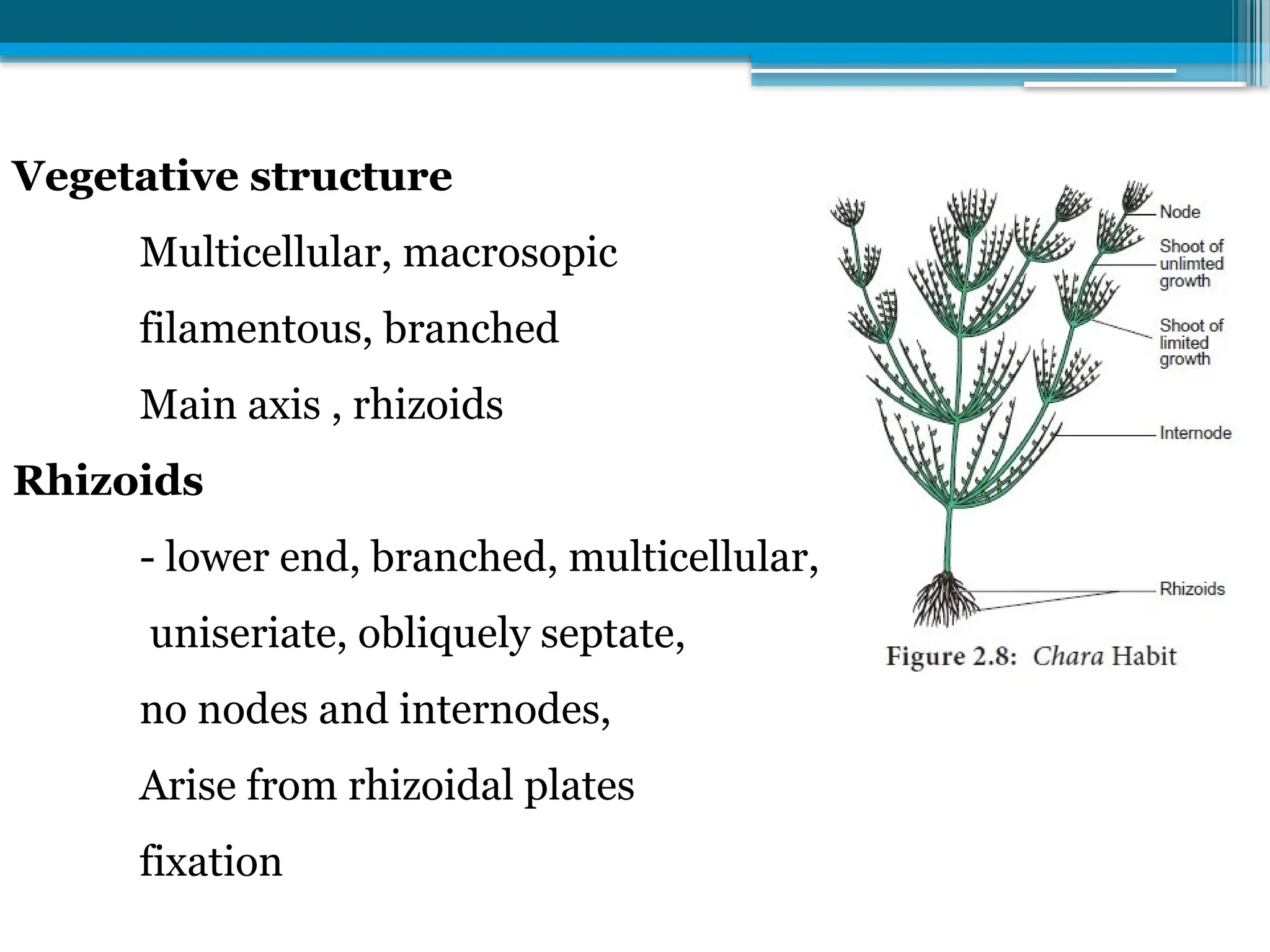
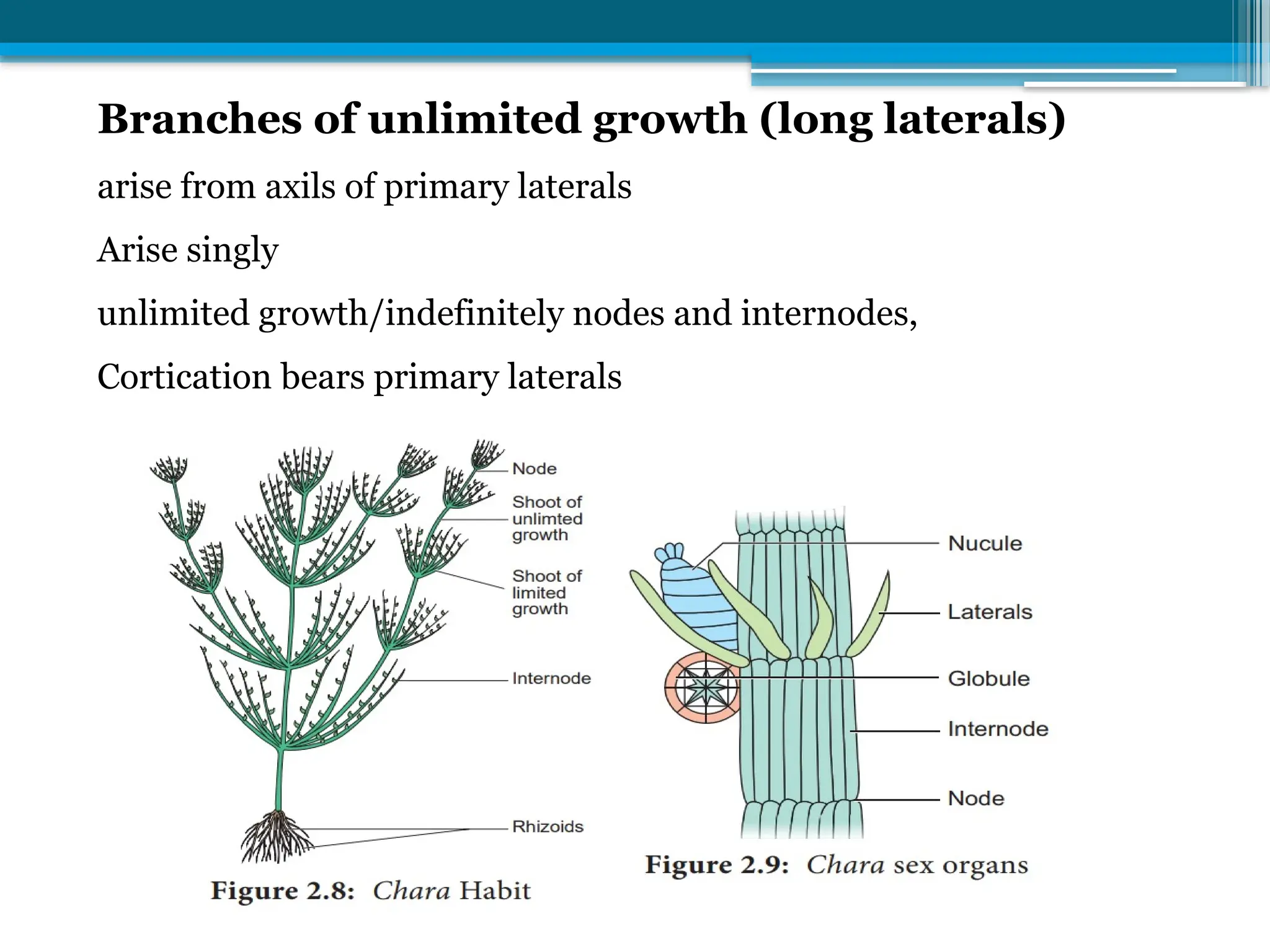
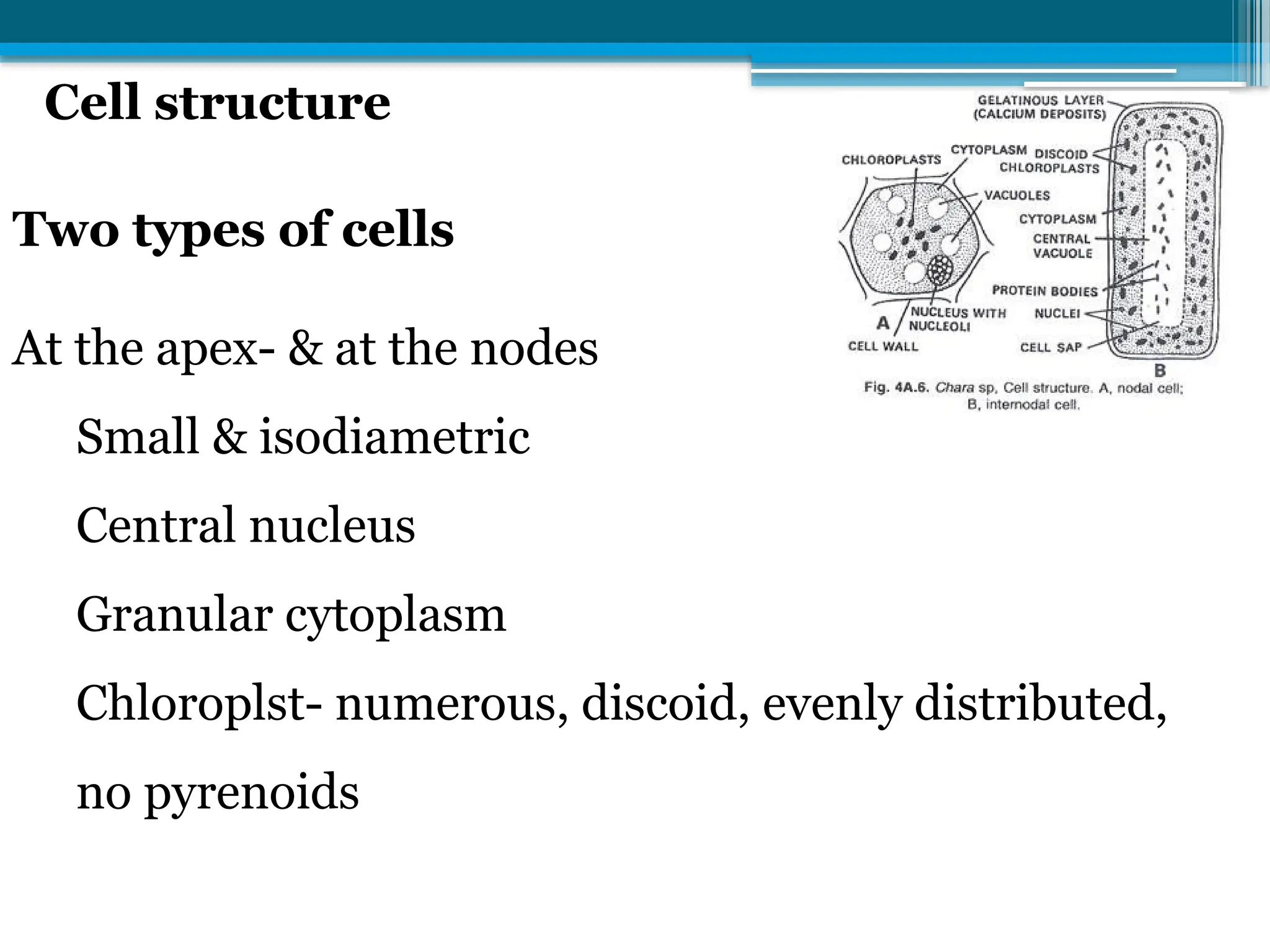
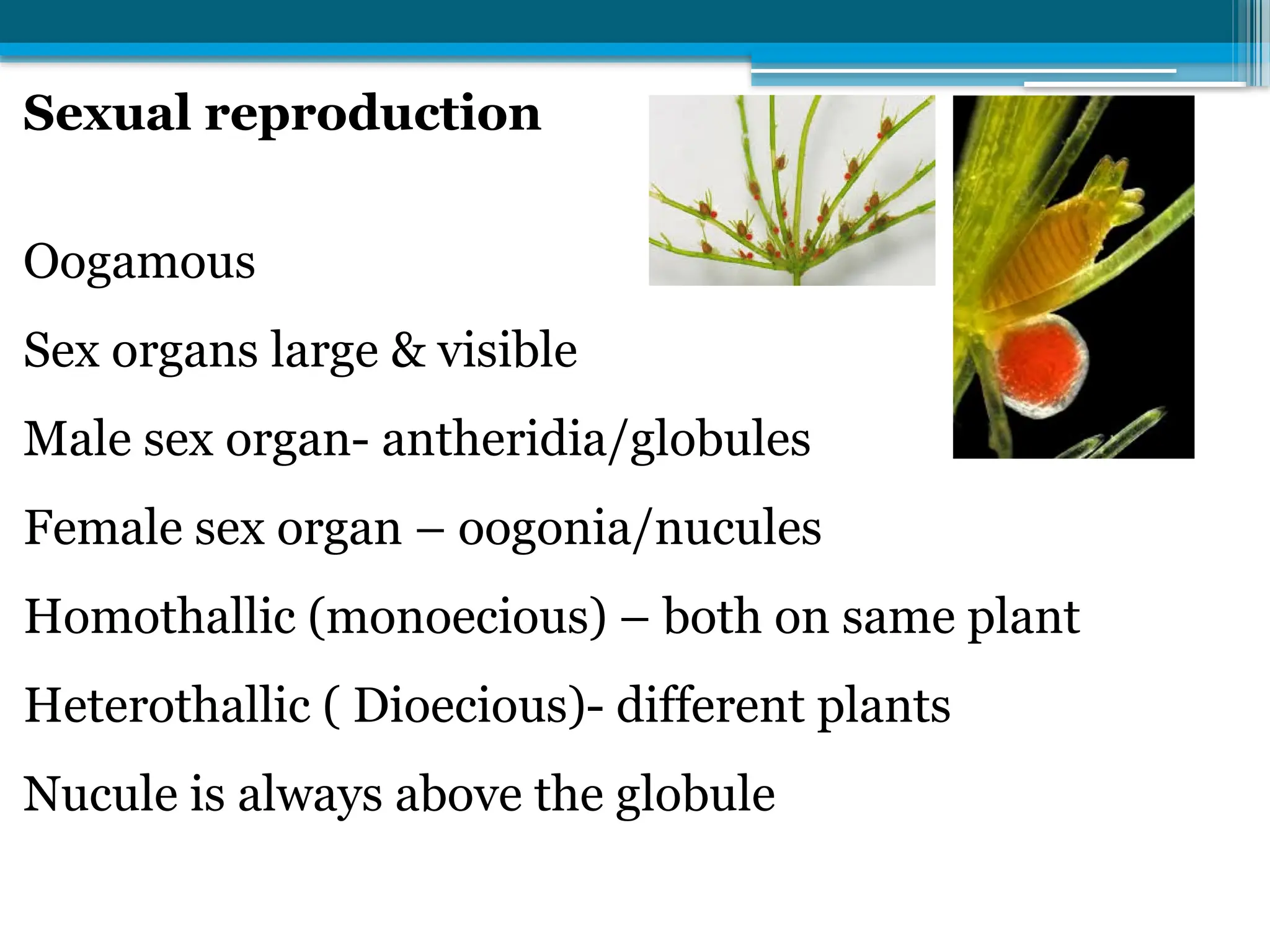
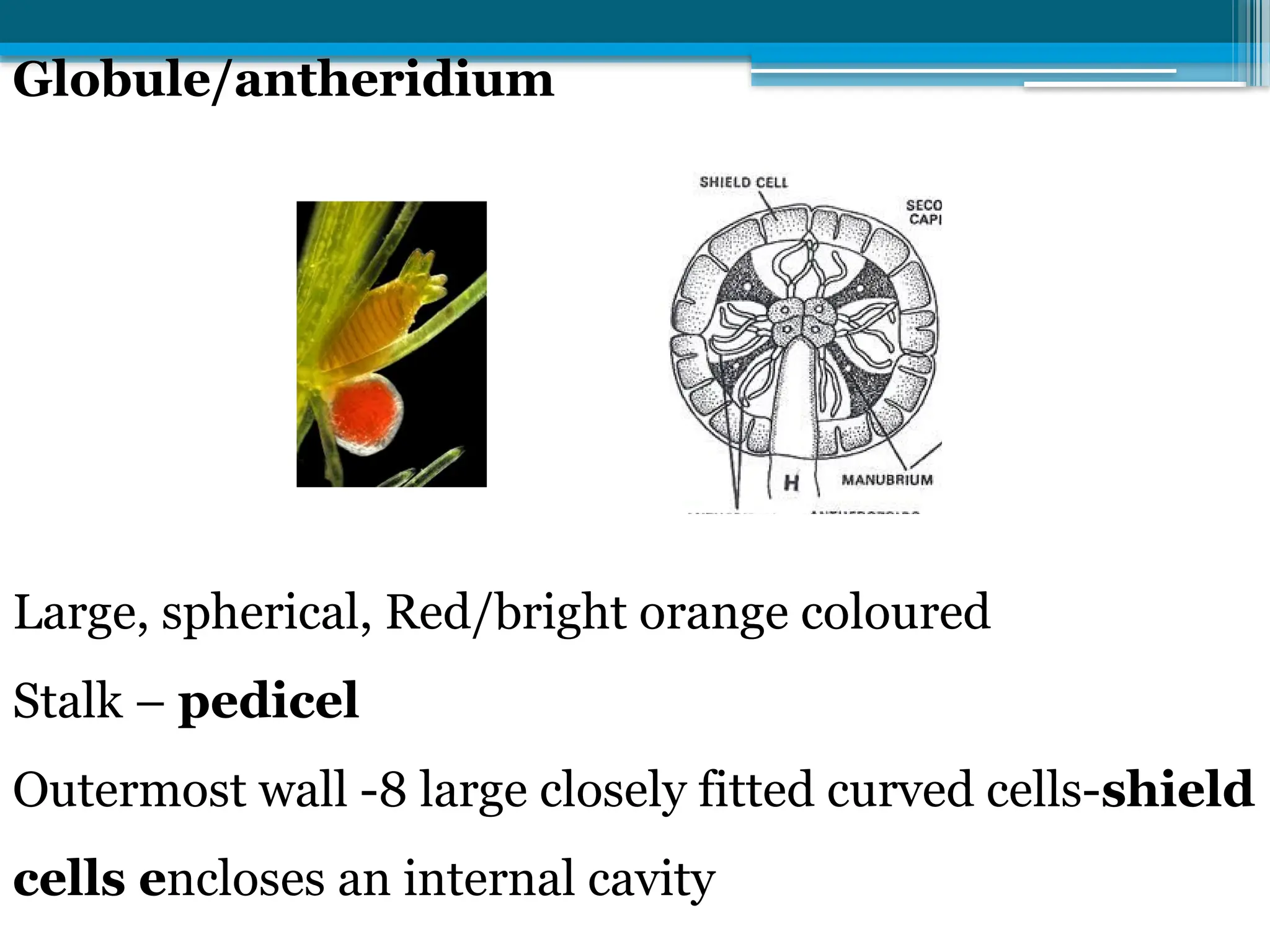
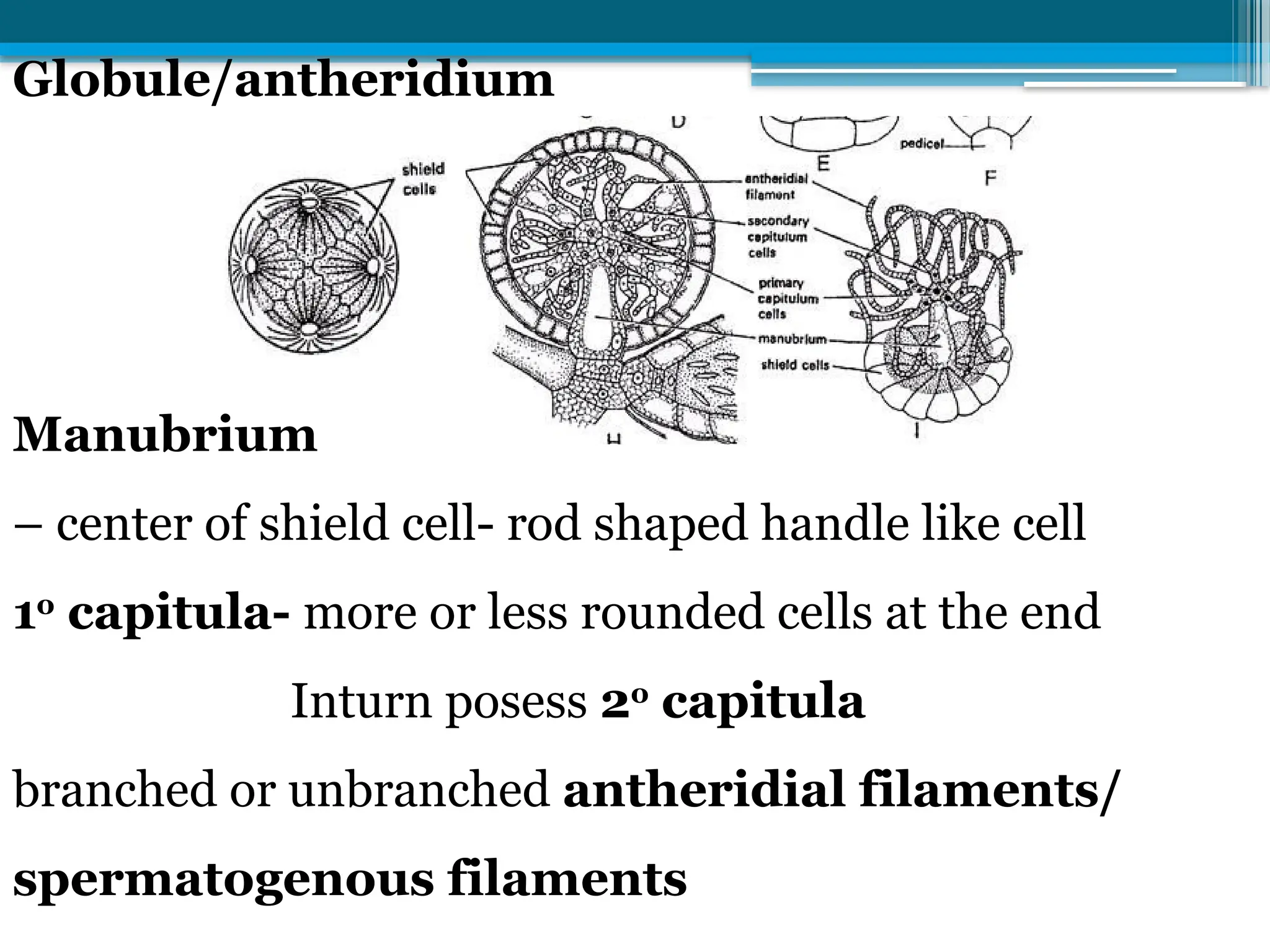
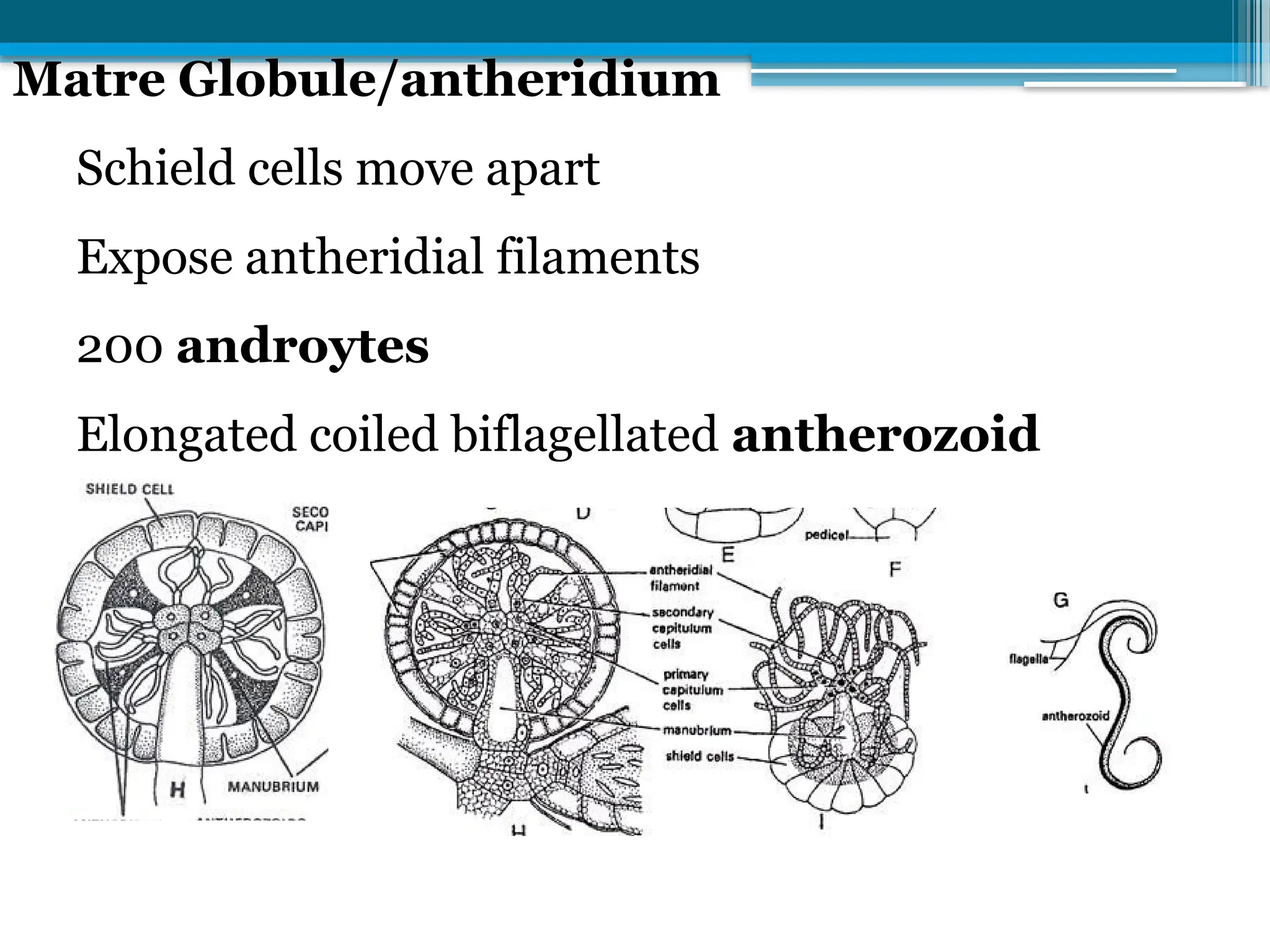
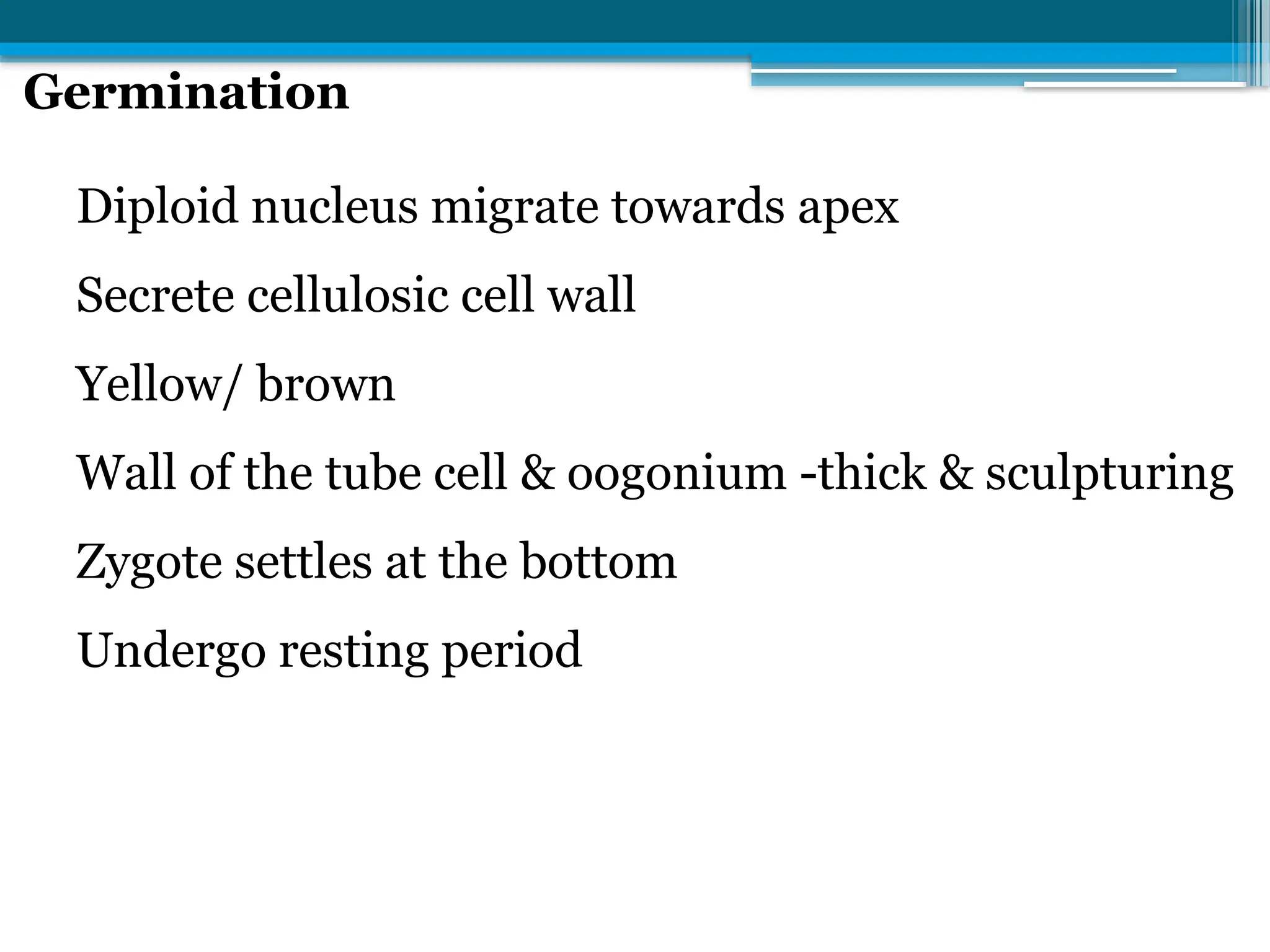
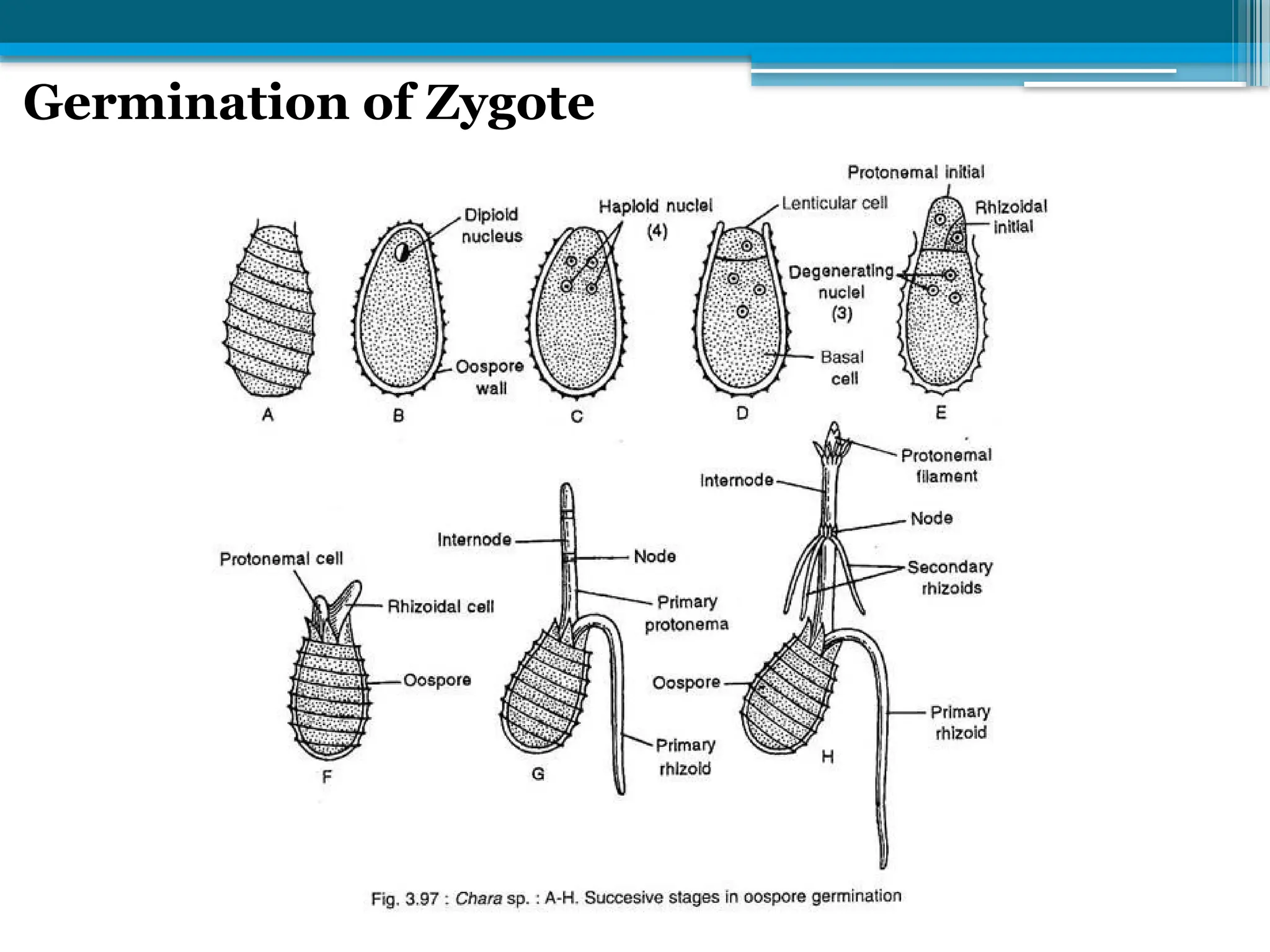
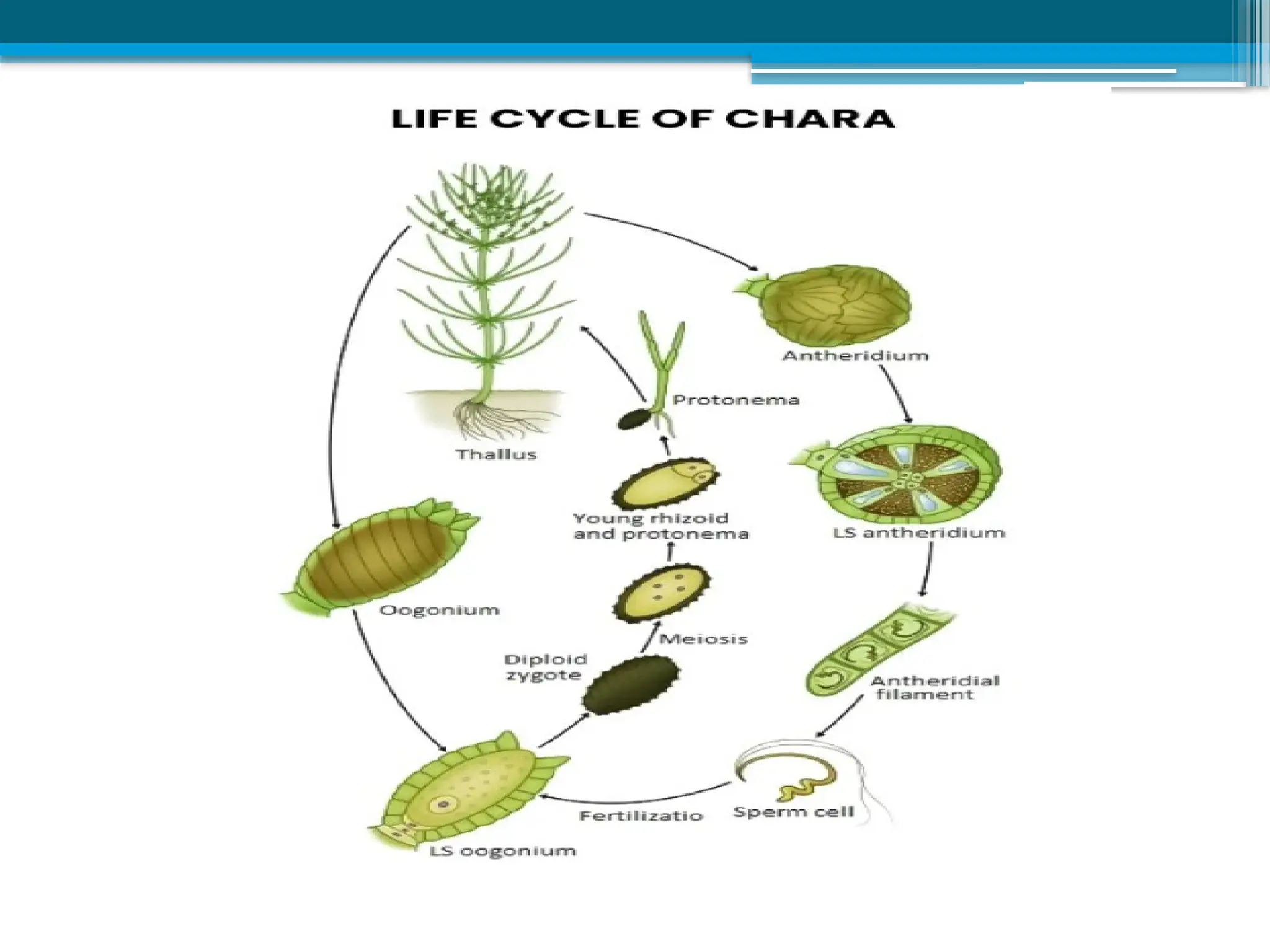
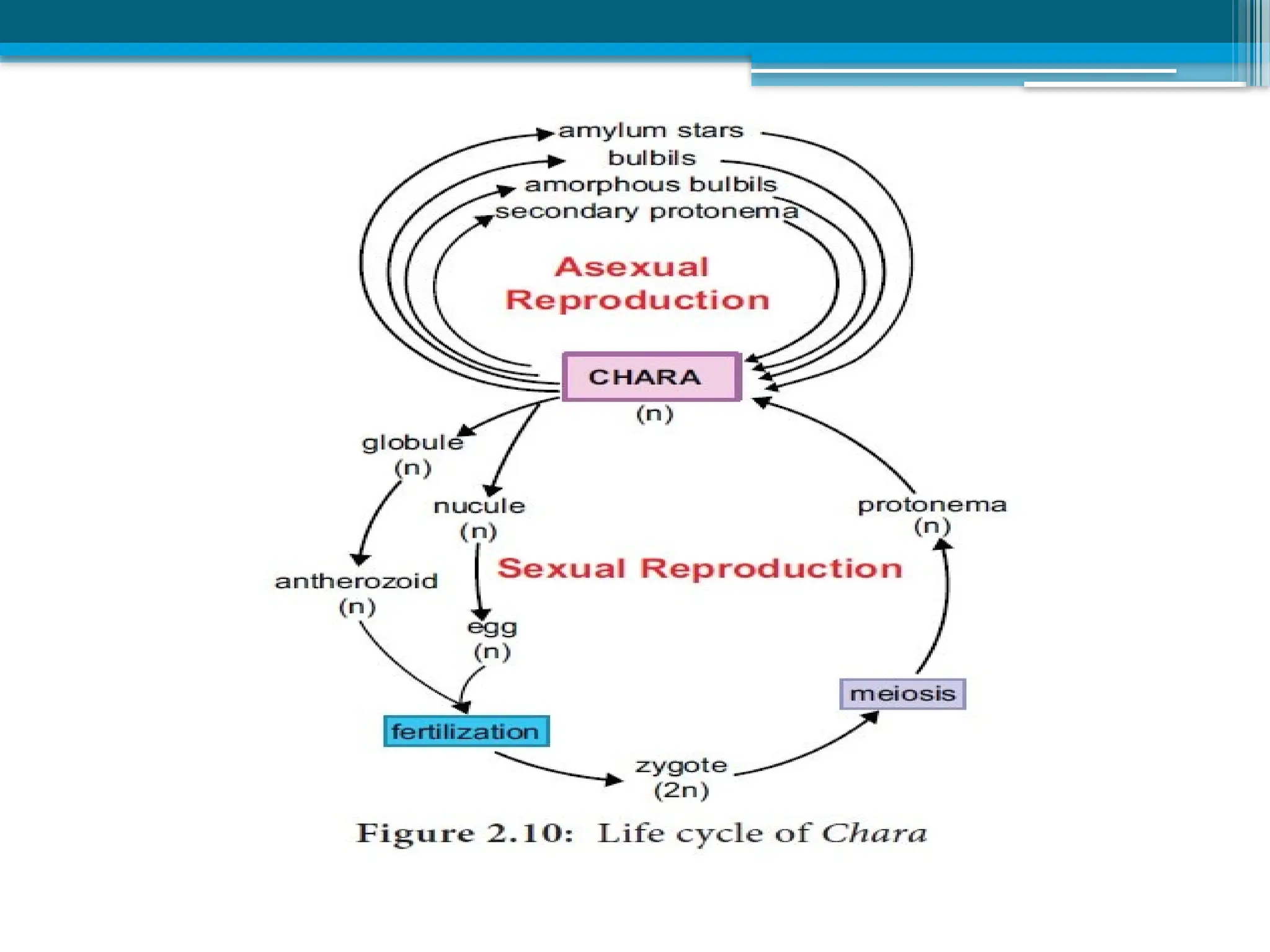
The document describes the structure, reproduction, and classification of the freshwater plant genus Chara within the division Chlorophyta. It details its multicellular filamentous structure, methods of vegetative and sexual reproduction, including descriptions of sex organs like antheridia and oogonia. Key cellular characteristics, including chloroplast distribution and cell wall composition, are also highlighted.