The document discusses sex-linked inheritance in humans and other species. Some key points:
- Sex-linked traits are determined by genes on the sex chromosomes (X in humans). Females have two X chromosomes while males have one X and one Y chromosome.
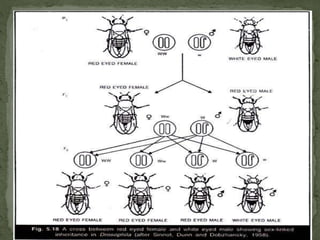
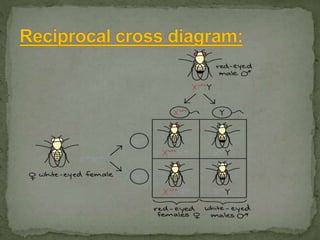
- Early work by Thomas Hunt Morgan in fruit flies established the first sex-linked trait (white eyes in males) and showed inheritance from father to daughter to grandson.
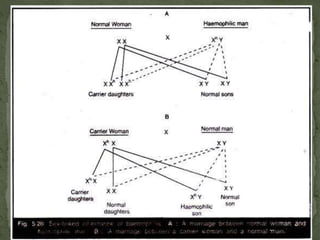
- Common human examples are color blindness and hemophilia, which are X-linked recessive traits mostly seen in males. Hemophilia is passed from carrier mothers to some sons.
- Genes on the Y chromosome in humans and the non-homologous region of the