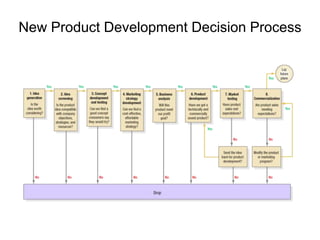
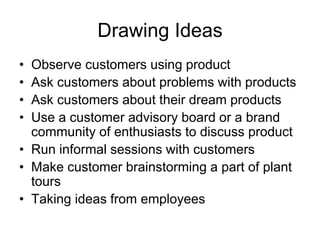
This document outlines the new product development process, including 7 key stages: 1) idea generation, 2) idea screening, 3) concept development and testing, 4) business analysis, 5) product development, 6) market testing, and 7) commercialization. It describes the activities that occur at each stage, such as generating ideas from customers and employees, evaluating ideas, developing product concepts, analyzing business feasibility, testing concepts with customers, and launching the product in select markets. The goal is to systematically evaluate and refine new product ideas before full commercialization.