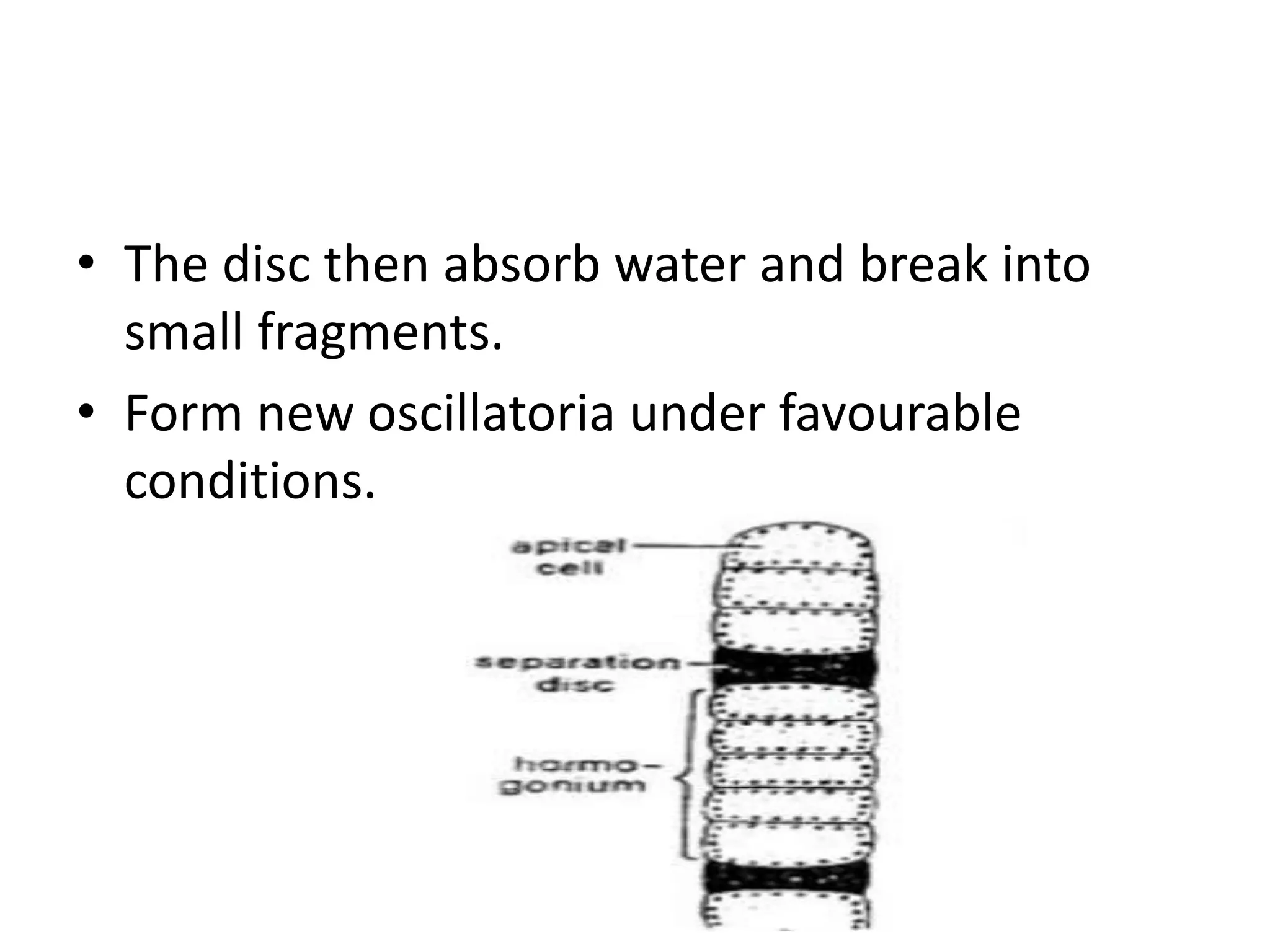
This document provides information about the cyanobacteria Oscillatoria. It discusses its systematic position as a genus in the order Oscillatoriales, describes its occurrence in moist places with decaying organic matter, and details its plant body structure as unbranched trichomes of cylindrical cells contained in a thin sheath. Reproduction is solely vegetative, occurring through the formation of harmogonia fragments or accidental trichome breakage. Oscillatoria has economic importance for soil reclamation, pollution indication, oxygen production, symbiotic associations, protein content, and nitrogen fixation.