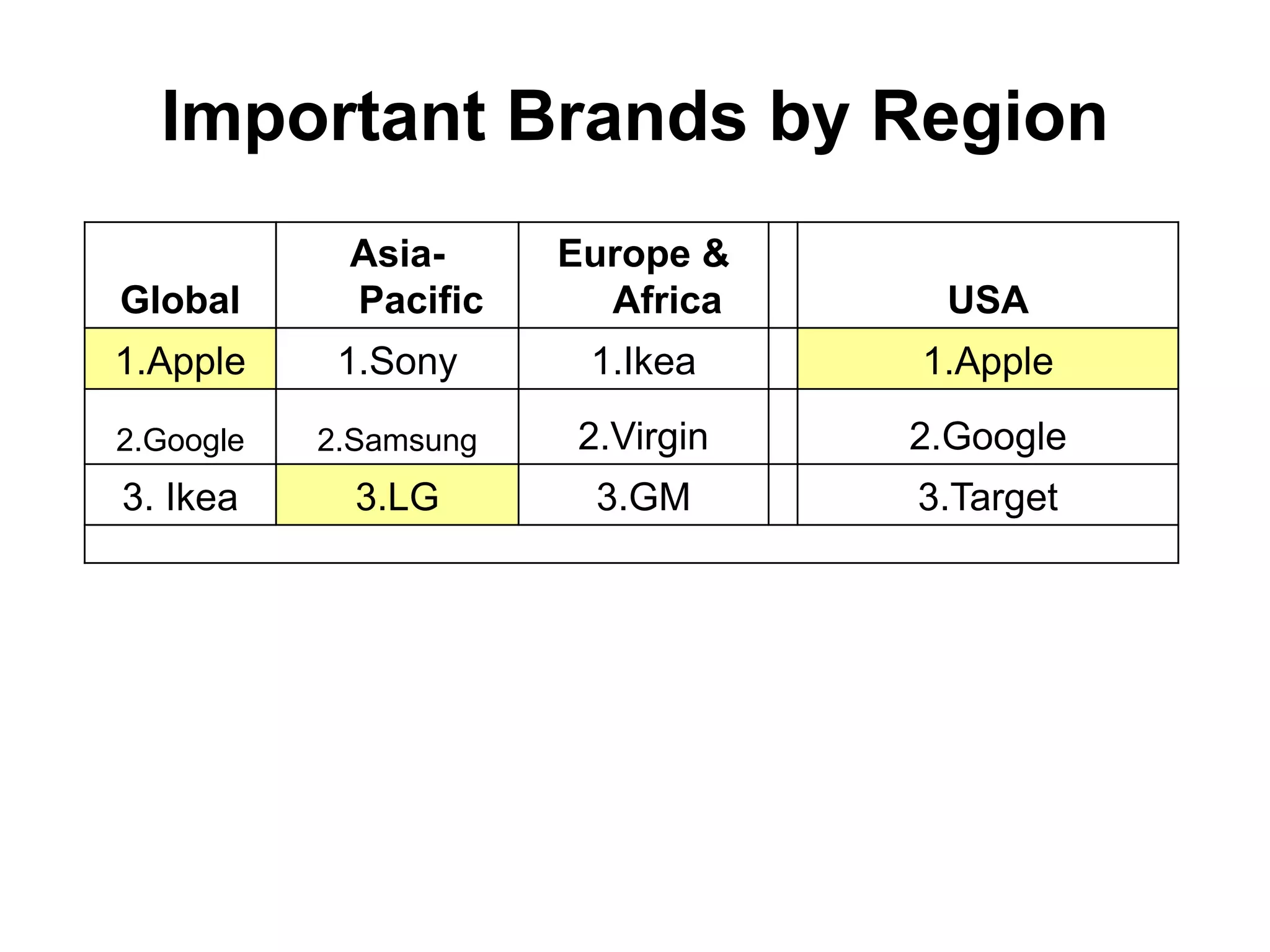
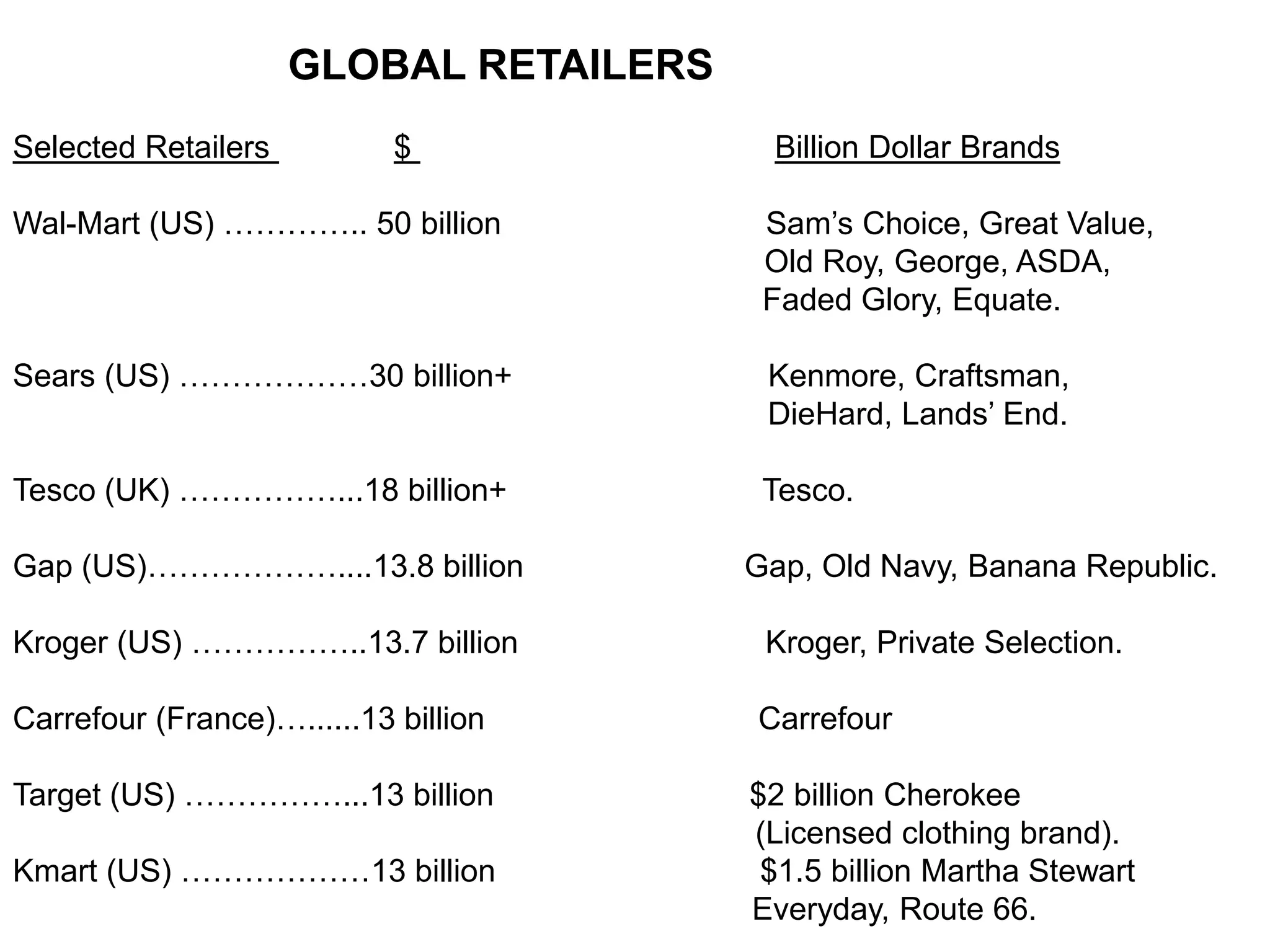
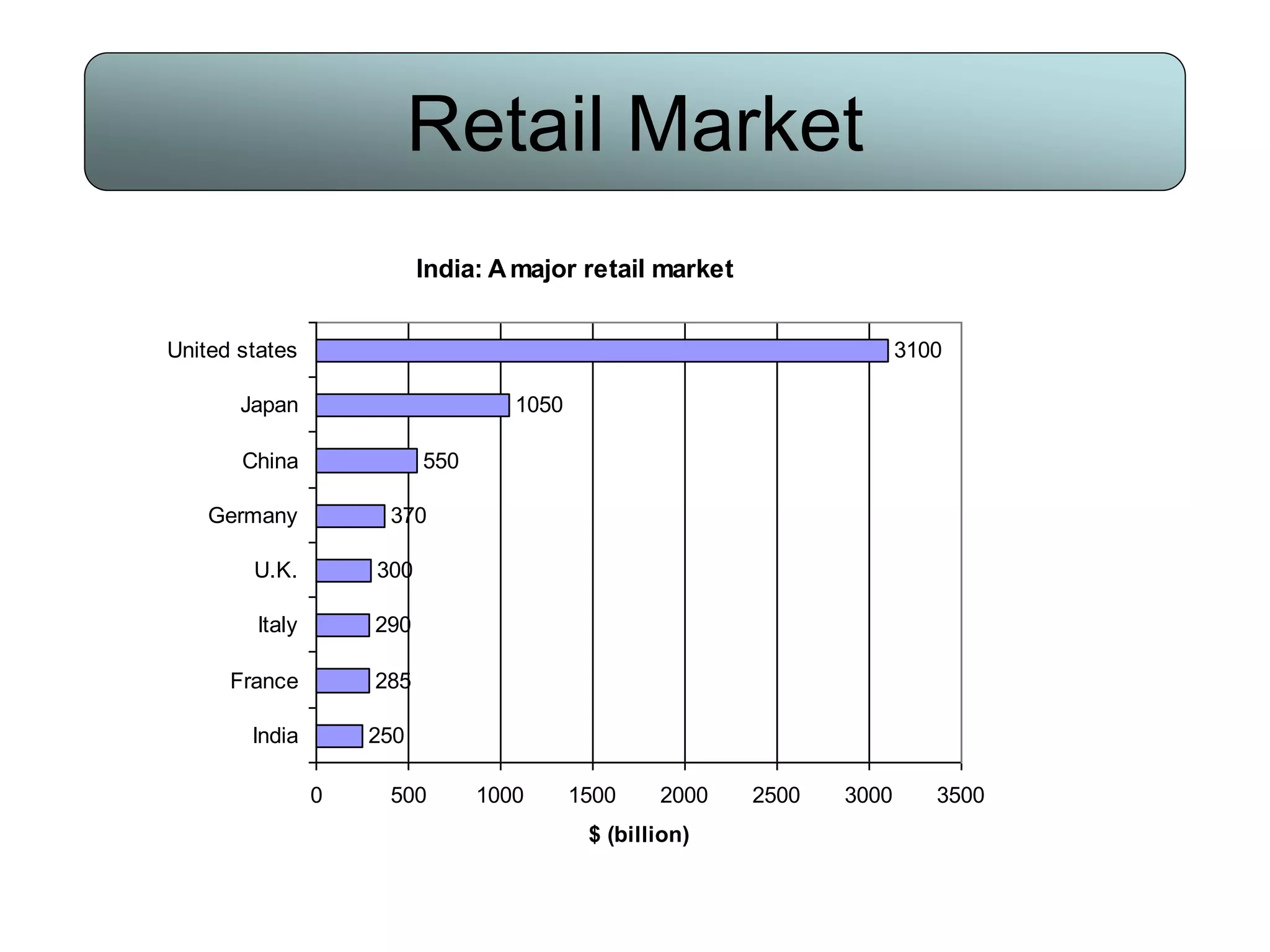
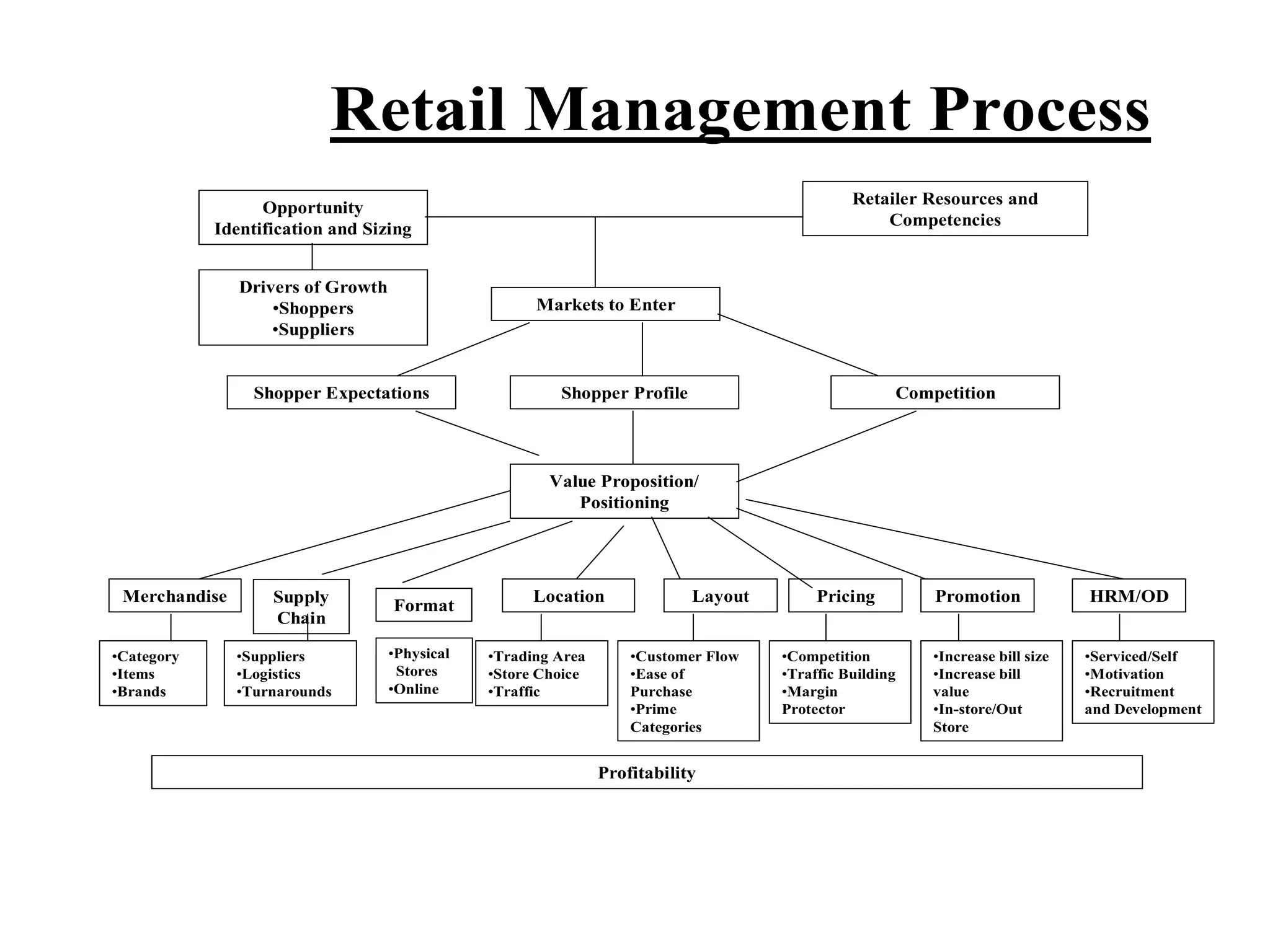
Retailing involves activities used to sell products or services to consumers for personal use. Key aspects of retailing include selecting store locations, sourcing and buying merchandise, store management, and building customer relationships. Successful retailers understand customer interests, apply technology to improve operations, and provide good service. Major retailers worldwide include Walmart, Amazon, Tesco, and Carrefour. India is also a major retail market, though smaller than markets like the US and China.