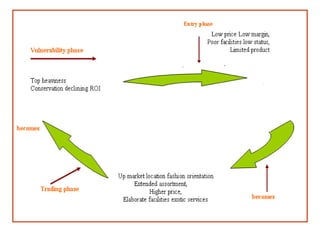
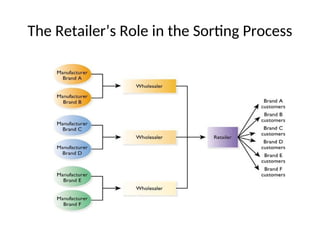
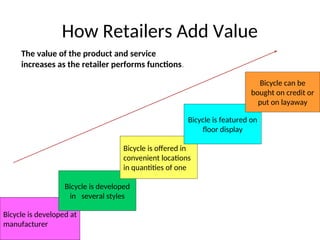
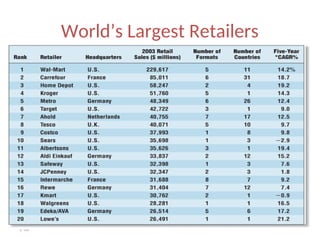
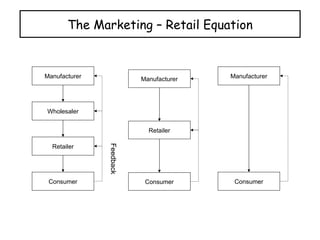
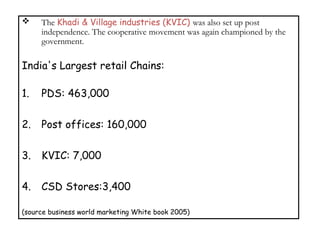
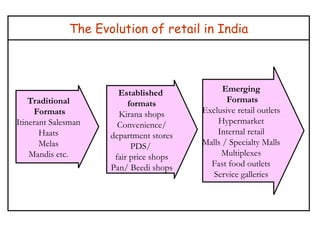
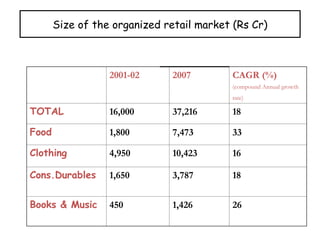
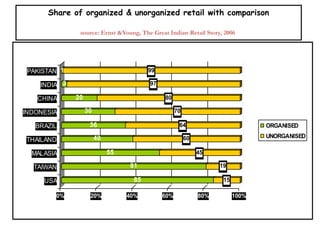
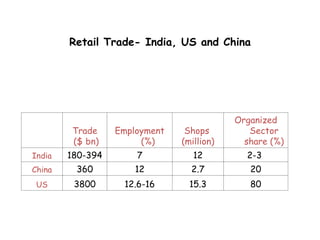
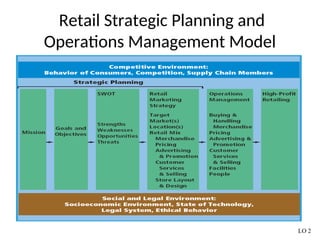
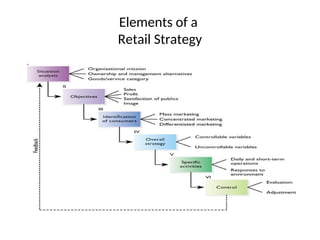
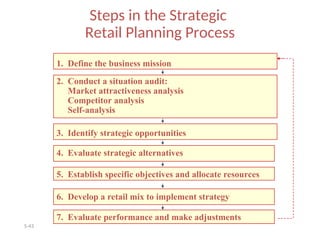
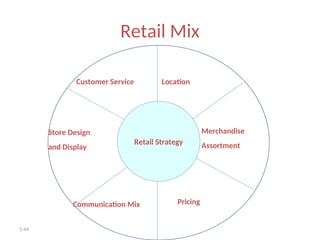
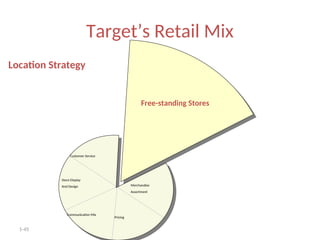
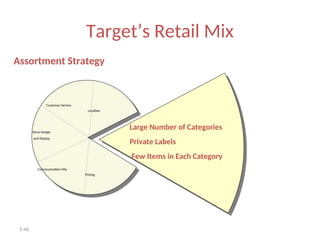
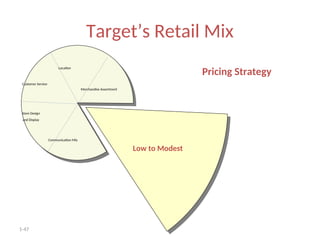
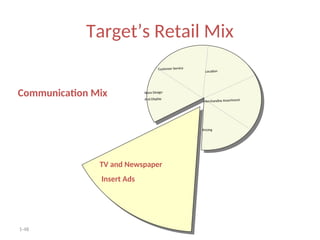
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the retail industry, focusing on the evolution and structure of retailing in India, including various types of retail formats and their functions. It discusses the significance of retail in the Indian economy, major drivers for retail growth, and the challenges faced by the sector. The document also outlines strategic retail planning, including the retail mix and customer relationship management.