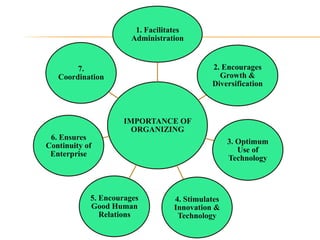
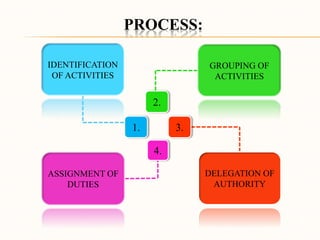
This document discusses the fundamentals of organizing, including its nature, importance, and process. It defines organizing as identifying and grouping work to be performed, defining responsibilities, and establishing relationships to enable efficient work. Organizing involves differentiating and integrating units through specialized tasks and coordination. An effective organization has groups working toward common objectives through divided work and cooperation, with central authority, communication, rules, and a dynamic structure. Organizing is important as it facilitates administration, encourages growth and innovation, optimizes technology use, and ensures continuity through coordination. The process of organizing involves identifying activities, grouping them, assigning duties, and delegating appropriate authority.