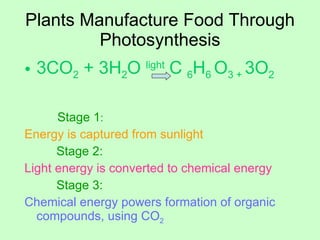
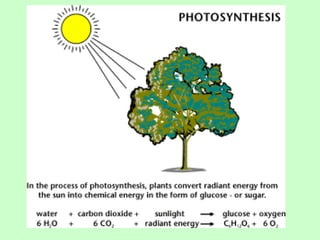
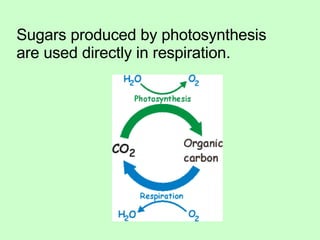
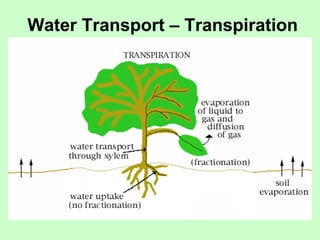
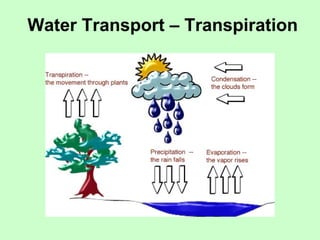
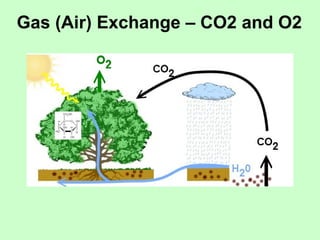
Leaves are essential structures in plants responsible for photosynthesis, which converts sunlight into chemical energy to produce sugars while releasing oxygen as a by-product. They also play crucial roles in gas exchange, protection of buds, water transport, and food storage during germination. Additionally, leaves help maintain the water cycle and support the continued life on Earth through their various functions.