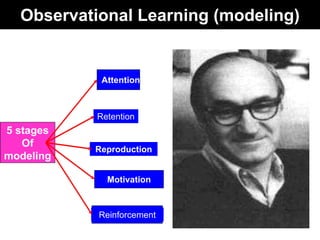
Observational learning, first discussed by Bandura, occurs by watching others and noting the consequences of their actions before imitating them. This process involves five stages: attention, retention, reproduction, motivation, and reinforcement, where one learns indirectly and modifies their behavior based on observations. Key factors influencing attention include the model's status, similarity to the observer, and distinctiveness of behavior.