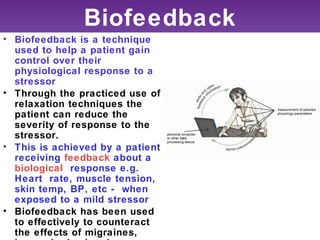
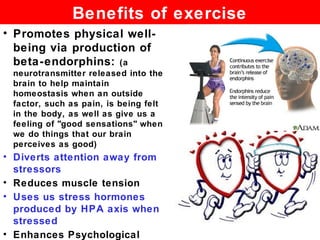
The document outlines various strategies for coping with stress, including biofeedback, relaxation techniques, exercise, and social support. Biofeedback helps individuals gain control over physiological responses to stressors, while meditation and relaxation reduce arousal levels. Additionally, both aerobic and anaerobic exercises, along with social support from stable relationships, play crucial roles in mitigating anxiety and improving overall well-being.