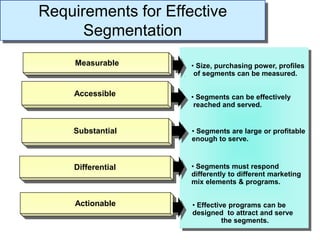
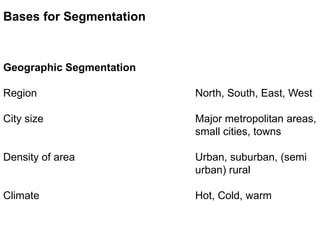
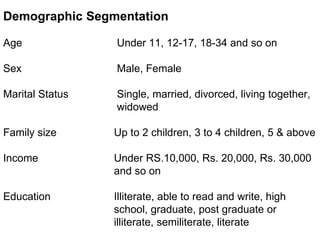
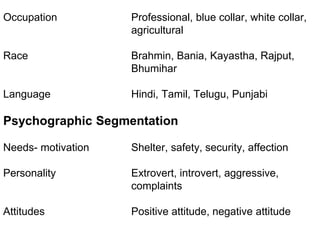
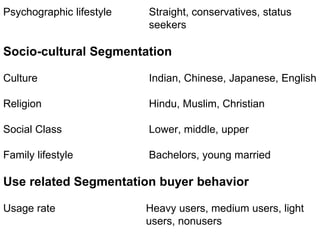
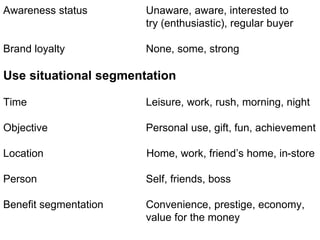
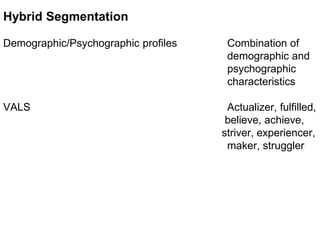
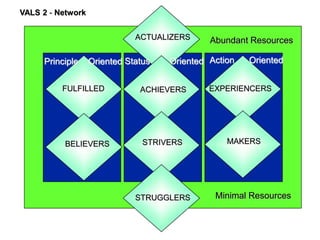
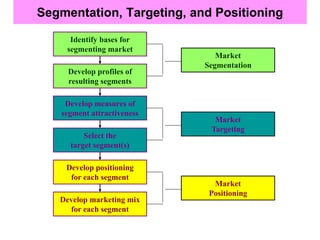
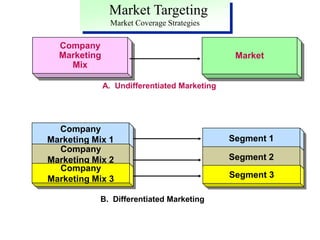
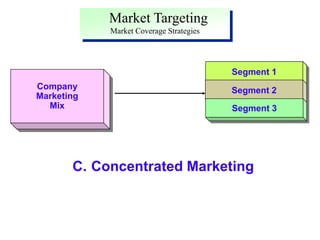
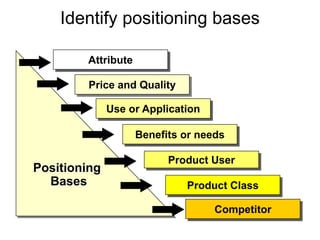
This document discusses market segmentation, targeting, and positioning. It defines market segmentation as dividing a market into subgroups of customers with similar needs or characteristics. Effective segmentation requires segments to be measurable, accessible, substantial, and responsive to different marketing mixes. Common bases for segmentation include geographic, demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and benefit factors. Targeting involves selecting specific segments to focus on based on factors like segment size, growth, and attractiveness. Positioning develops a specific marketing mix to influence customers' perceptions of a brand relative to competitors. It identifies attribute, benefit, user, and competitor bases for positioning. The document also discusses differentiation, market coverage strategies, and repositioning.