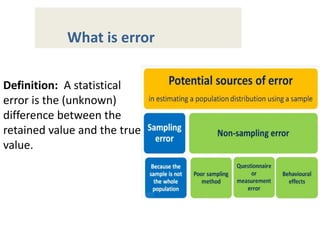
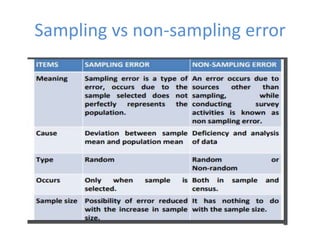
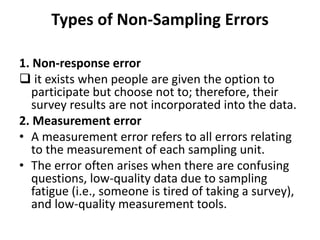
A statistical error is the difference between a sample value and the true population value. There are two main types of error - sampling error and non-sampling error. Sampling error occurs when the sample is not fully representative of the population, while non-sampling error can arise from factors like non-response, measurement issues, interviewer errors, adjustments to the data, or processing mistakes. Common ways to measure and reduce sampling error include calculating the standard error, sample size, and sample design.