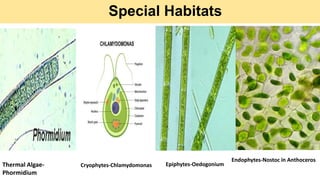
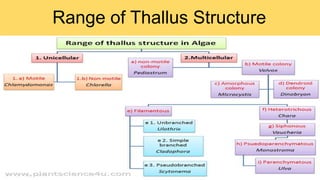
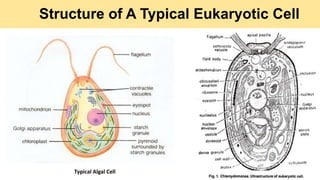
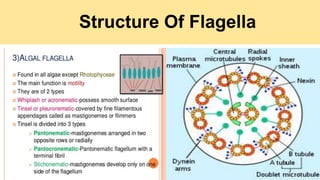
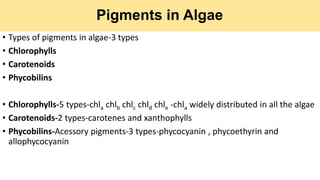
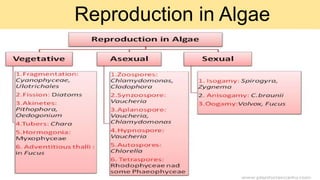
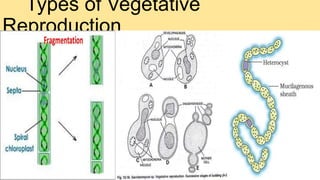
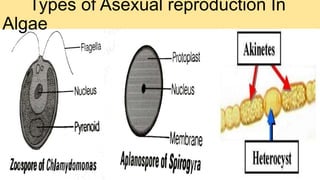
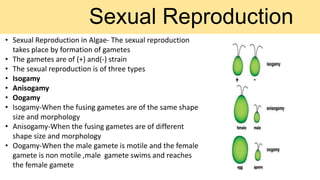
Algae are a diverse group of primitive, mostly aquatic photosynthetic organisms that are found in a wide range of habitats around the world. They can be unicellular or multicellular and exhibit significant variation in their morphology, pigmentation, and life cycles. Algae are divided into aquatic, terrestrial, and special habitat types depending on where they grow. Aquatic algae include phytoplankton that float in water and benthic algae that attach to surfaces at the bottom of water bodies. Terrestrial algae grow in moist soil or on the surface of soil and rocks. Special habitat algae are found in extreme environments like hot springs, polar regions, inside or on the surfaces of other organisms. Al