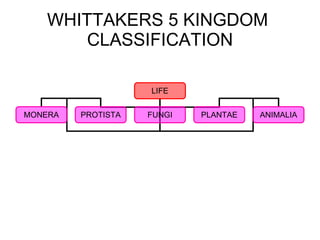
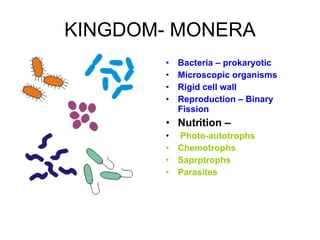
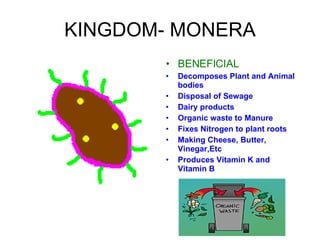
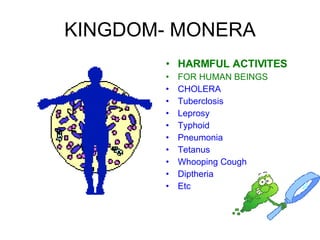
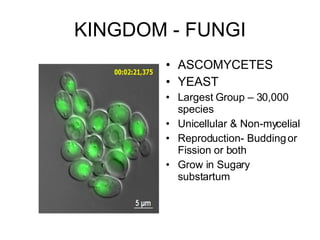
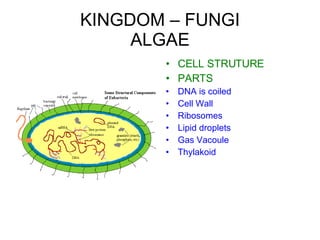
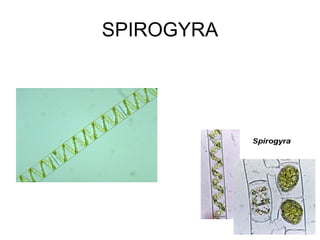
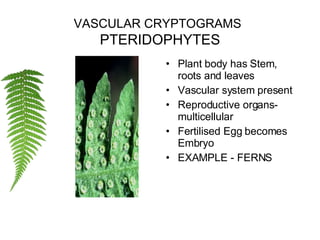
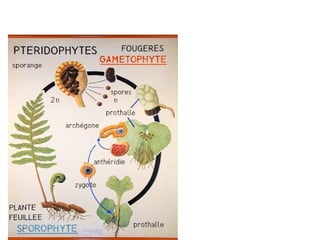
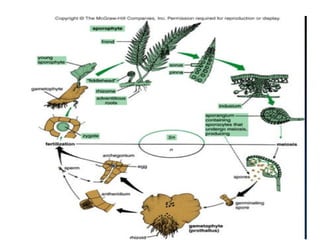
The document discusses Robert Whittaker's five kingdom classification system from 1969 which divides life into five kingdoms - Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. It provides details on the Monera kingdom, which includes bacteria, and notes both their beneficial roles like decomposition and nitrogen fixation as well as harmful pathogenic bacteria. It also summarizes the characteristics of the Protista, Fungi, and Plantae kingdoms.