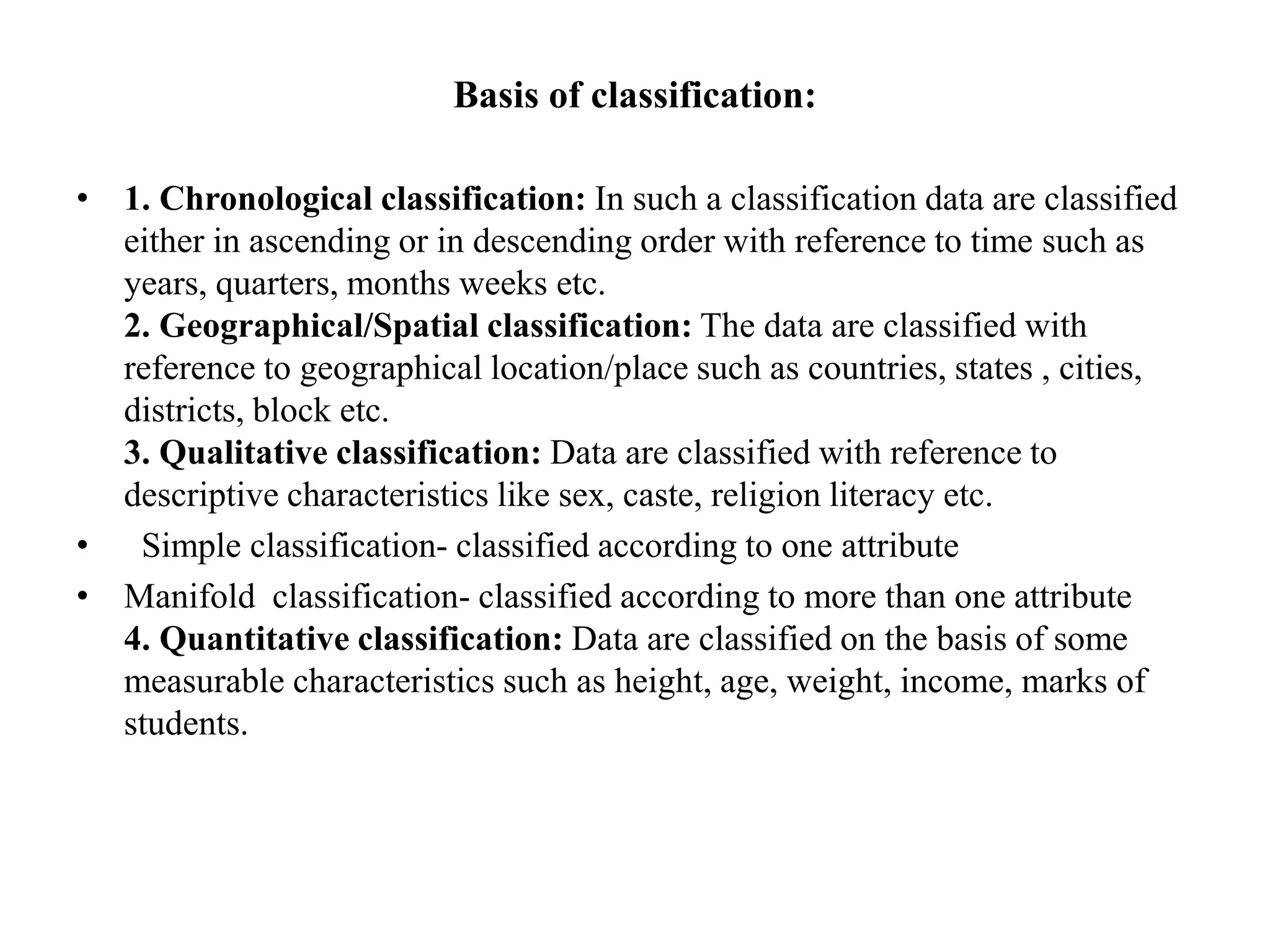
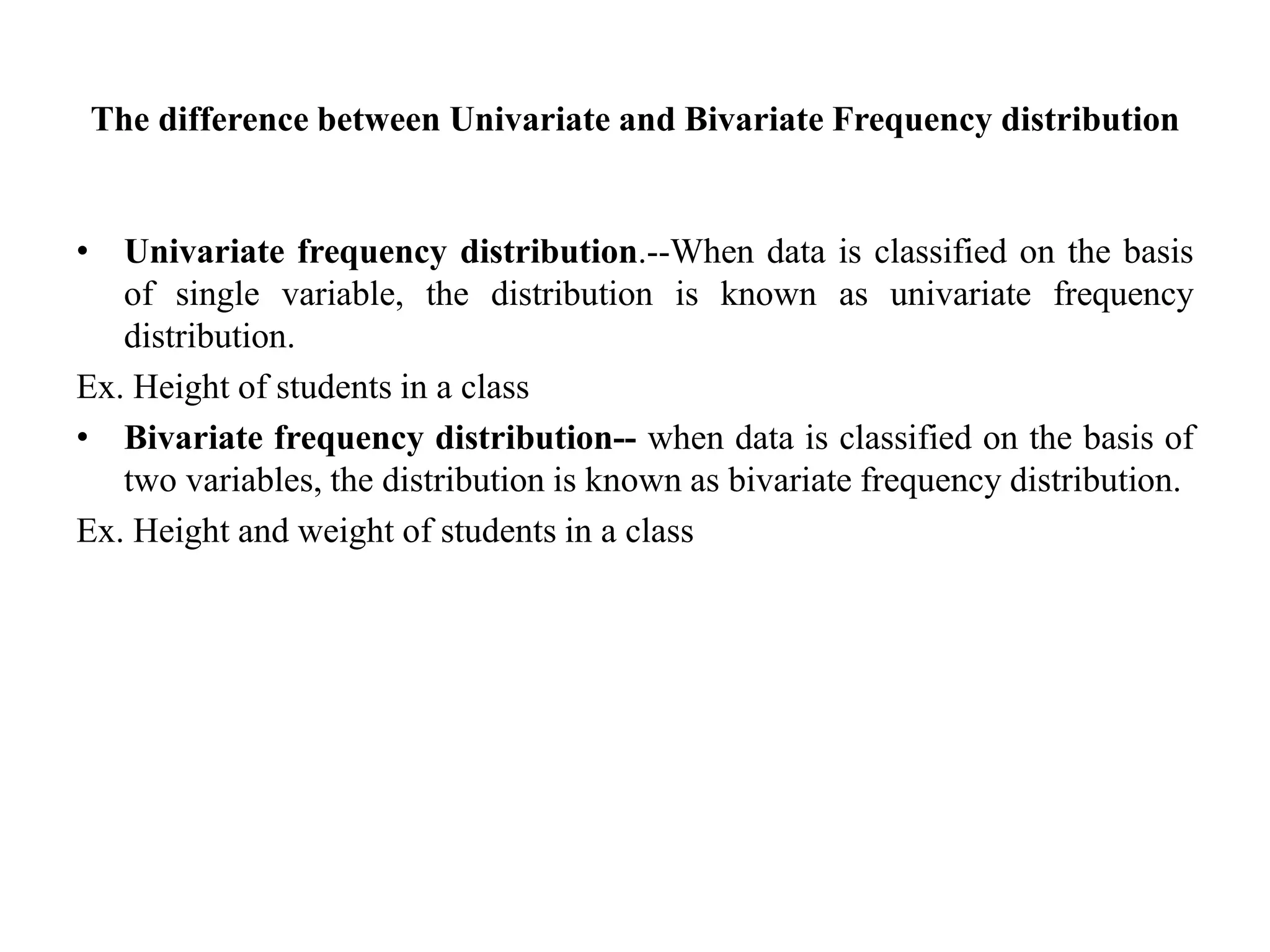
This document discusses the organization and classification of data. It defines raw data as unorganized information and explains that classification involves arranging data into logical groups based on common attributes. The objectives of classification are to simplify, explain relationships, facilitate comparison and prepare data for tabulation. Classification can be done chronologically, geographically, qualitatively or quantitatively. Frequency distributions then arrange classified data into class intervals along with the frequency of observations in each interval. Univariate distributions use one variable, while bivariate distributions use two variables.