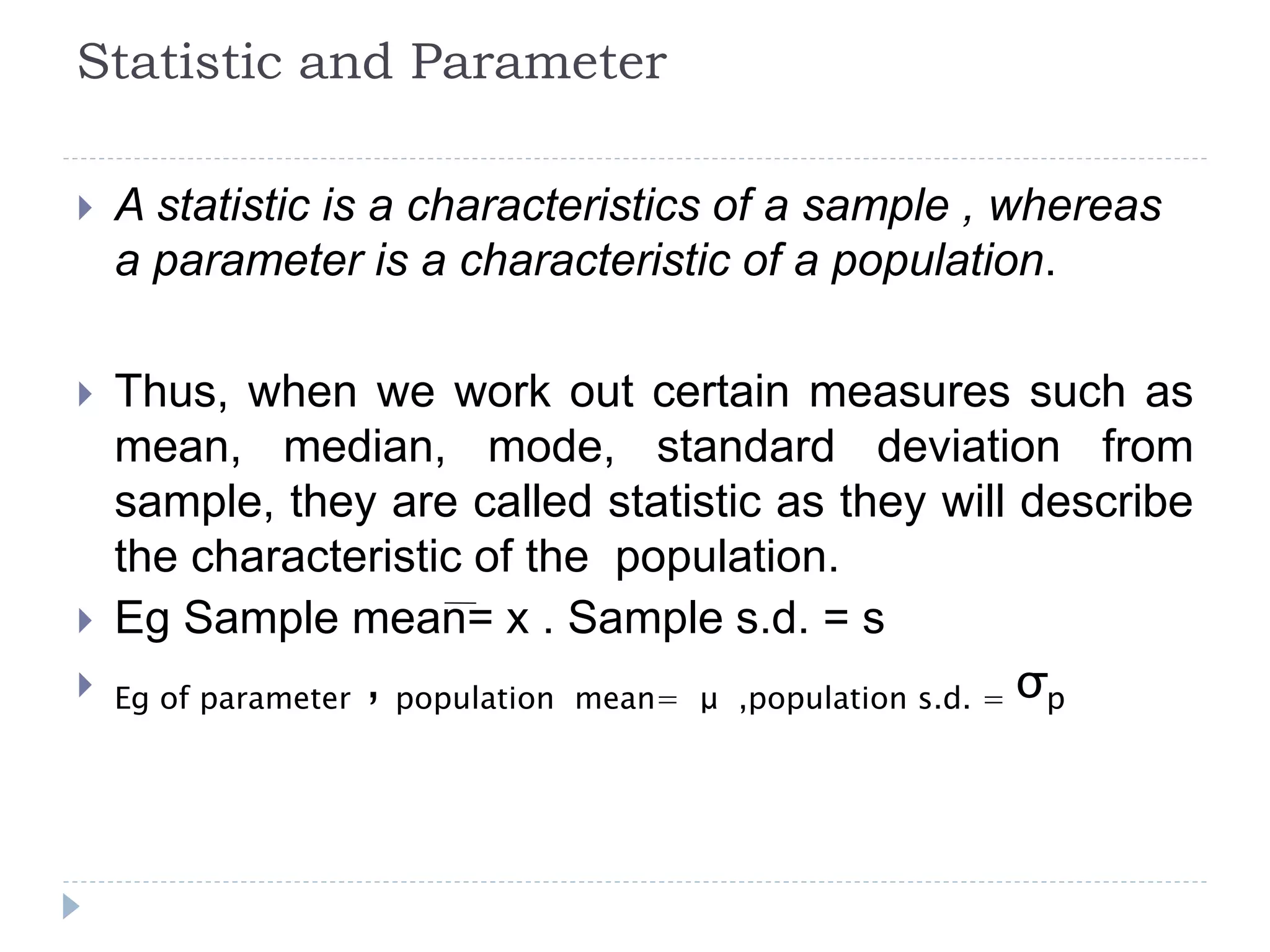
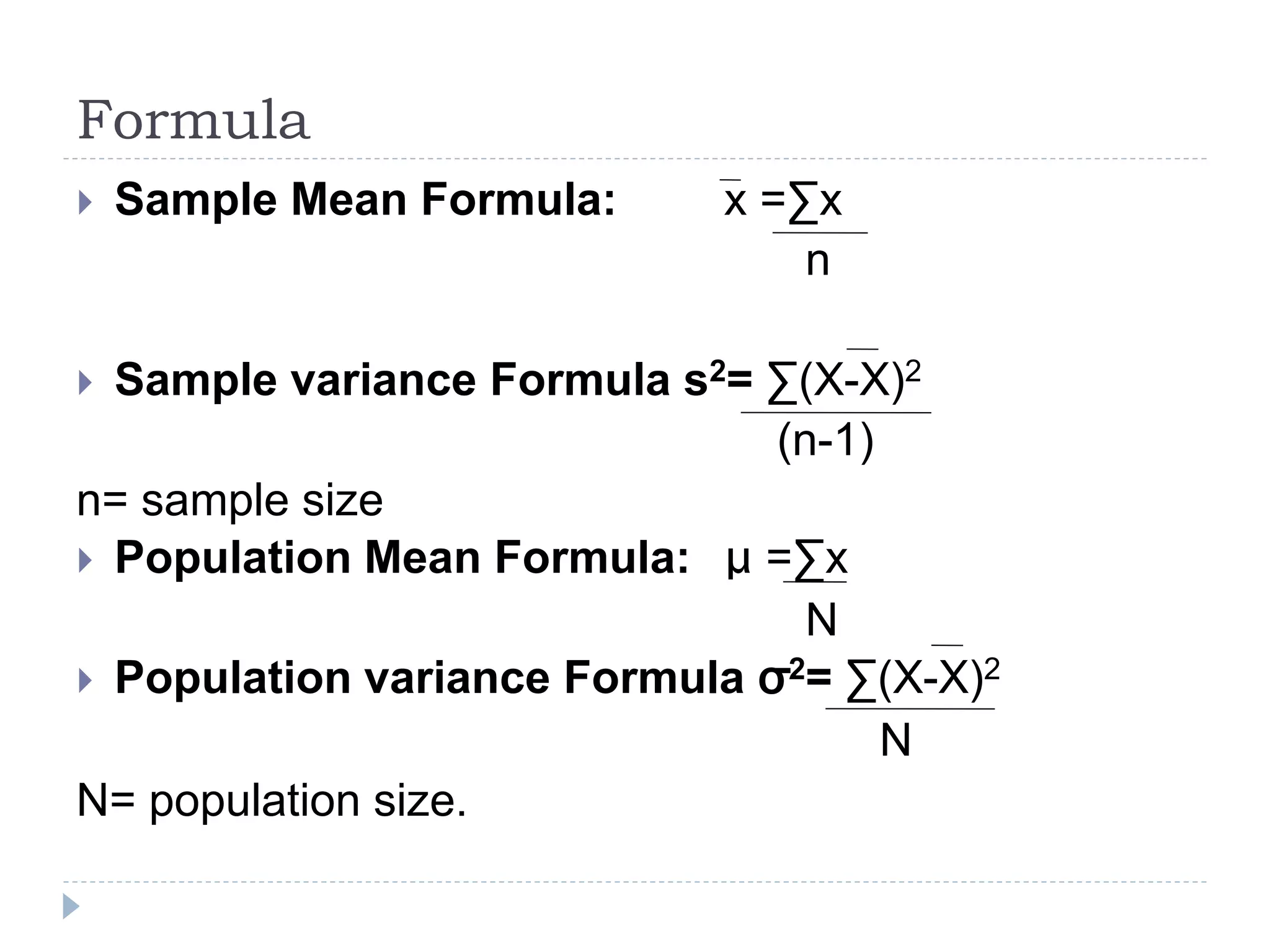
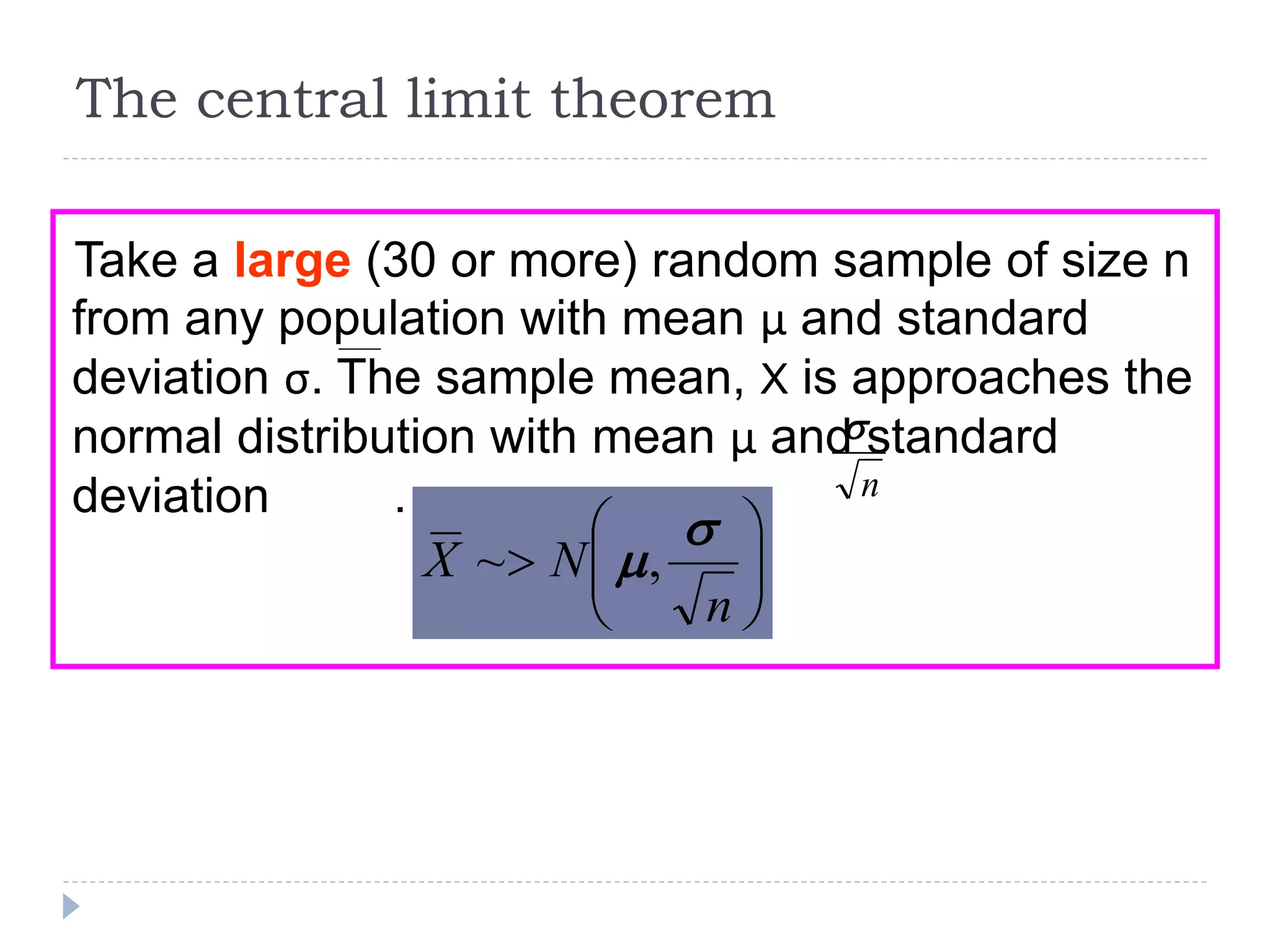
1. Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of items from a population to make inferences about the entire population. It is often used instead of a complete census or enumeration due to the time, cost, and resources required for a census.
2. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every item has a known, non-zero chance of being selected, and non-probability sampling, where items are selected in a non-random way based on the researcher's judgment.
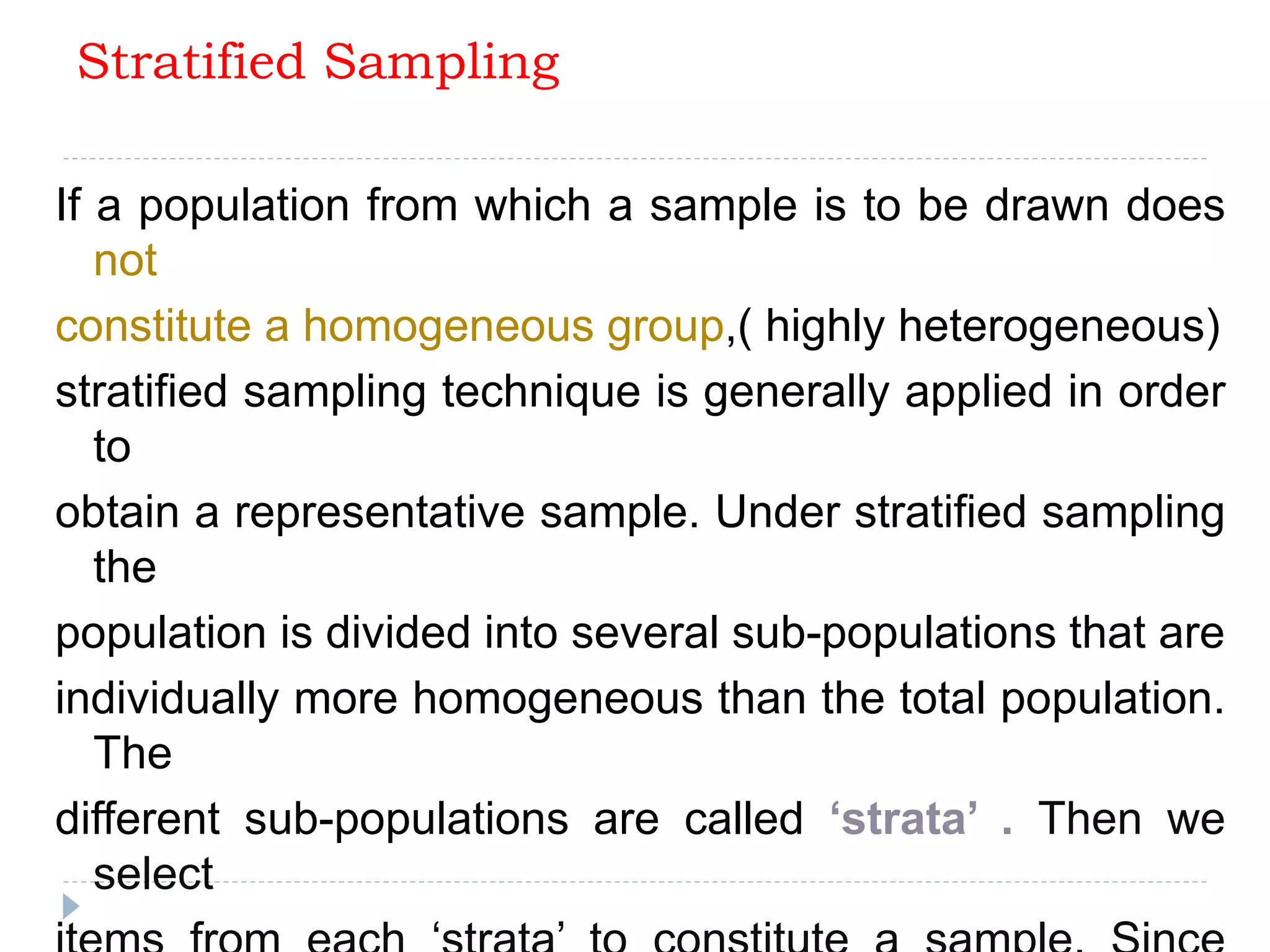
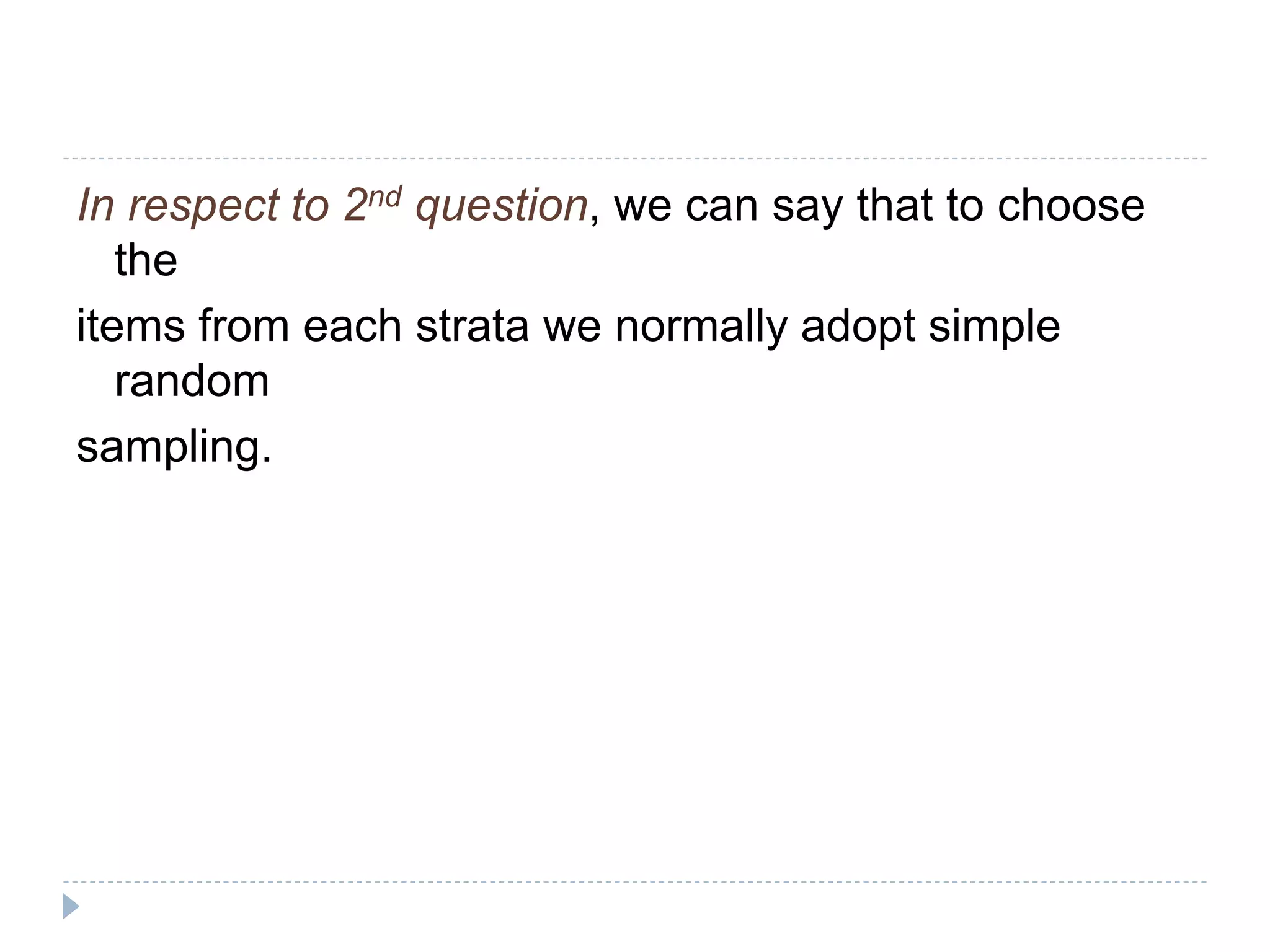
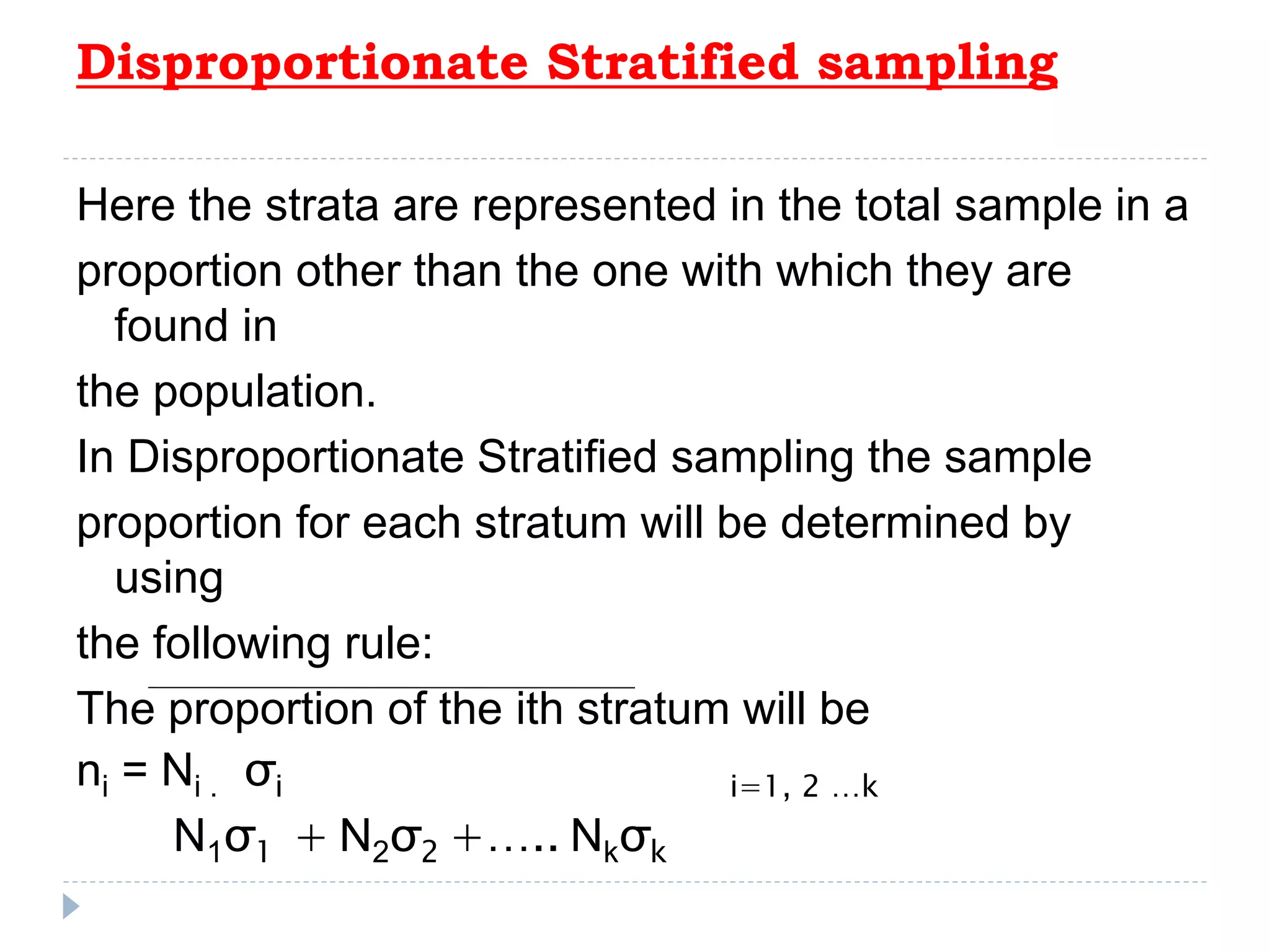
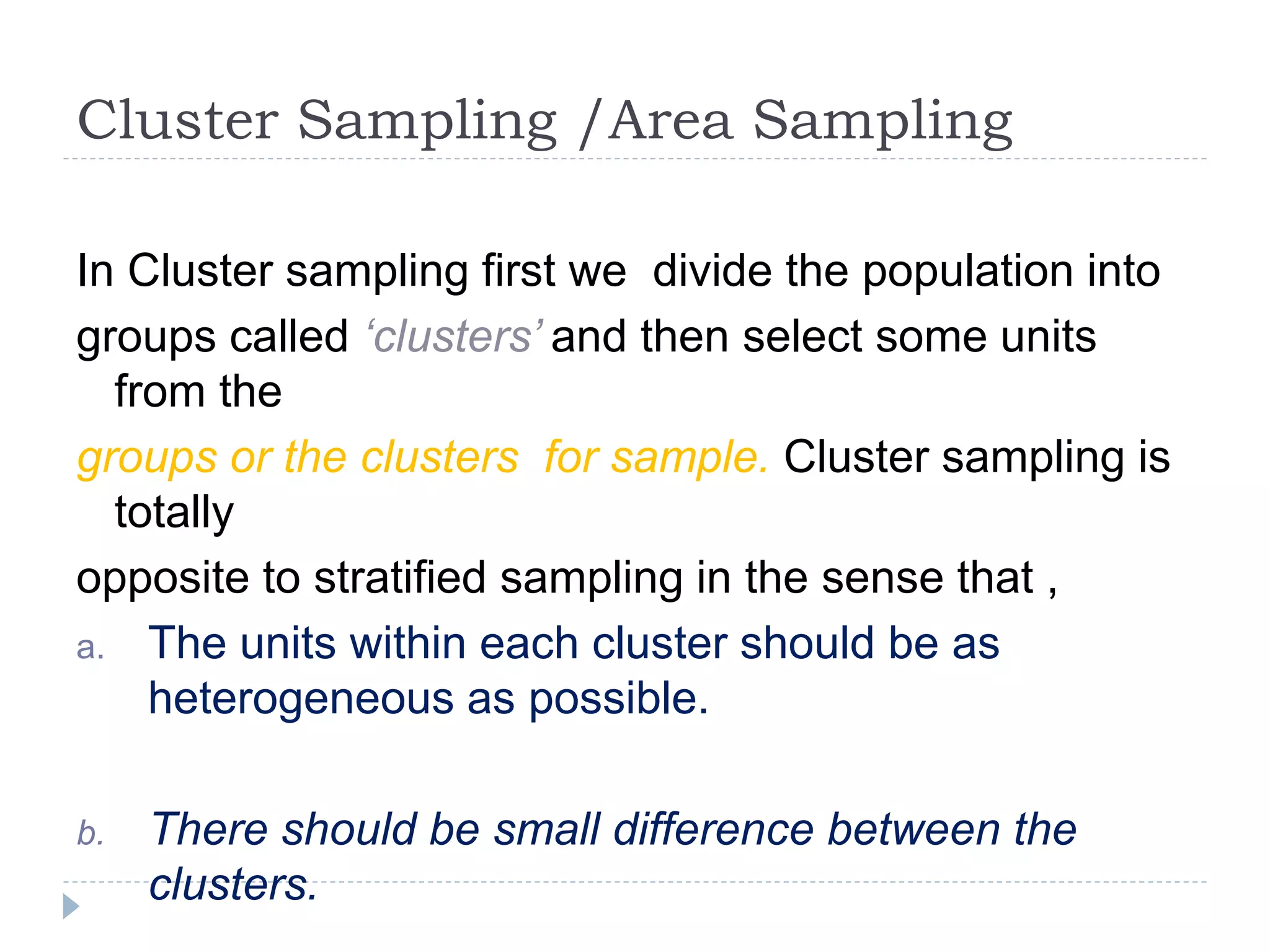
3. Common probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Common non-probability methods include convenience sampling and purposive sampling. The appropriate sampling method depends on the