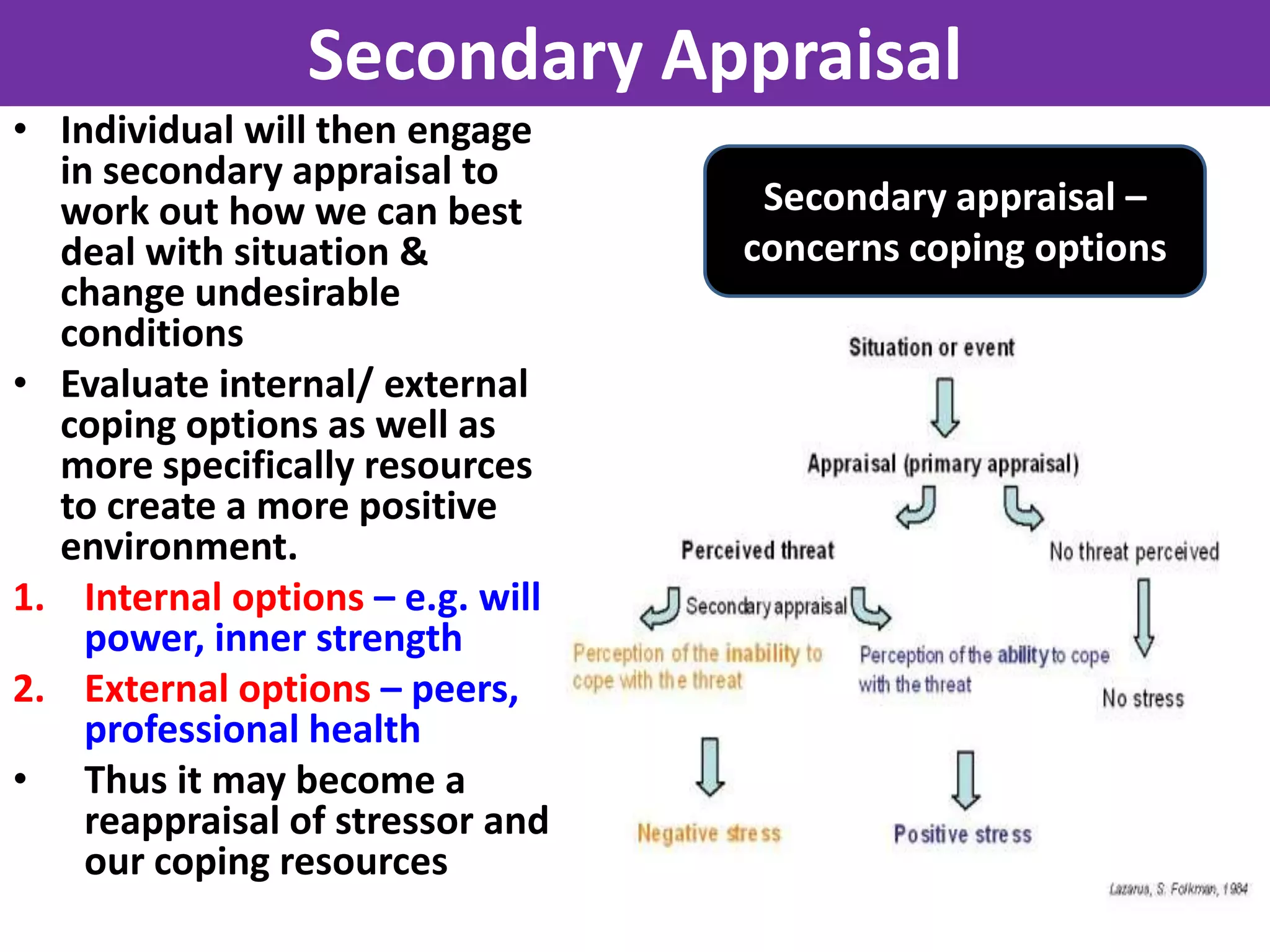
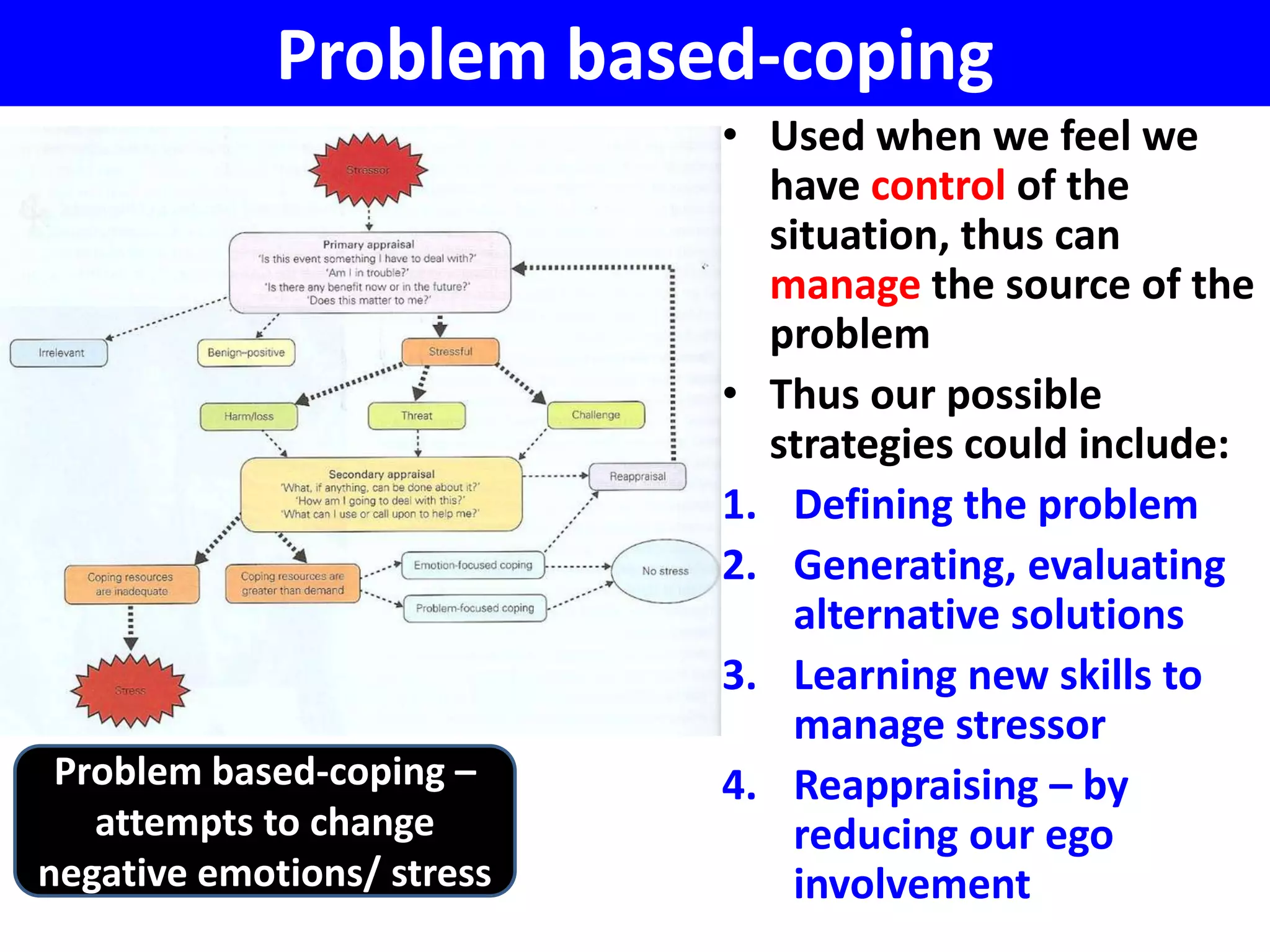
Lazarus and Folkman's transactional model of stress and coping emphasizes the interaction between an individual and their environment, where stress arises from an imbalance between demands and coping resources. The model includes primary appraisal, which assesses the significance of stressors, and secondary appraisal, which evaluates coping options, offering problem-based coping strategies for manageable situations and emotional-based coping strategies for those beyond control. While the model is dynamic and considers individual differences, it has weaknesses such as lack of empirical evidence and difficulty in distinguishing appraisal stages.