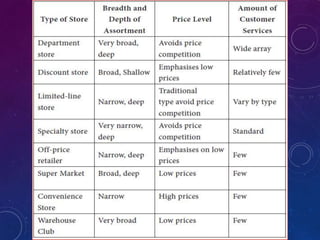
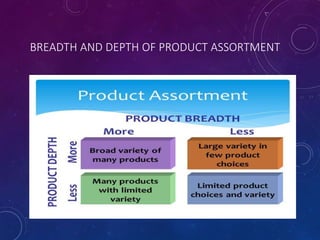
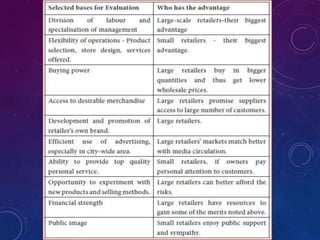
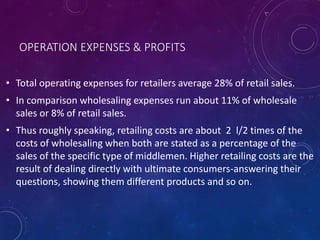
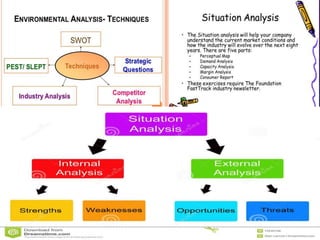
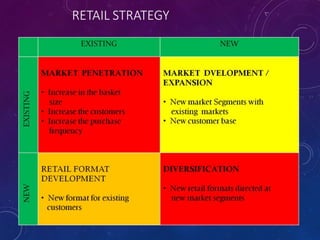
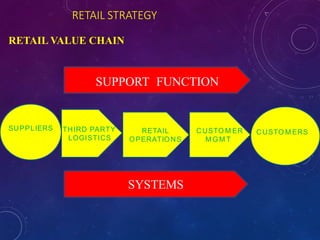
The document discusses the significance of formulating a retail strategy that balances strategic alignment with customer satisfaction, emphasizing aspects such as pricing, location, and service to build a competitive advantage. It outlines the steps involved in creating a retail strategy, which includes defining the mission, conducting situation analyses, setting objectives, and exploring various market entry methods. Additionally, it highlights the importance of adapting strategies to both existing and new markets while considering operational efficiency and financial performance.