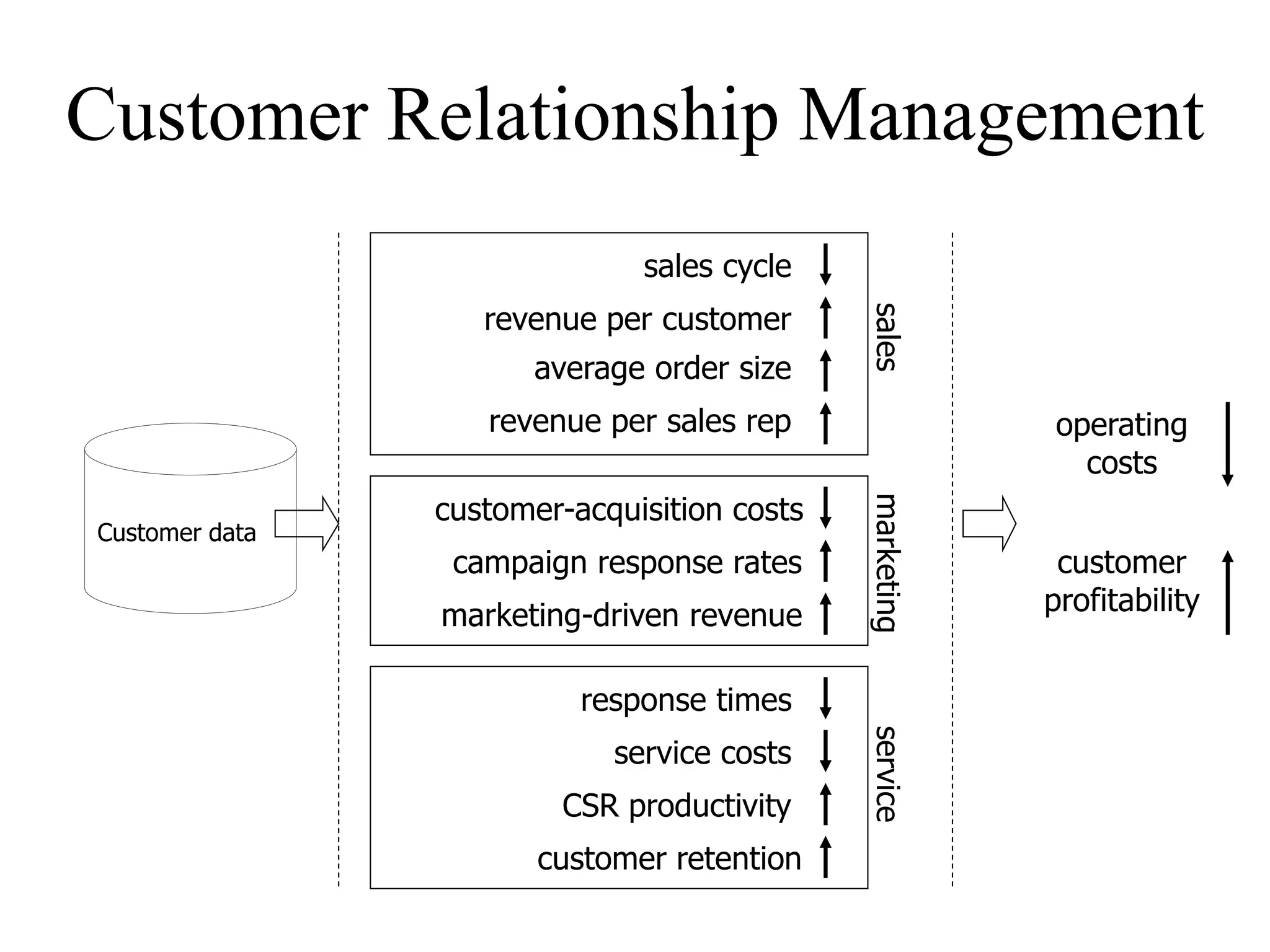
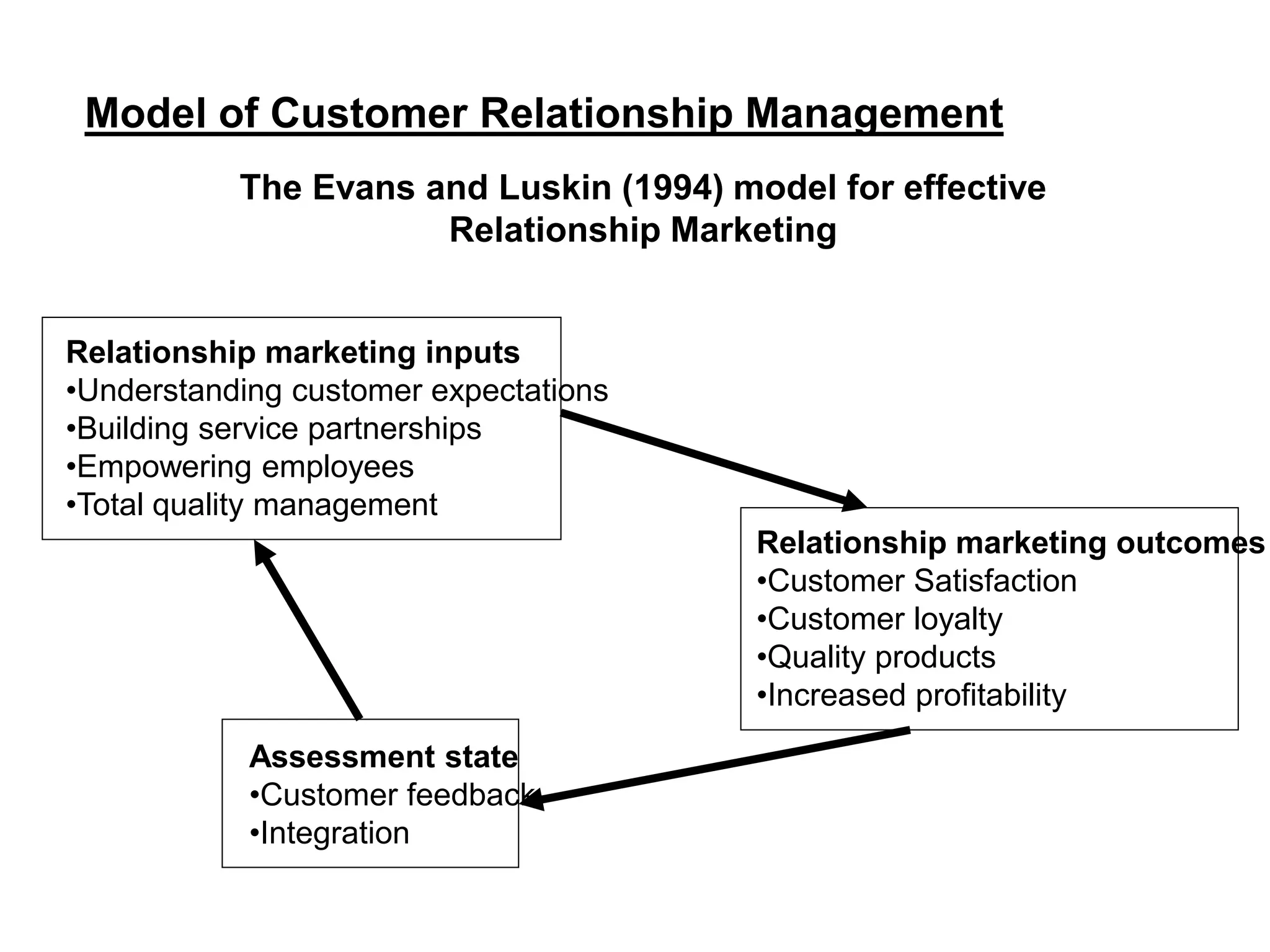
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a business strategy that aims to understand, anticipate, and manage customer needs. It involves strategic, process, organizational, and technological changes to better manage a company around customer information. CRM can help companies retain existing customers, attract new customers, improve response times, meet customer requirements, and increase customer satisfaction and revenue while reducing costs. Successful CRM relies on understanding customer expectations, building service partnerships, empowering employees, and implementing total quality management.