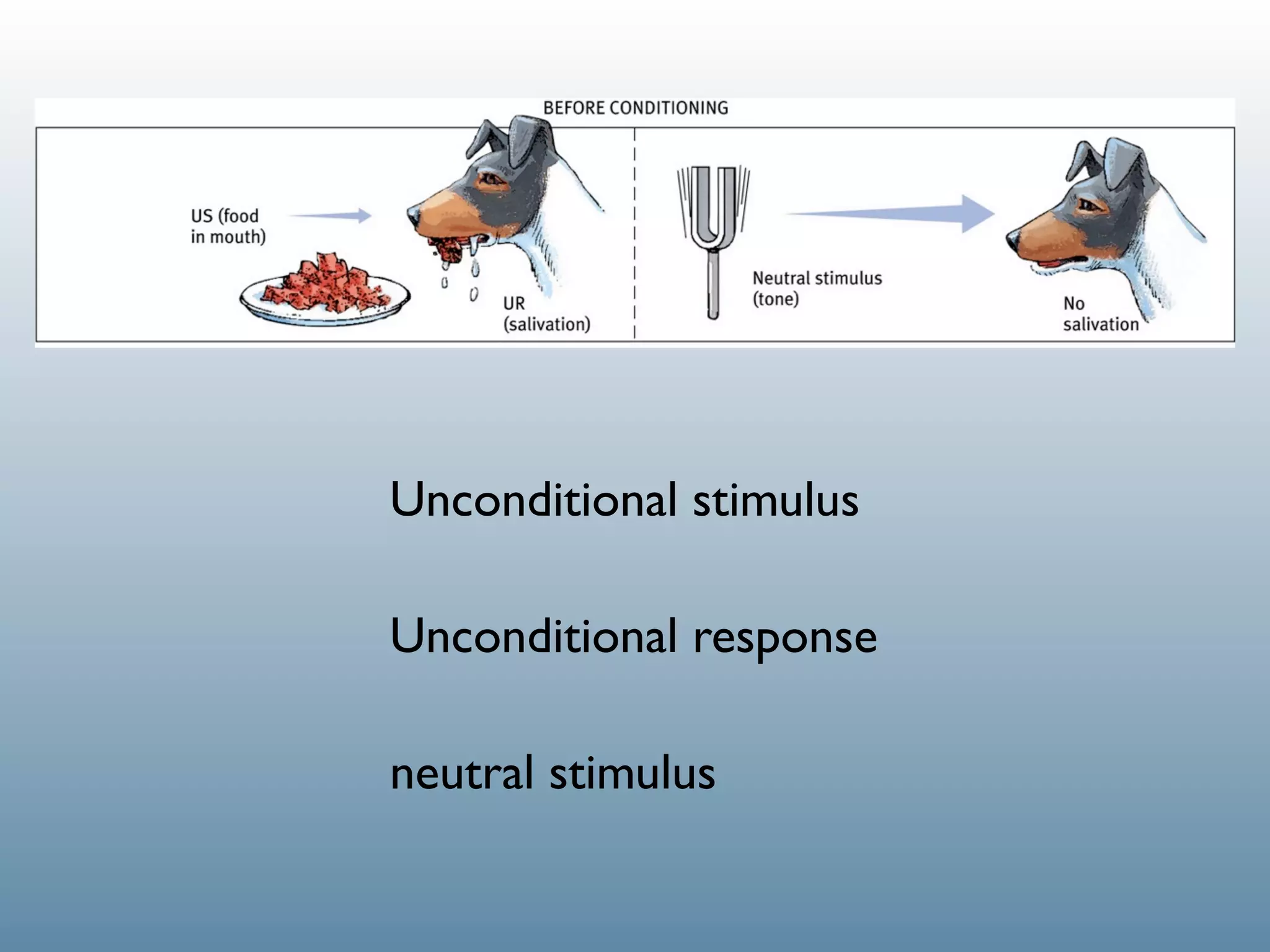
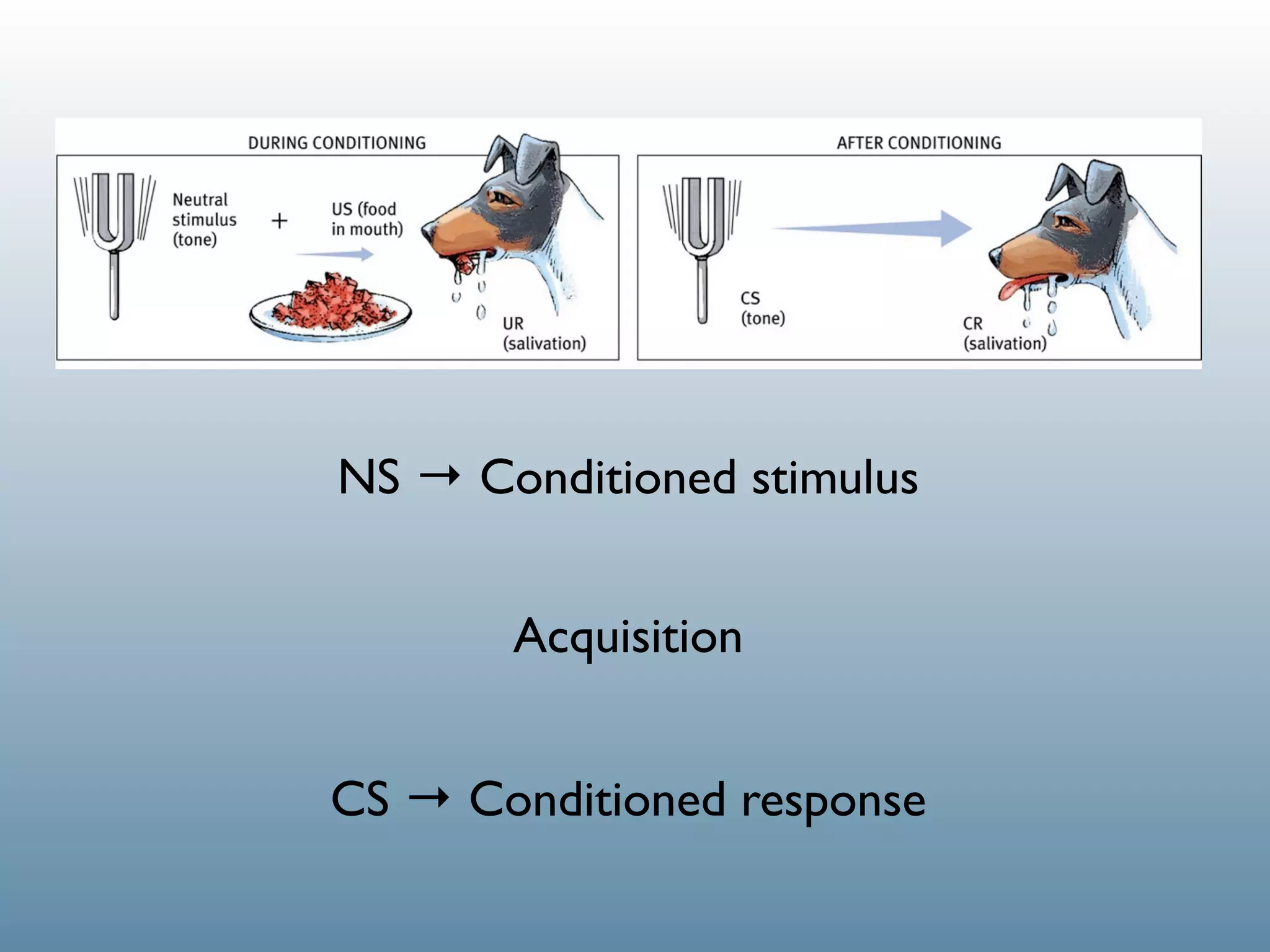
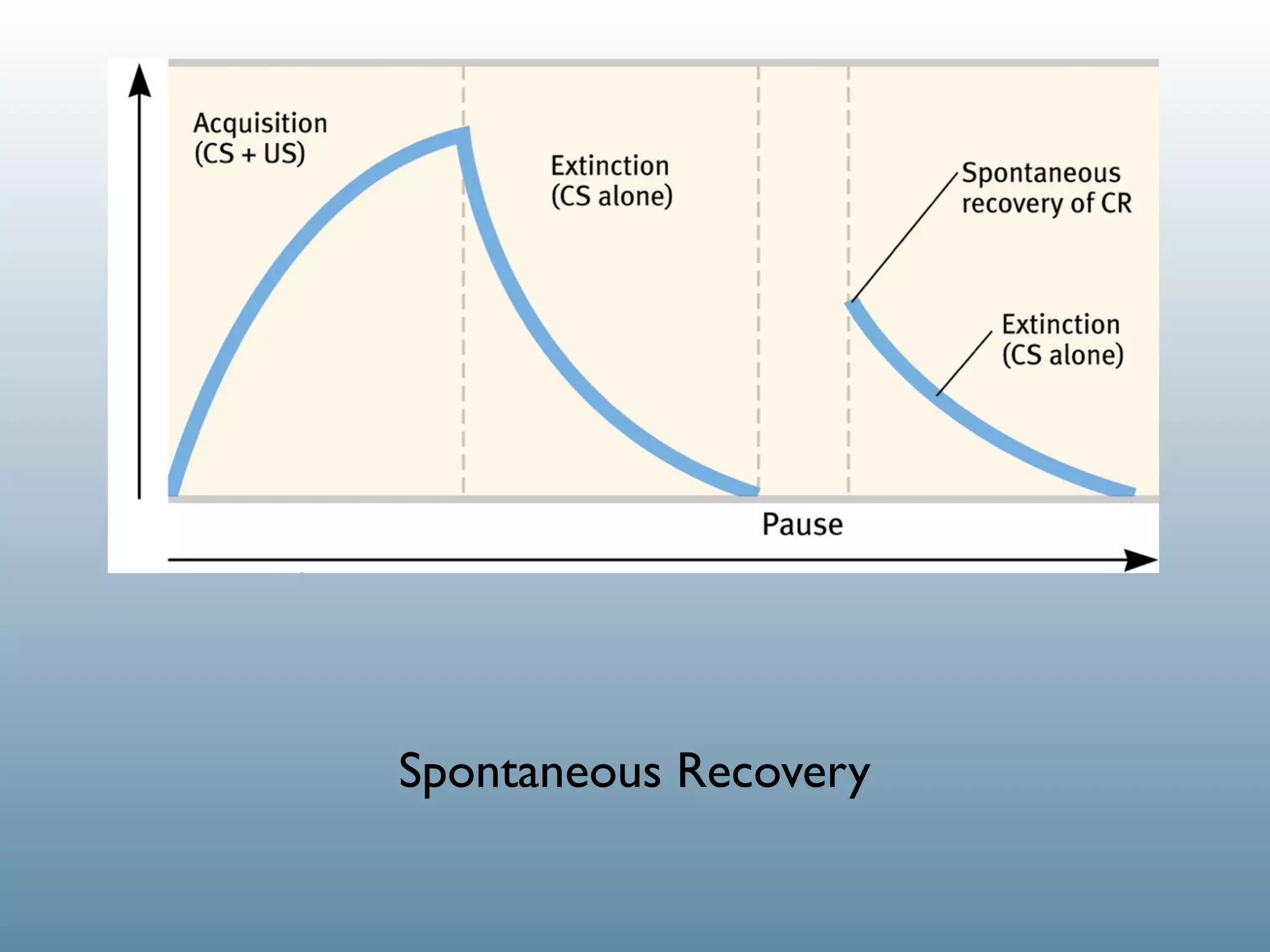
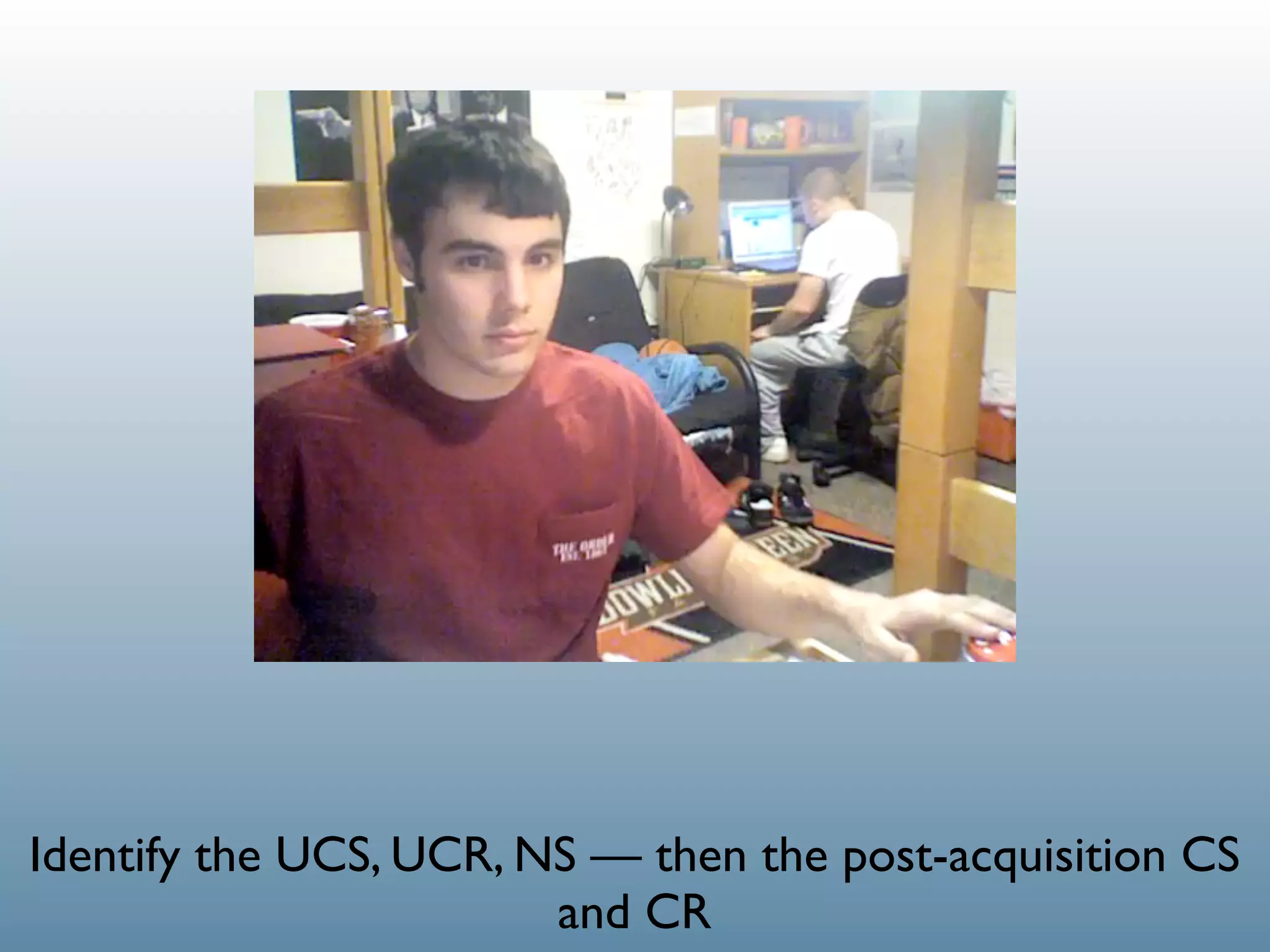
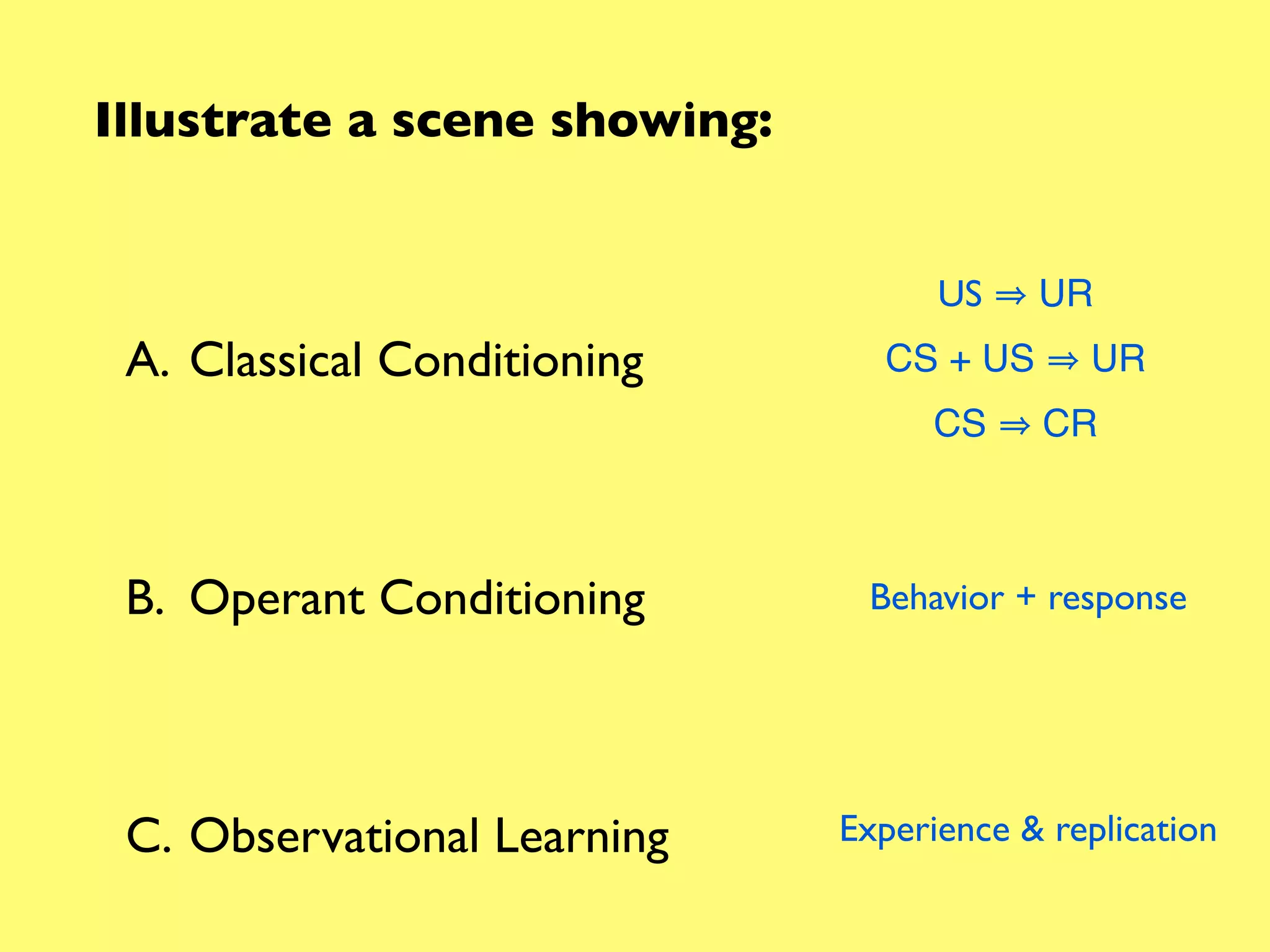
1. Classical conditioning: A dog salivating (UR) in response to food (US), then later salivating (CR) at the sound of a bell (CS) that was paired with the food.
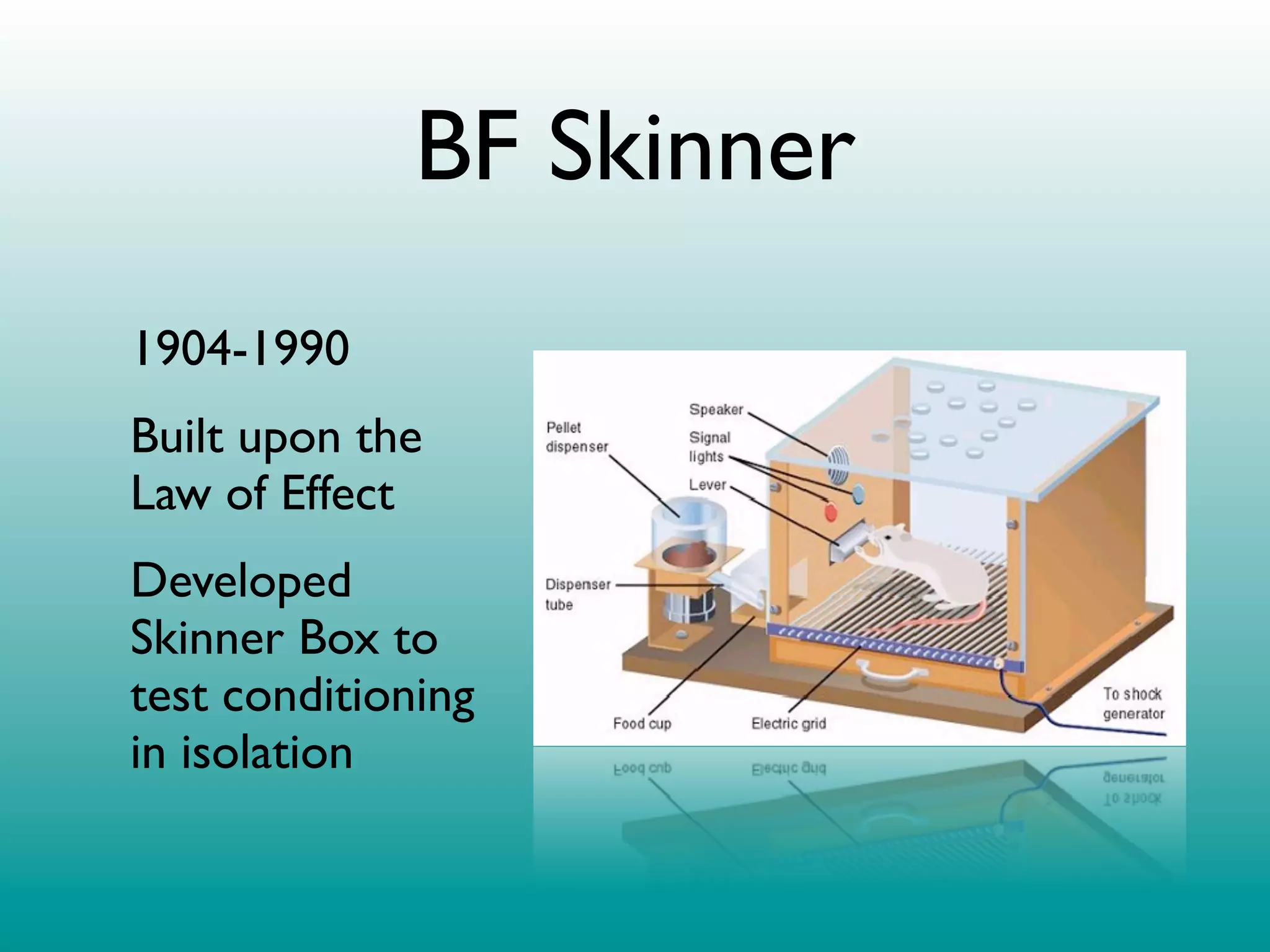
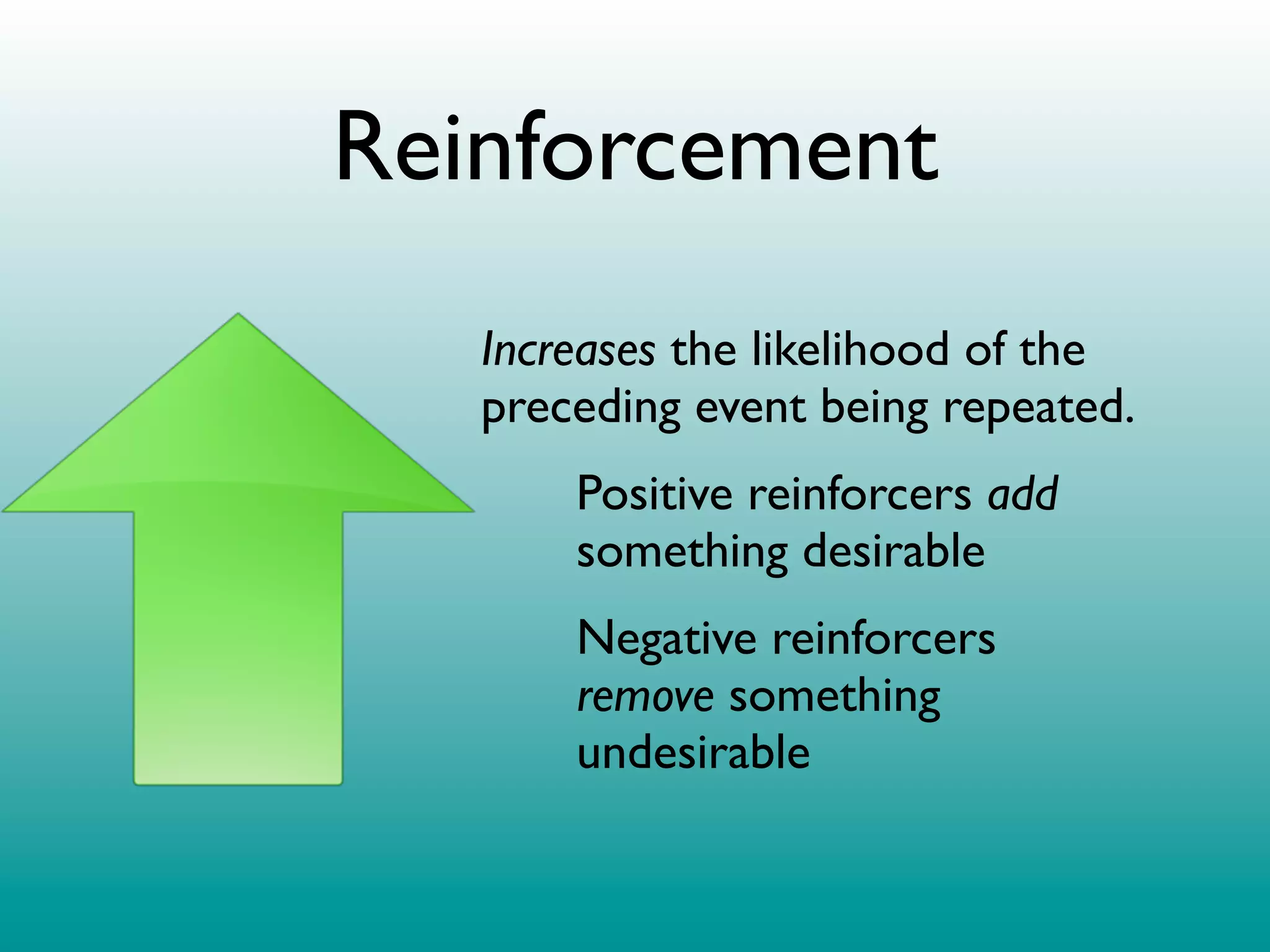
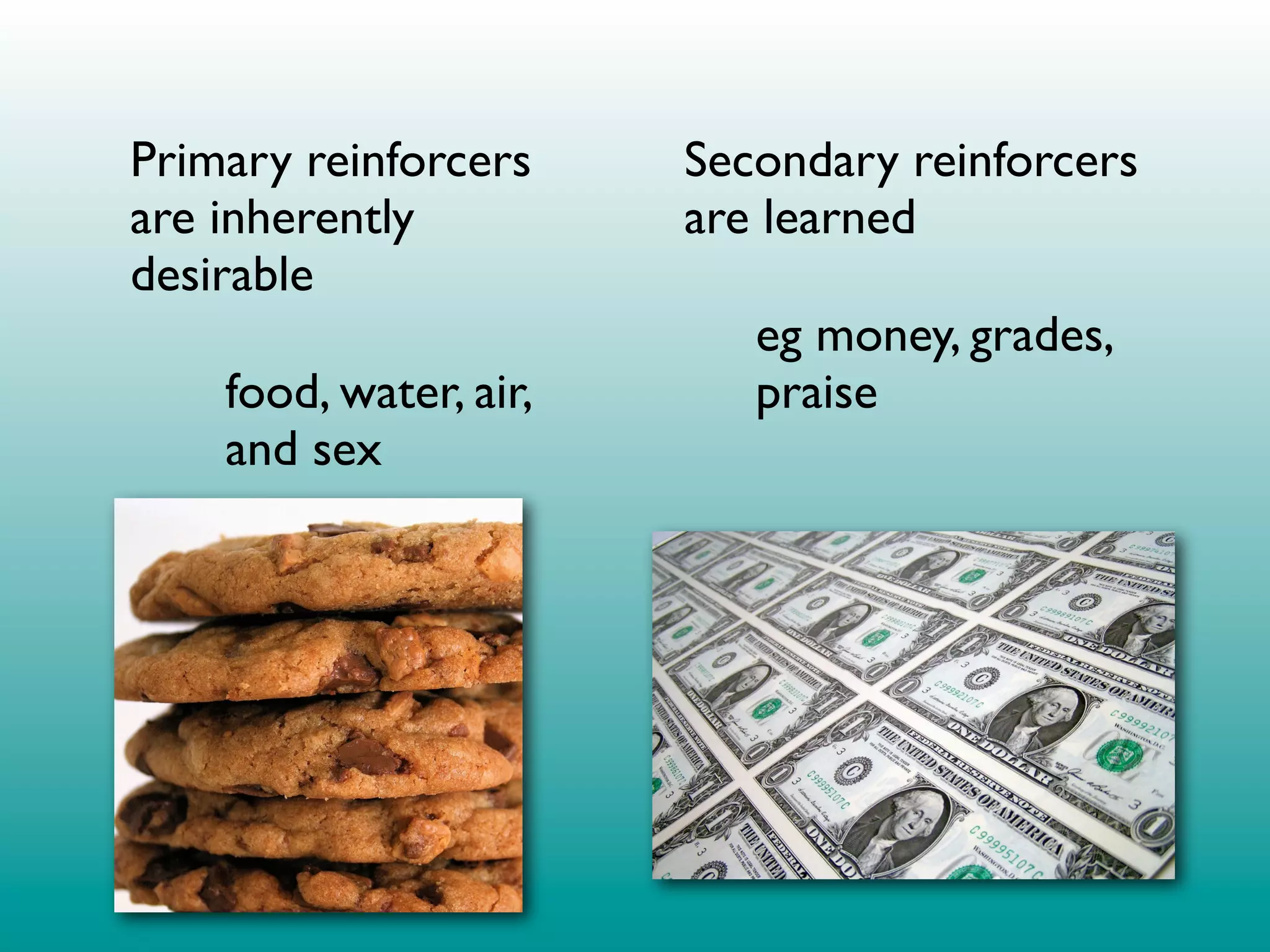
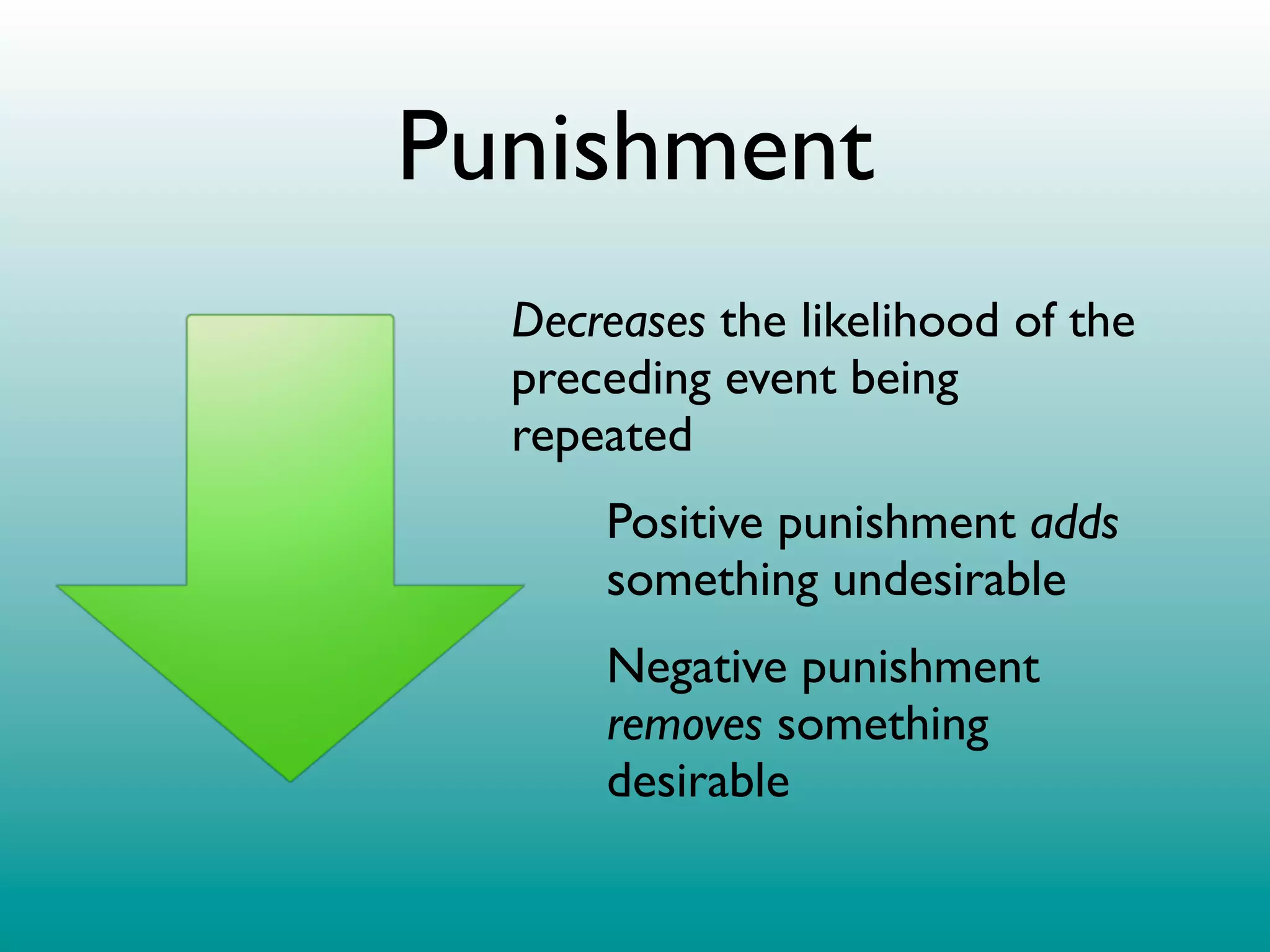
2. Operant conditioning: A rat pressing a lever and receiving a food pellet (reinforcement), learning that the behavior of lever pressing results in receiving food.
3. Observational learning: A child watching another child receive praise for helping clean up toys, then the observing child also helping to clean up toys in order to receive similar praise.