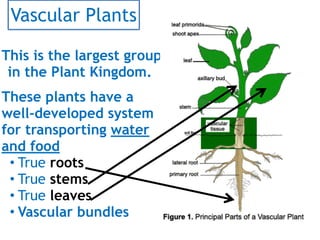
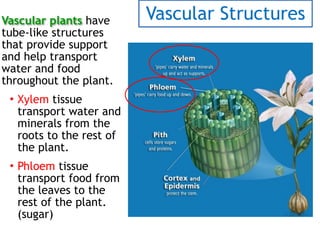
This document provides information about classifying plants into the vascular and non-vascular categories based on their internal structures. It explains that vascular plants have well-developed systems for transporting water and food through tissues like xylem and phloem, while non-vascular plants lack these structures and transport nutrients cell to cell only. Examples are given of vascular plants like trees and grasses that have true roots, stems, and leaves, as well as non-vascular plants like mosses that remain small without specialized transport systems.