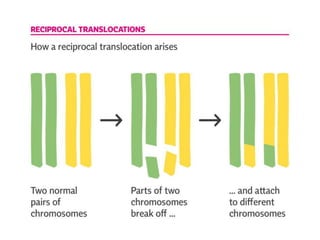
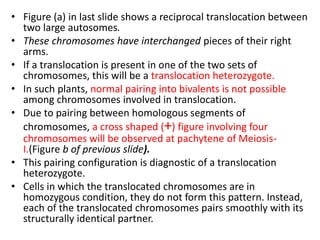
1) A reciprocal translocation occurs when pieces of two non-homologous chromosomes are exchanged without loss of genetic material.
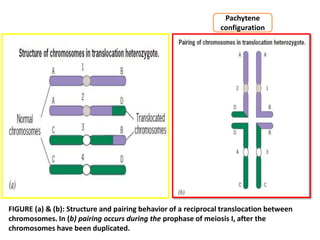
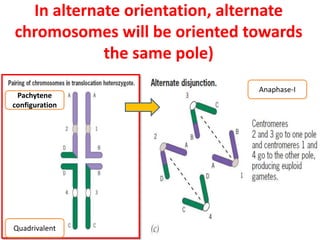
2) In a translocation heterozygote, the chromosomes involved in the translocation cannot pair normally during meiosis I. Instead, they form a cross-shaped structure called a quadrivalent.
3) The orientation of the quadrivalent at metaphase I determines whether the gametes will receive normal or unbalanced chromosome complements, with adjacent orientations producing non-functional aneuploid gametes and explaining reduced fertility in translocation heterozygotes.