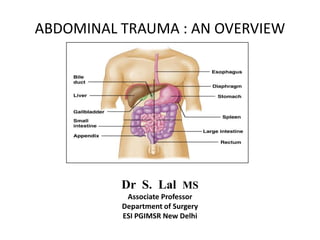
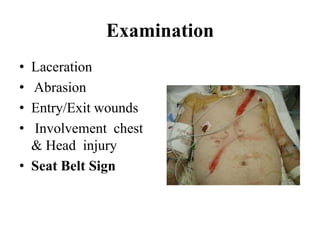
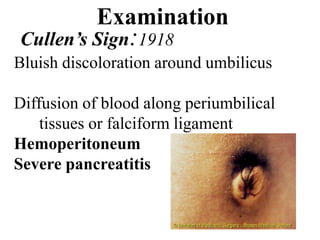
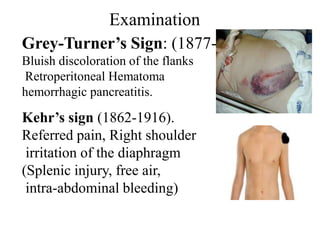
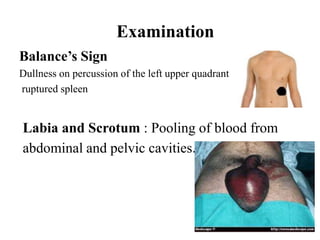
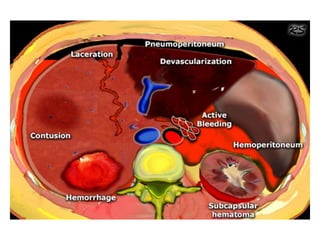
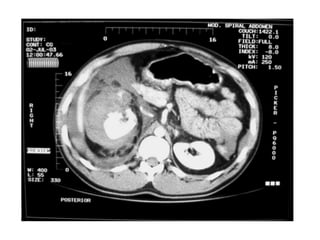
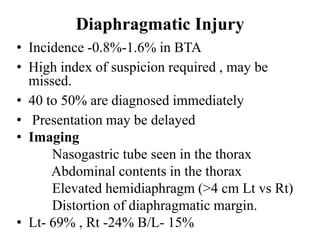
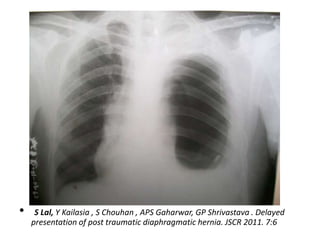
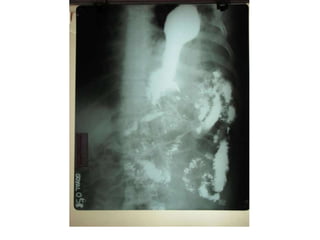
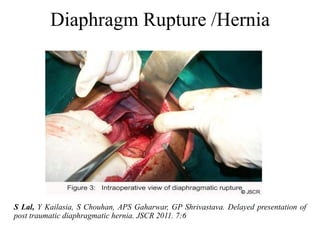
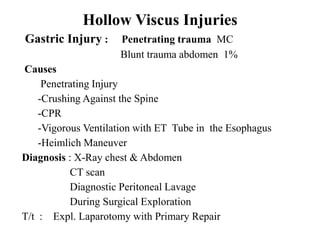
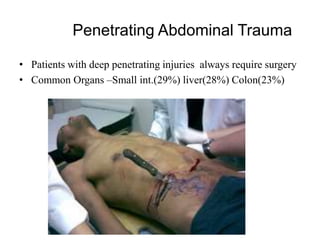
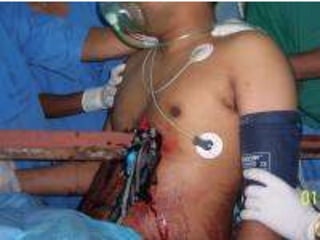
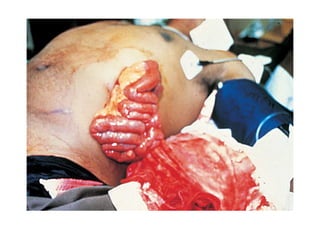
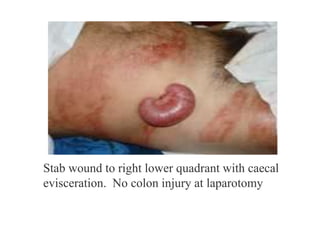
1. Abdominal trauma is commonly encountered in emergency departments and can be life-threatening. Blunt and penetrating injuries can cause damage to solid organs like the spleen, liver, and pancreas.
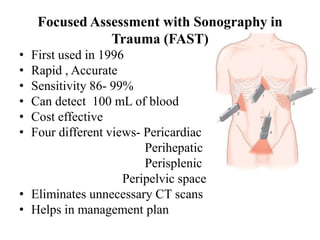
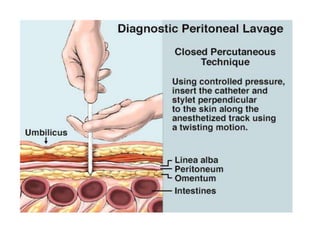
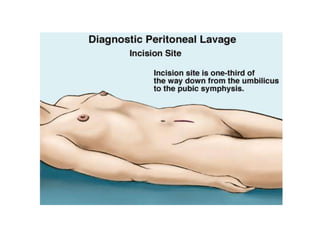
2. A thorough primary and secondary survey is essential to identify injuries. Diagnostic tools like FAST ultrasound, CT scans, and laparoscopy help evaluate injuries. Conservative management is appropriate for many mild organ injuries.
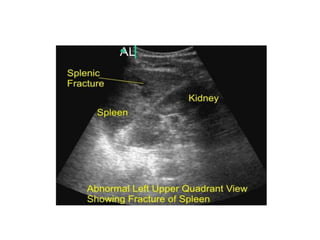
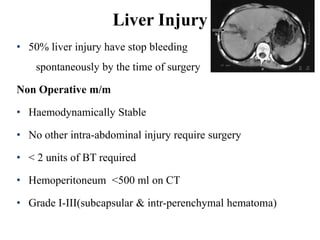
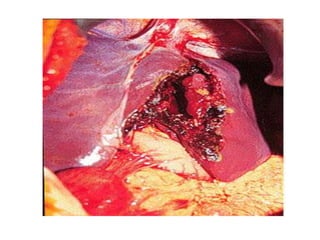
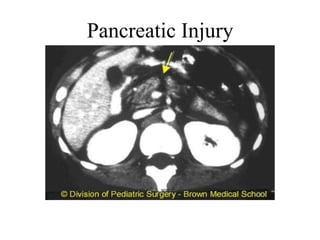
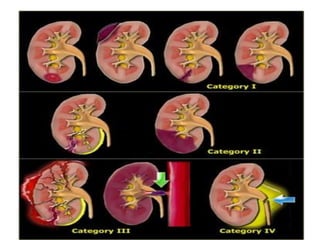
3. Splenic injuries require close monitoring or surgery depending on grade. Liver injuries often stop bleeding spontaneously but may require packing or resection. Pancreatic injuries are difficult to diagnose and usually repaired surgically. Proper identification and treatment of abdominal injuries is critical for patient outcomes.