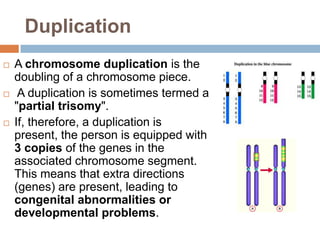
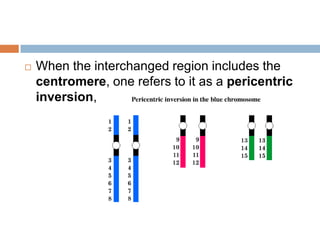
Chromosomal and gene aberrations such as duplications, deletions, inversions, and translocations can be caused by errors during meiosis. Structural aberrations result from chromosomal breaks and can include deletions where a chromosome segment is missing, duplications where an extra copy is present, inversions where a segment is reversed, and translocations where segments are exchanged between non-homologous chromosomes. While some structural aberrations like balanced translocations may not cause phenotypic effects, others can result in disorders depending on the genes involved. Modern techniques like FISH allow for detection of smaller aberrations compared to traditional staining and microscopy.