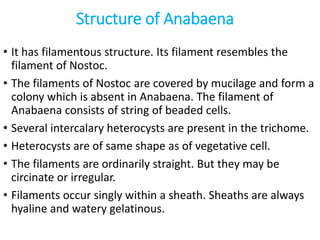
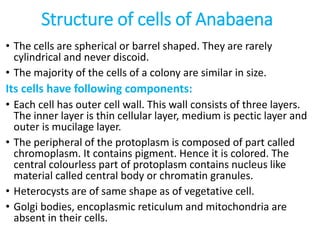
Anabaena is a genus of filamentous cyanobacteria that exists as plankton. They perform oxygenic photosynthesis and are able to fix nitrogen. Anabaena has filamentous structures consisting of strings of beaded cells, including heterocysts that convert nitrogen to ammonia. Certain species of Anabaena form symbiotic relationships with plants and some produce toxins. Anabaena is believed to have produced much of Earth's oxygen and studies of its hydrogen production could provide renewable energy.