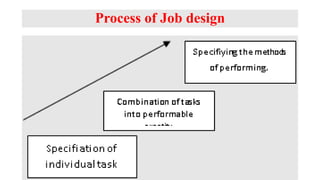
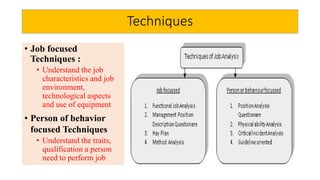
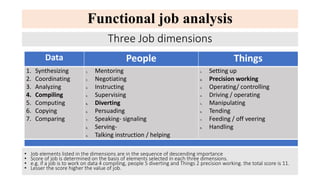
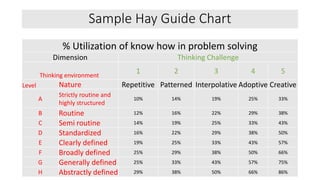
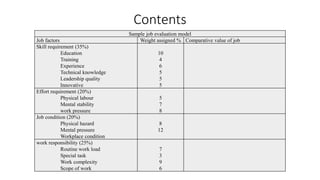
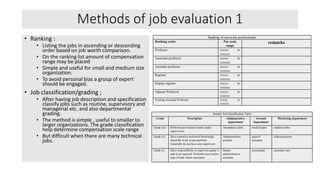
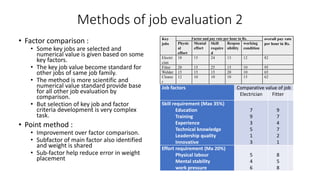
The document outlines the concepts of job, task, position, occupation, and the various methods involved in job design, analysis, and evaluation within an organization. It describes job elements, tasks, and duties, highlighting their interrelationships and importance in structuring work efficiently to enhance productivity and employee satisfaction. Additionally, it provides guidelines for creating job descriptions and specifications, conducting job evaluations, and the benefits of systematic job analysis.