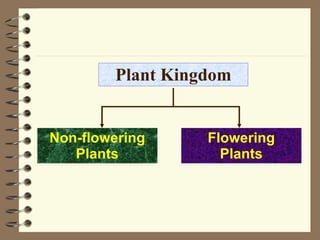
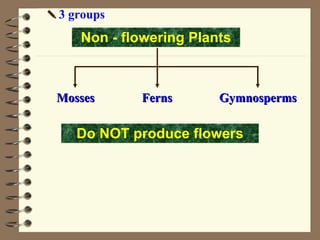
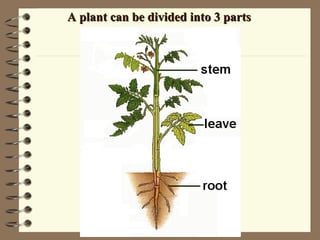
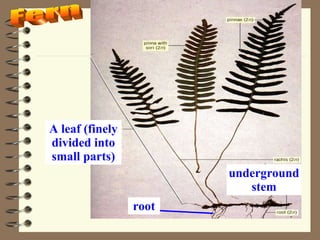
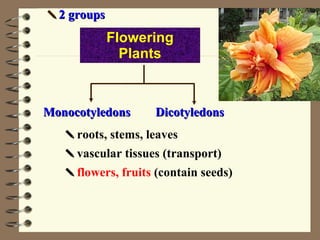
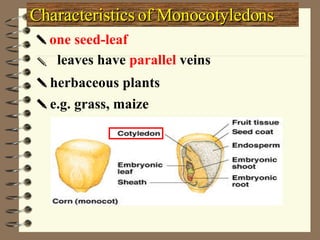
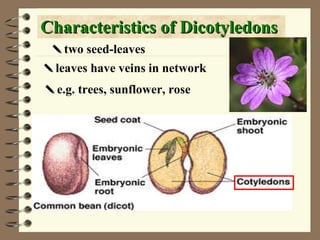
The document classifies plants into two main groups: flowering plants and non-flowering plants. Non-flowering plants are further divided into mosses, ferns, and gymnosperms. Mosses have no true roots or vascular tissues, simple stems and leaves, and reproduce via spores from capsules dispersed by wind. Ferns have roots, feathery leaves, underground stems, and vascular tissues, reproducing via spores on leaf undersides. Gymnosperms are tall evergreen trees like pine trees with needle-shaped leaves, cones, and naked seeds in female cones. Flowering plants are divided into monocots and dicots based on their seed and leaf characteristics.