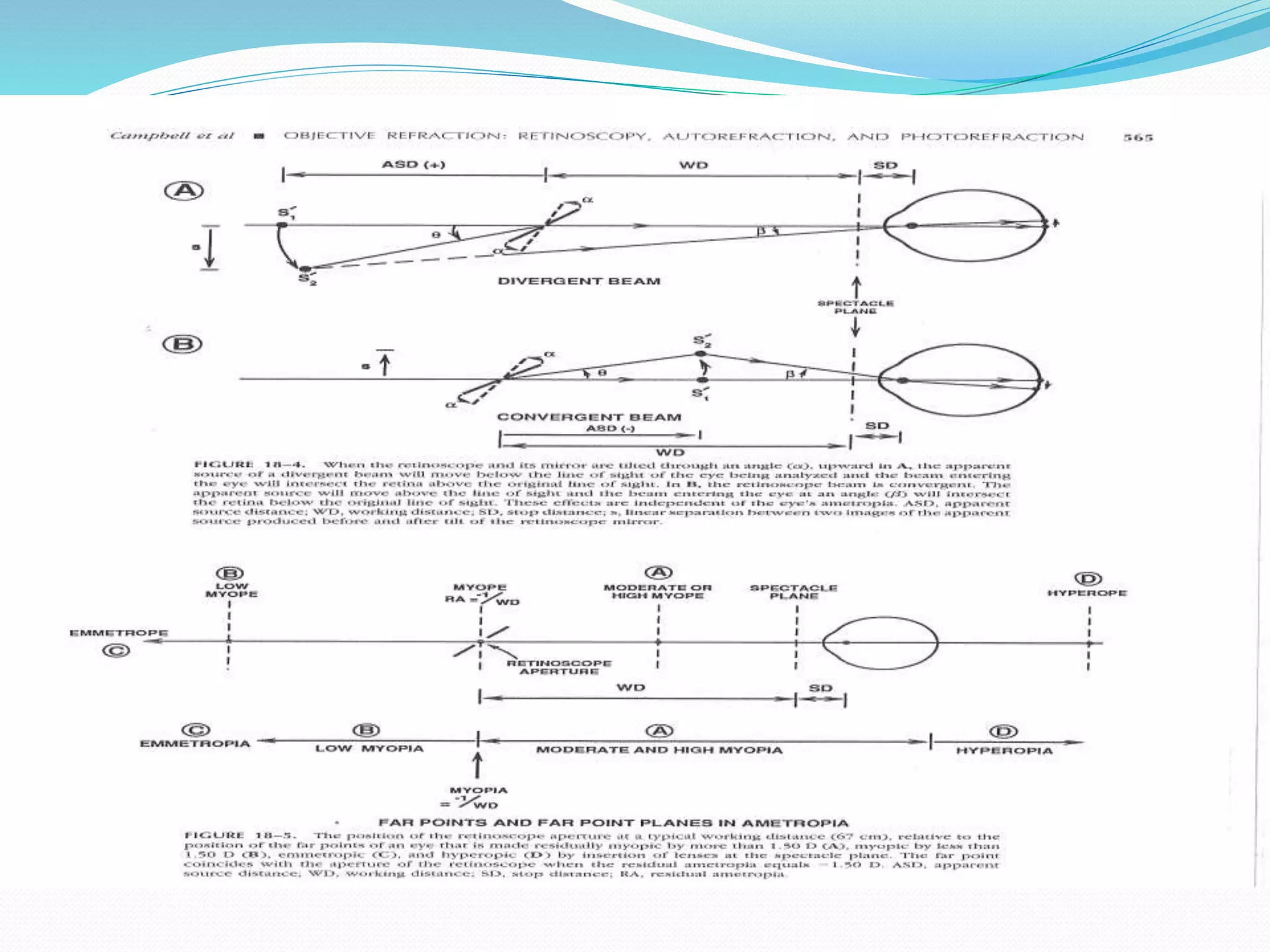
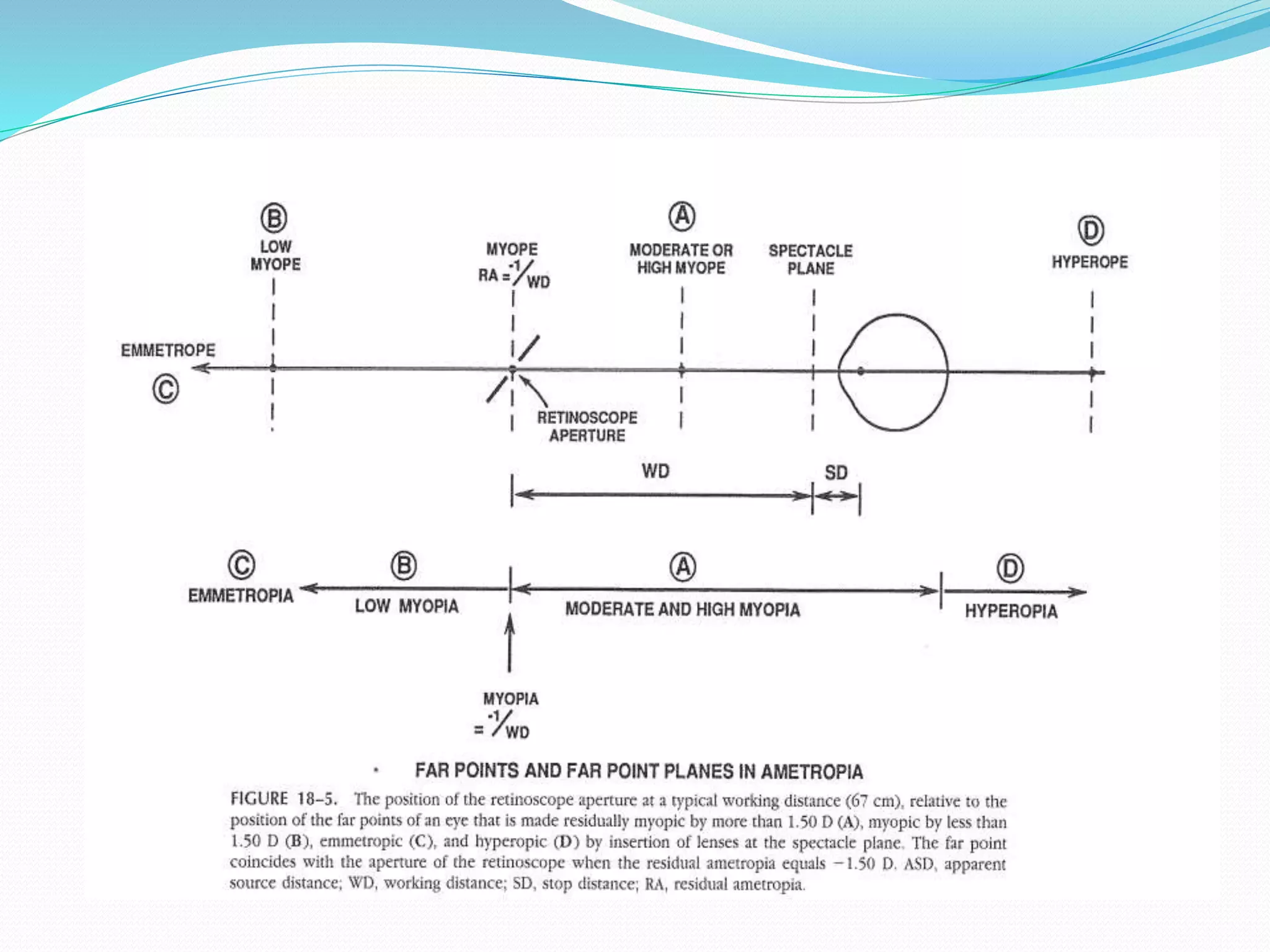
![ The objective of static R is to find the position of the paraxial far point
]punctum remotum (PR) [ of the eye , an optical theory initially
advocated by landolt in 1878.
The “spot R” reflects a beam of light from a circular source whereas the
“streak retinoscpe” emits a beam from a line source .
Between these two forms of retinoscpes , the streak R is more useful
clinically because it can be more readily applied to the determination
of astigmatic corrections by assessment of the axis of cylinder and
refractive powers in the two primary amertopic meridians.
The use of streak retinoscpy has generally replaced the use of spot R in
ophthalmic practice .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectiverefraction-150727161420-lva1-app6891/75/Objective-refraction-14-2048.jpg)